A Geographically Distributed Graph Computing Method and System Based on Differential Privacy
A differential privacy and distributed technology, applied in computing, transmission systems, digital transmission systems, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in noise convergence and low data availability of experimental results, so as to improve usability, improve convergence ability, and reduce the impact of noise. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
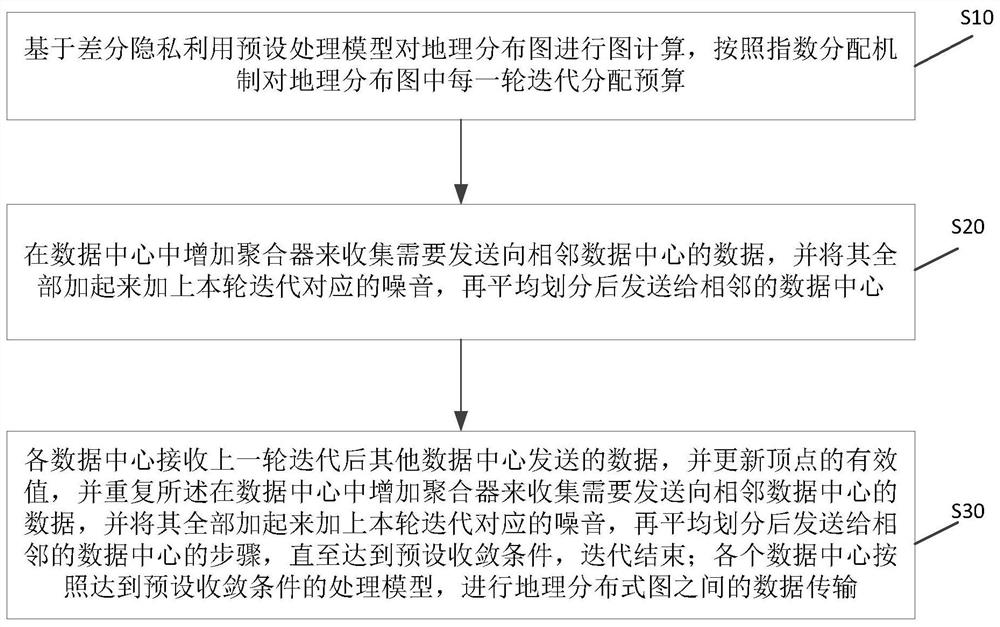
[0041] Embodiments of the present invention provide a differential privacy-based geographic distributed graph computing method, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
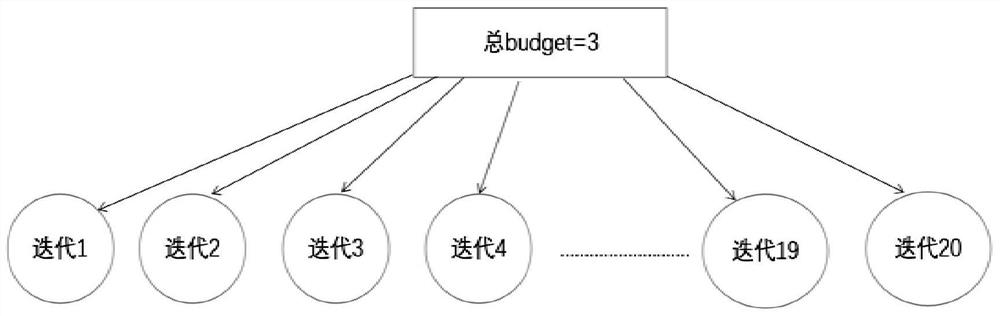
[0042] Step S10: Graph calculation is performed on the geographic distribution map by using a preset processing model based on differential privacy, and a budget is allocated to each iteration of the geographic distribution map according to an index allocation mechanism.
[0043] Differential privacy is a strictly proven differential technology that can protect personal privacy. It adds random noise to the communication between different DCs (the noise is generally added in two ways: exponential mechanism and Laplace mechanism). , to achieve differential privacy. Define differential privacy as: with random algorithm M, P M is the probability of the set of all possible outputs of M, for any two adjacent datasets D and D' and P M any subset S of M , if the algorithm M satisfies:
[0044]P{M(D...
Embodiment 2
[0075] The embodiment of the present invention provides a geographically distributed graph computing system based on differential privacy, such as Image 6 shown, including:
[0076] Each iteration budget allocation module 10 is configured to perform graph calculation on the geographic distribution map using a preset processing model based on differential privacy, and allocate a budget to each iteration of the geographic distribution map according to an index allocation mechanism. This module executes the method described in step S10 in Embodiment 1, and details are not repeated here.
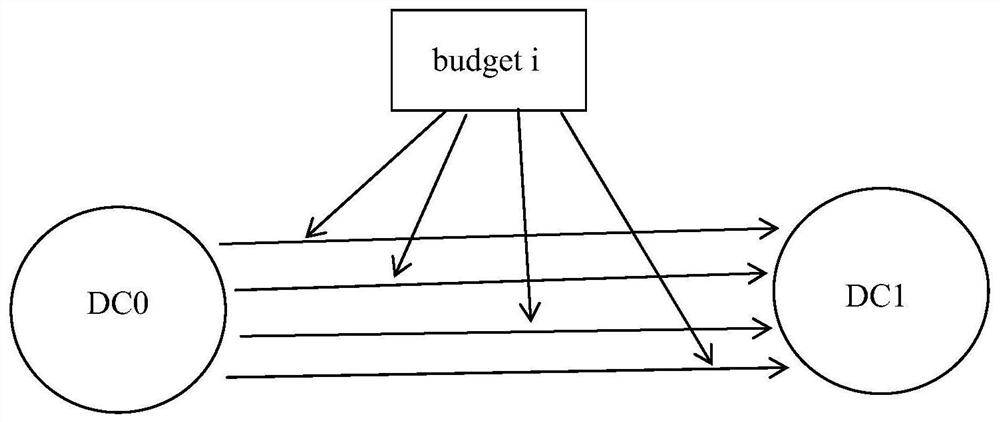
[0077] The noise adding module 20 is used to add an aggregator in the data center to collect the data that needs to be sent to the adjacent data center, add all of them together with the noise corresponding to this round of iteration, and then divide it evenly and send it to the adjacent data center In the data center, the noise is obtained by transforming the budget allocated by this round of...
Embodiment 3
[0083] An embodiment of the present invention provides a computer device, such as Figure 8 As shown, the device may include a processor 51 and a memory 52, wherein the processor 51 and the memory 52 may be connected by a bus or other means, Figure 8 Take connection via bus as an example.
[0084] The processor 51 may be a central processing unit (Central Processing Unit, CPU). The processor 51 may also be other general-purpose processors, digital signal processors (Digital Signal Processor, DSP), application specific integrated circuit (Application Specific Integrated Circuit, ASIC), Field-Programmable Gate Array (Field-Programmable Gate Array, FPGA) or Other programmable logic devices, discrete gate or transistor logic devices, discrete hardware components and other chips, or a combination of the above types of chips.
[0085] As a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium, the memory 52 can be used to store non-transitory software programs, non-transitory computer-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com