ATP chemiluminiscence detection method based on enzyme digestion assisted label-free aptamer sensor
A chemiluminescence detection and aptamer sensor technology, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve problems such as poor application effect, cumbersome detection steps, unstable results, etc., to achieve fully automatic detection, shorten detection time, and meet the effects of rapid detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
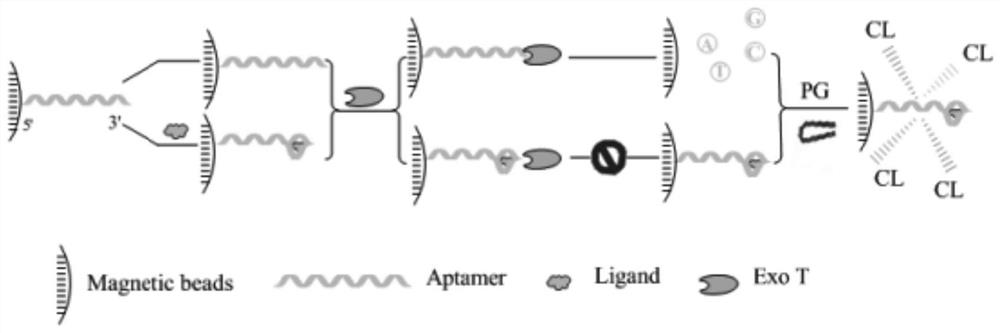
[0036] 1 Experimental principle
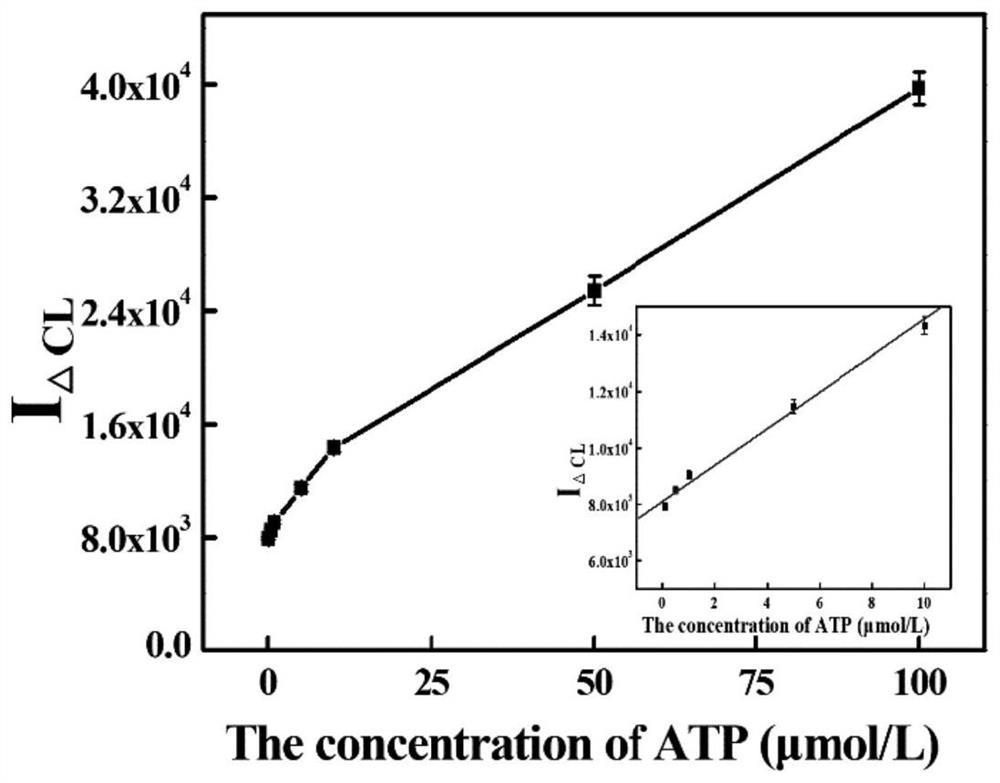
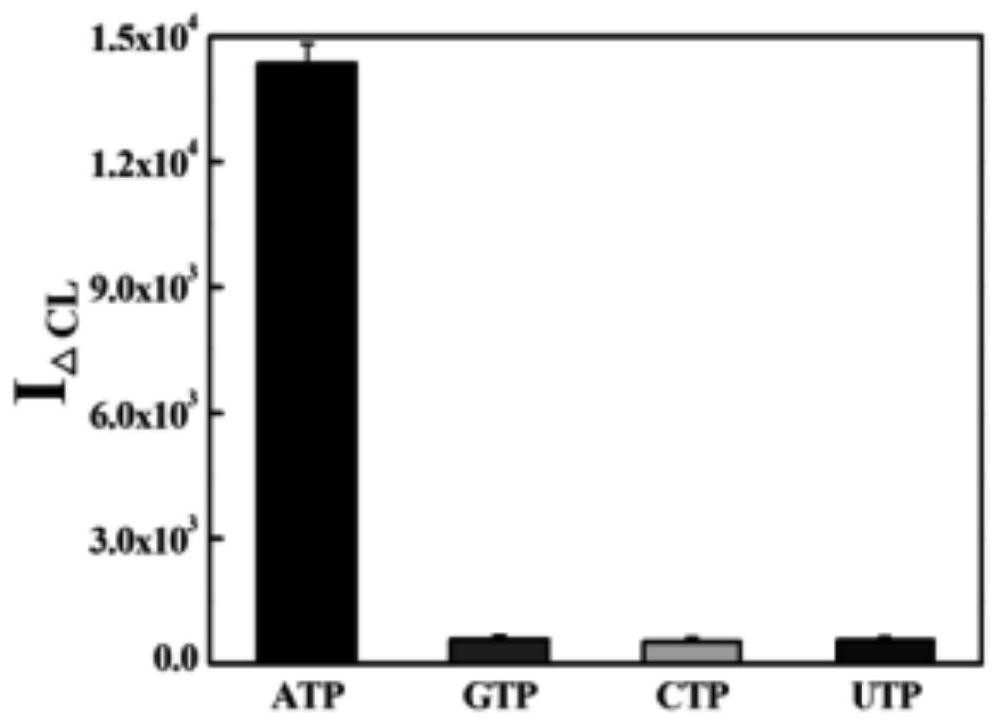
[0037] In this experiment, carboxyl magnetic microspheres were used as the separation carrier to construct an ATP aptamer sensor on the surface of the magnetic microspheres. The positive correlation between the amount of ATP aptamer immobilized on the surface of the magnetic microspheres and the ATP concentration and the G base in the ATP aptamer sequence and The transient derivatization reaction of the chemiluminescence reagent PG realizes the enzyme cleavage-assisted chemiluminescence detection of ATP. First, the amino aptamer is immobilized on the surface of the carboxyl magnetic microsphere through the aminocarboxyl binding reaction; then; finally, the magnetic microsphere is separated by a magnetic separator, and the amount of the ATP aptamer fixed on the surface of the microsphere is detected by using a chemiluminescence method, thereby Indirect quantitative detection of ATP. When no ATP exists (i.e. blank group), the ATP aptamers immob...
Embodiment 2
[0056] A method for detecting ATP chemiluminescence based on an enzyme-assisted unlabeled aptamer sensor, comprising the following steps:
