Double-power turbo-supercharger free of hysteresis and capable of dissipating heat quickly
A turbocharger, dual-power technology, used in engine components, combustion engines, machines/engines, etc., can solve the problem that turbocharger bearings and sealing components cannot achieve long-life use, turbocharger lag, and oil burning. and other problems, to achieve the effect of reducing the power loss of exhaust gas, reducing the transmission ratio and reducing the load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
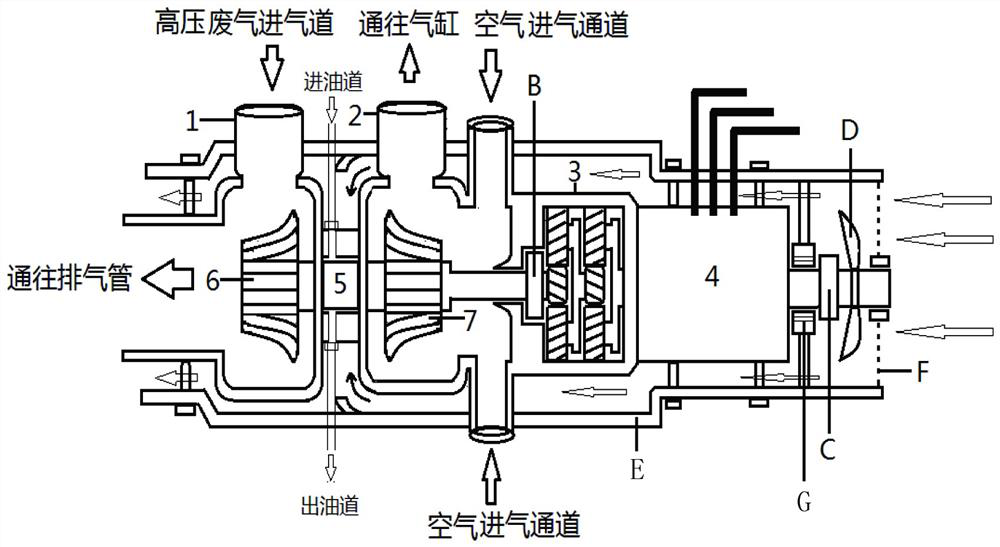
[0028] The turbocharger uses the high-speed and high-pressure exhaust gas discharged from the engine to drive the impeller at the exhaust end of the turbocharger to rotate at a high speed, driving the impeller of the compressor on the other side connected to it to rotate at the same time, compressing the intake air and injecting it into the cylinder for combustion. Increase engine power. But the turbocharger needs a large flow of exhaust gas to start, which can only be provided when the engine speed reaches about 1250 rpm. When the car just started, before the engine speed increased from idling 500~600 rpm to more than 1200 rpm, the amount of exhaust gas discharged was not enough to drive the supercharger to work as intake boost, and there was a time lag between the increase in engine power and speed. Therefore, a car equipped with an exhaust gas turbocharger will have a power lag when accelerating from a start.
