Method for making activated carbon rod by using inorganic bonding material
An inorganic bonding and activated carbon technology, which is applied in the field of activated carbon rods, can solve the problems of difficulty in popularizing water purifiers, high prices, and high prices of activated carbon rods, and achieves enhanced sterilization function, reduced production costs, improved strength and water resistance. performance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] A kind of method adopting inorganic binding material to make activated carbon rod, it comprises the following steps:
[0031] 1) Stir and mix 1 kg of water glass, 0.2 kg of additives and 10 kg of cement, and control the water-cement ratio to 0.8 to obtain the first material, add 60 kg of activated carbon powder and 5 kg of zeolite powder to the first material and stir evenly to obtain the second material;
[0032] 2) Sending the second material into an extruder for extrusion molding, and curing the formed carbon rods to obtain the activated carbon rods.
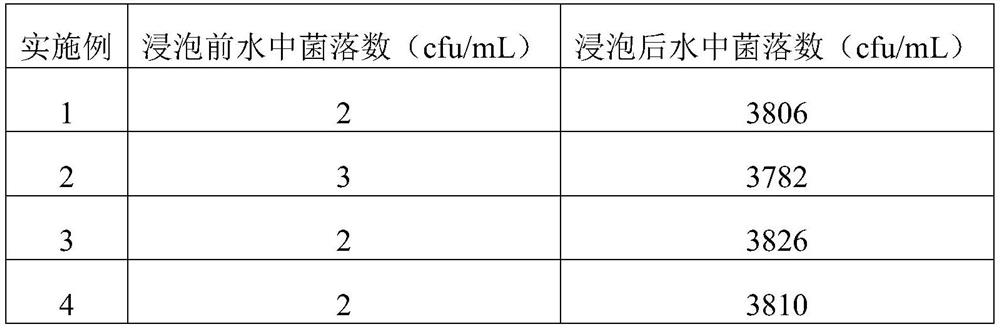
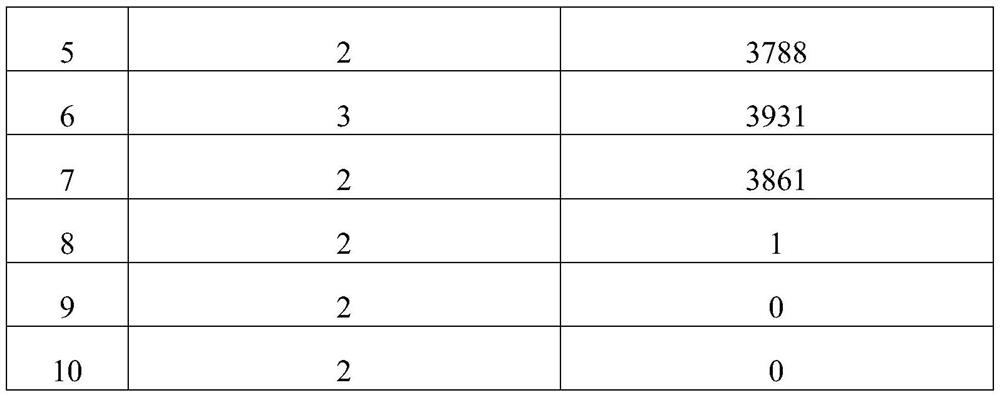
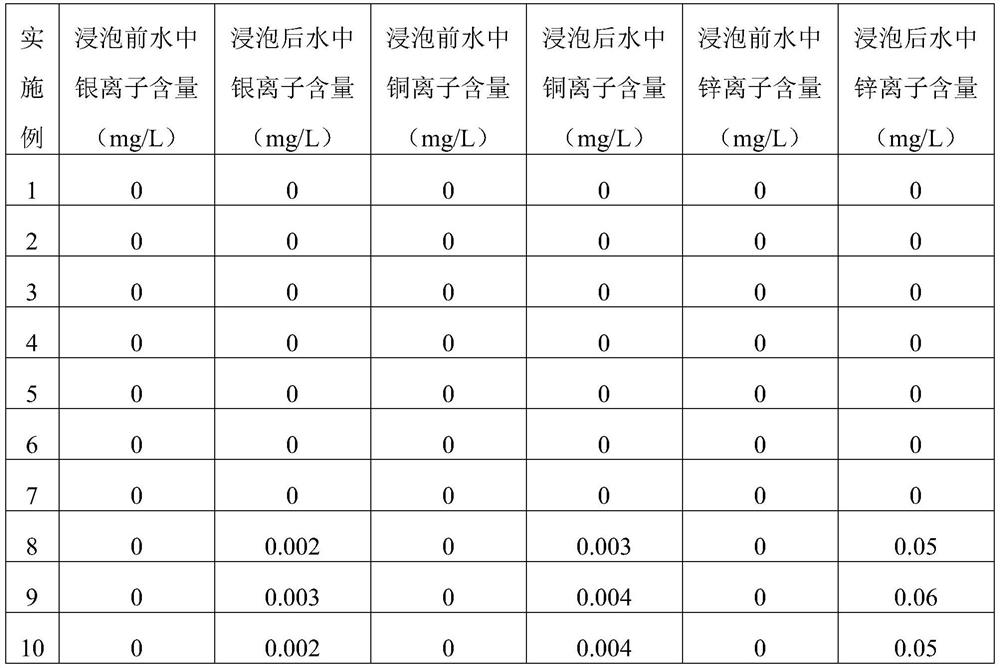
[0033] The carbon rod prepared in this example passed the standard addition test, and the removal rate of residual chlorine was over 99.9%, and the removal rates of heavy metals lead, cadmium, mercury, chromium and arsenic were all over 99.9%.
Embodiment 2
[0035] 1) Stir and mix 3 kilograms of water glass, 1 kilogram of additives and 20 kilograms of cement, and control the water-cement ratio to 1.5 to obtain the first material. Add 80 kilograms of activated carbon powder and 10 kilograms of zeolite powder to the first material and stir evenly to obtain the second material;
[0036] 2) The second material is fed into an extruder for extrusion molding, and the formed carbon rod is steamed and cured for 4 hours to obtain the activated carbon rod.
[0037] The carbon rod prepared in this example passed the standard addition test, and the removal rate of residual chlorine was over 99.9%, and the removal rates of heavy metals lead, cadmium, mercury, chromium and arsenic were all over 99.9%.
Embodiment 3
[0039] 1) Stir and mix 2 kilograms of water glass, 0.6 kilograms of additives and 15 kilograms of cement, and control the water-cement ratio to 1.1 to obtain the first material, add 70 kilograms of activated carbon powder and 8 kilograms of zeolite powder to the first material and stir evenly to obtain the second material;
[0040] 2) The second material is sent into an extruder for extrusion molding, and the activated carbon rod is brushed with a layer of the third material before the formed carbon rod is naturally cured, and steamed and cured for 5 hours to obtain the obtained Described activated carbon stick; Wherein, 1 kilogram of water glass, 0.2 kilogram of additives and 20 kilograms of cement are stirred and mixed, and the water-cement ratio is controlled to be 1, obtains the 3rd material.
[0041] The carbon rod prepared in this example passed the standard addition test, and the removal rate of residual chlorine was over 99.9%, and the removal rates of heavy metals lea...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com