Method for constructing semantic map on line by utilizing fusion of laser radar and visual sensor
A visual sensor and laser radar technology, applied in the direction of re-radiation, instrumentation, electromagnetic wave re-radiation, etc., can solve the problem of large data volume, achieve the effect of driving convenience, improving the efficiency of update iterations, and improving the efficiency of map reuse
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
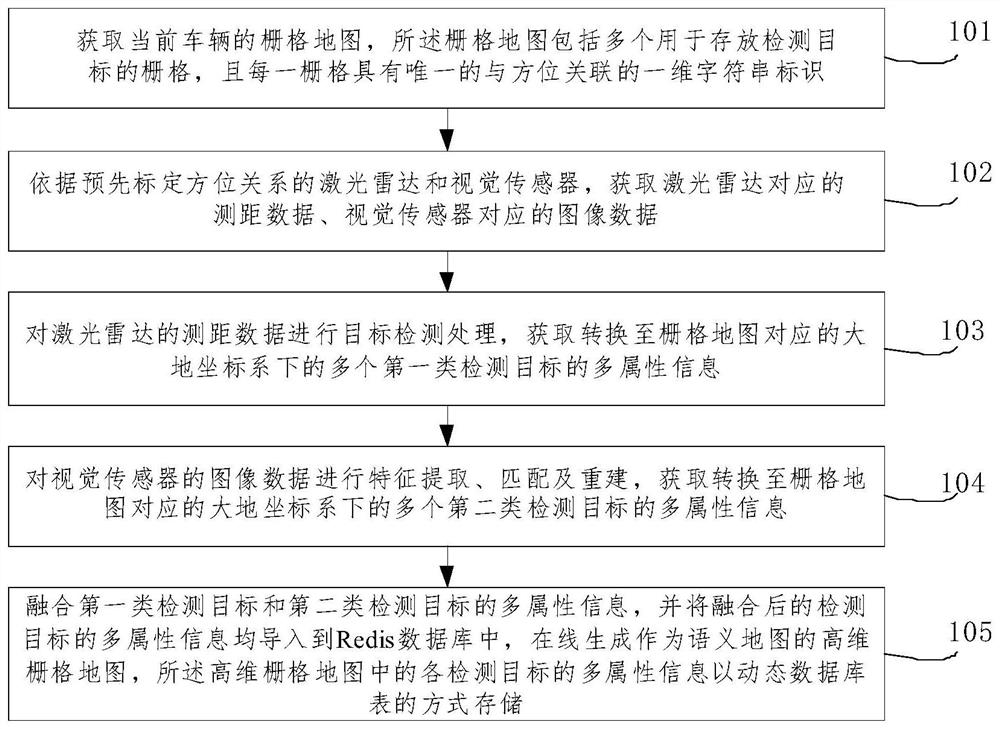
[0067] like figure 1 as shown, figure 1 It shows a schematic flowchart of a method for constructing a semantic map online by fusion of laser radar and visual sensor provided by an embodiment of the present invention. And vision sensor, method of the present invention may comprise the following steps:
[0068] 101. Obtain the grid map of the current vehicle, the grid map includes a plurality of grids / grids for storing detection targets, and each grid / grid has a unique one-dimensional string identifier associated with the orientation .
[0069] For example, this step 101 may include the following sub-steps:
[0070] 101-1. Obtain the current vehicle location information by means of GPS-RTK.
[0071] It is understandable that the absolute position information (latitude and longitude) of the vehicle obtained through GPS-RTK, the centimeter-level positioning accuracy, and then an initialization grid is established around it (the minimum unit of the grid is 15cm), but the diff...
Embodiment 2
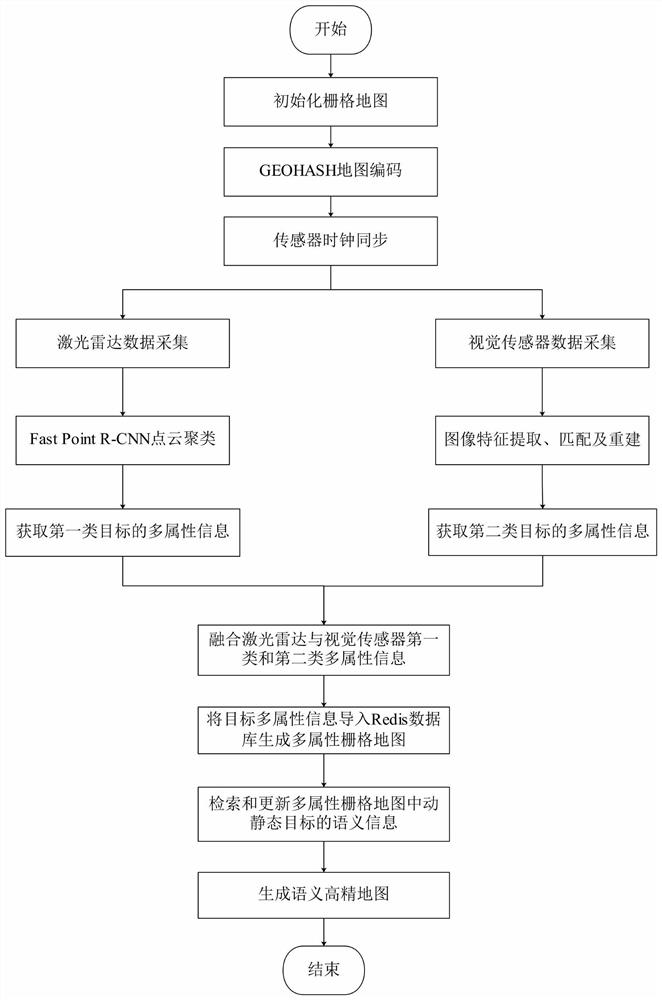