[0029] Shortly after the engine is started, the exhaust gas te...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is that a deflector is provided on the air guide cover.
[0040] A deflector facing the position of the bearing box is provided on the inner side wall of the air guide cover E located outside the exhaust gas turbine housing 1 and the intake turbine housing 2 . When the intake fan blade D rotates, the air outside the air guide cover E is sucked into the air guide cover E, and is discharged outward along the guide gap between the air guide cover E and the inner shells. The air in the air guide cover E will be guided by the deflector and directly blown onto the bearing box to cool it down, thereby improving the heat dissipation efficiency of the bearing box.
Embodiment 3
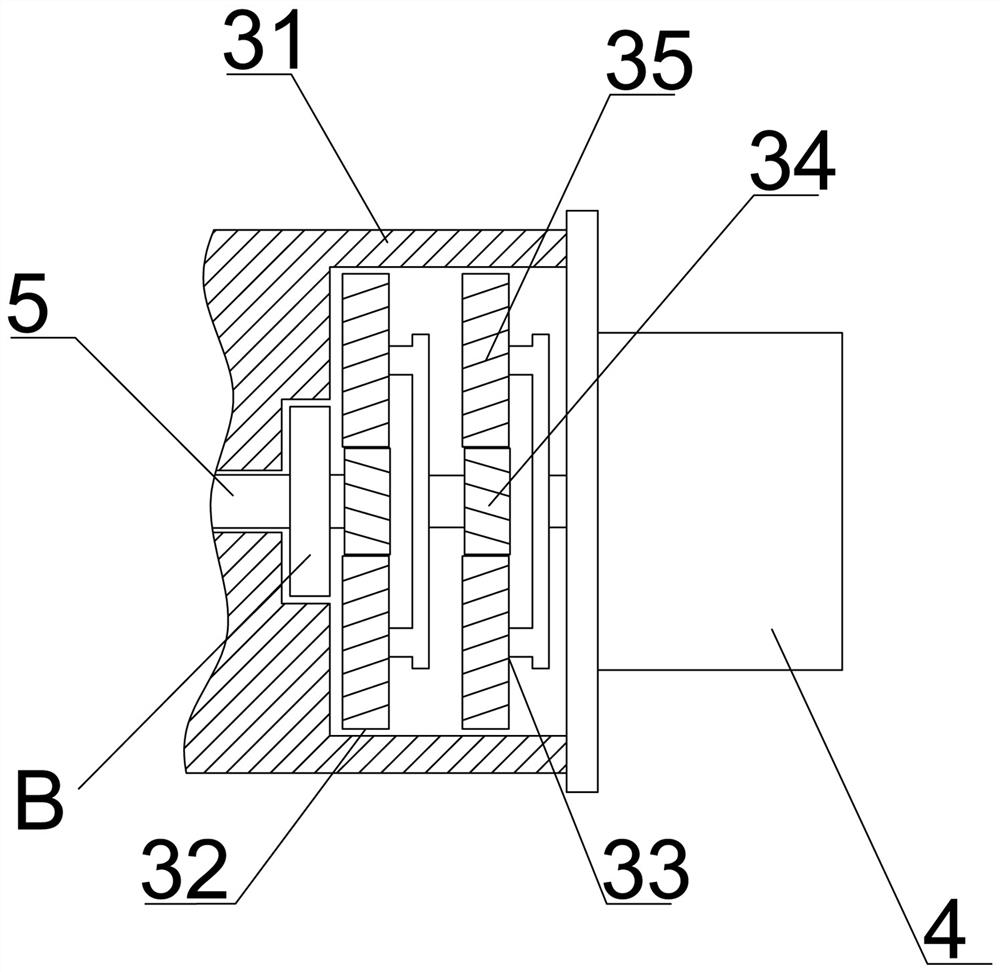
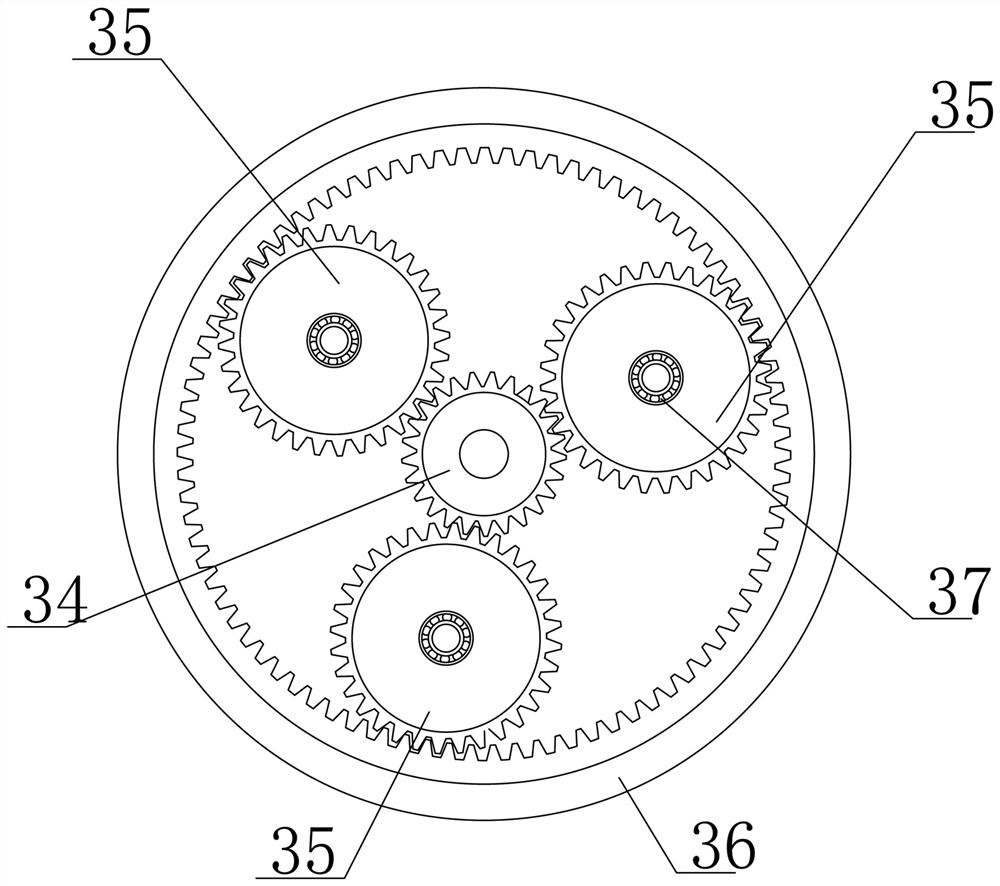
[0042] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 2 is that the sealed bearing box is provided with an oil pipe that enters the bearing box from one side of the sealed bearing box and discharges from the other side. Lubricating oil is injected into the box, and the injected lubricating oil directly lubricates and cools the inside of the bearing box. When the controller automatically controls the motor / generator 4 to continue to work after the engine is turned off, the rotating intake turbine shaft will cause the lubricating oil at the bearing to continue to lubricate the inside of the sealed bearing box to avoid engine oil remaining at the turbine shaft Oxidation (carbon deposition) occurs due to "thermal shutdown".
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com