[0057] 1) Immobilizing the amino-modified aptamer on the surface of the carboxyl magnetic microspheres through an aminocarboxyl reaction to obtain a magnetic microsphere-aptamer complex;
[0058] 2) Add the sample to be tested to the magnetic microsphere-capture probe complex, so that the aptamer can specifically bind to ATP, so that the ATP capture can be indirectly connected to the surface of the magnetic microsphere, and the solid phase can be taken after the reaction to obtain the ATP aptamer sensor;
[0059] 3) Mix the ATP aptamer sensor described in step 2) with 50 μL of 1-fold concentration Exo T buffer solution and a certain unit amount of Exo T solution, and then detect the CL value of the luminescence signal.
[0060] On the basis of the above technical solutions, the following conditions are met:
[0061] Step 1) includes the ...
Embodiment 3
[0069] A method for detecting ATP chemiluminescence based on an enzyme-assisted unlabeled aptamer sensor, comprising the following steps:
[0070] 1) Immobilizing the amino-modified aptamer on the surface of the carboxyl magnetic microspheres through an aminocarboxyl reaction to obtain a magnetic microsphere-aptamer complex;
[0071] 2) Add the sample to be tested to the magnetic microsphere-capture probe complex, so that the aptamer can specifically bind to ATP, so that the ATP capture can be indirectly connected to the surface of the magnetic microsphere, and the solid phase can be taken after the reaction to obtain the ATP aptamer sensor;
[0072] 3) Mix the ATP aptamer sensor described in step 2) with 50 μL of 1-fold concentration Exo T buffer solution and a certain unit amount of Exo T solution, and then detect the CL value of the luminescent signal.
[0073] On the basis of the above technical solutions, the following conditions are met:
[0074] Step 1) includes the f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com