[0105] combine Figure 2 to Figure 6 As shown, the two-dimensional grid map of the current vehicle position is established and initialized. The GEOHASH algorithm is used to encode the initialized two-dimensional grid map into a one-dimensional string, and then the lidar and vision sensors are fused to obtain synchronous data, and the lidar and vision Multi-attribute information such as static and dynamic target categories, locations, and scales detected by the sensor is imported into the Redis database to generate a multi-attribute raster map, such as figure 2 Shown is the process of constructing a semantic high-precision map, and the specific steps are as follows:
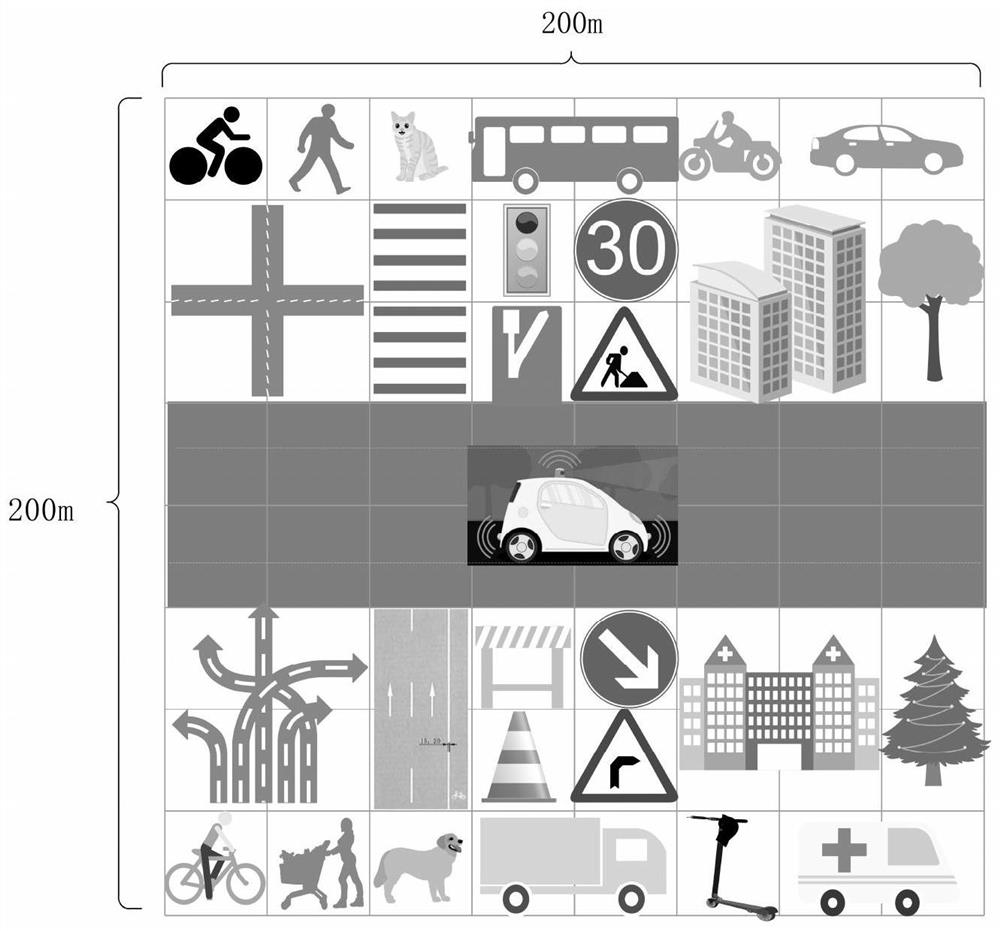
[0106] Step 1. Create a grid map. Create a 192m×192m square grid within 96 meters around the vehicle. Each grid size is 15cm×15cm. There are 1,638,400 grids in total, and each grid represents a unique geographic location. The location code value, and the following multi-attribute information of each detected tar...
Embodiment 3
[0176] According to another aspect of the embodiment of the present invention, the embodiment of the present invention also provides a smart car driving system, which may include: a control device and a multi-eye imaging device connected to the control device, the multi-eye imaging device Including: lidar and vision sensors;
[0177] After the control device receives the ranging data and image data respectively collected by the laser radar and the visual sensor, it constructs the three-dimensional semantic map of the smart car by using the method for constructing the semantic map online described in the first or second embodiment above.
[0178] In practical applications, an embodiment of the present invention also provides a smart car, which may include the above-mentioned smart car driving system.
[0179]Those skilled in the art should understand that the embodiments of the present invention may be provided as methods, systems or computer program products. Accordingly, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com