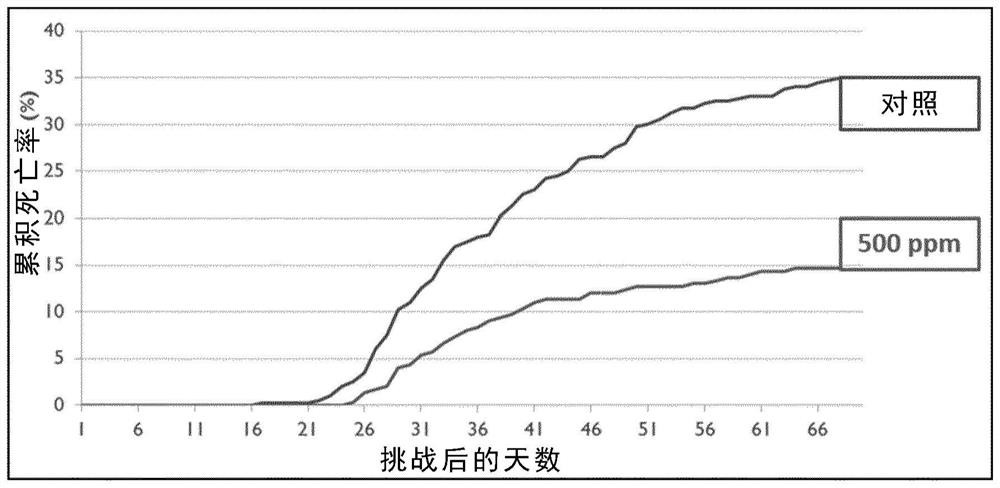
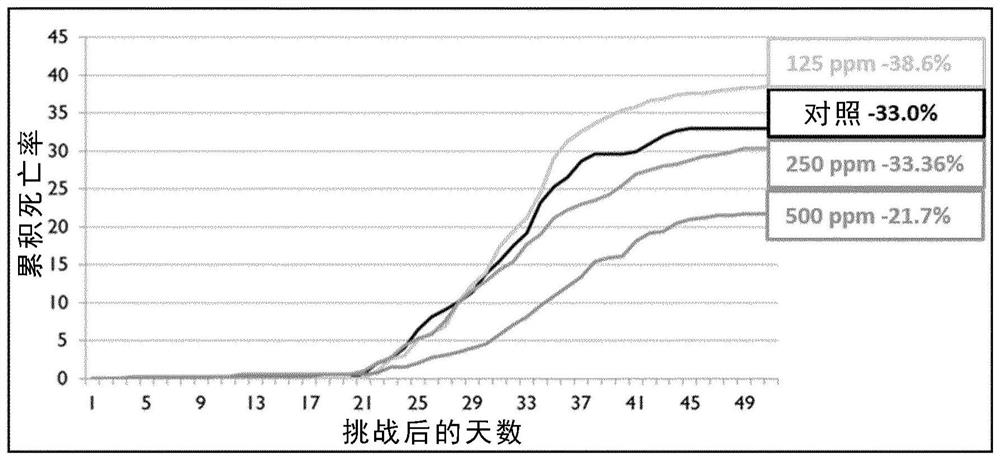
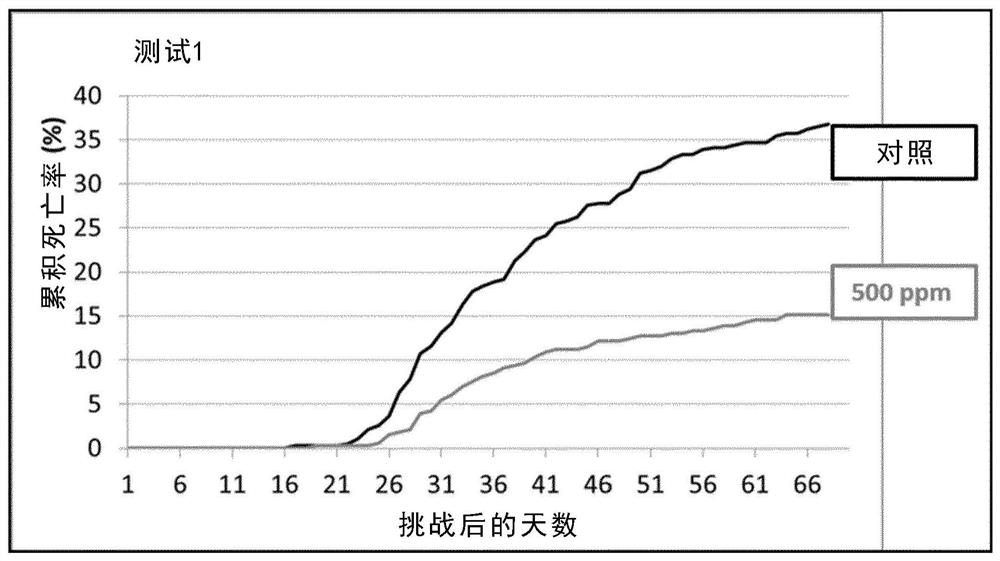
Use of alpha lipoic acid as a feed additive for aquatic animals
A technology for aquatic animals and lipoic acid, applied in animal feed, molding or processing of animal feed, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve problems such as negative effects on fish performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0175] Embodiment 1: the preparation of pressing fish feed
[0176] The main raw materials are ground and mixed. Minor ingredients are then added to the mixer and a homogeneous mixture is conditioned by adding water and steam to this mass in the preconditioner. This starts the cooking process of the starch fraction (bound components). This material is fed into a granulator. The material is forced through the die of the mill, and the ribbons are broken into pellets on the outside of the die. The moisture content is low, so there is no need to dry the feed.
[0177] Additional oil comprising a fish feed composition according to the invention is then sprayed onto the surface of the pellets, but since the pellets are quite dense, the total lipid content rarely exceeds 24%. The added oil may be fish oil, microbial / algae oil or vegetable oil, such as rapeseed oil or soybean oil, or a mixture of oils. After oil coating, the pellets were cooled in a cooler and bagged. The final ...
Embodiment 2
[0178] Embodiment 2: the preparation method of extruding fish feed
[0179] The main raw materials are ground and mixed. The minor ingredients comprising the fish feed composition according to the invention are added to the mixer. A homogeneous mixture is conditioned by adding water and steam to the mass in a preconditioner. Additional oil may also be added to the feed at this stage. This starts the cooking process of the starch fraction (bound components). Feed the material into the extruder. Extruders can be of the single-screw or twin-screw type. Due to the rotational movement of the material in the extruder, the material is further mixed. Additional oil, water and steam can be added to the feed in the extruder. At the end of the extruder, the temperature of the material is above 100°C and the pressure is above ambient pressure. Material is forced through openings in the extruder pull die. Due to the reduction in temperature and pressure, some of the moisture will i...
Embodiment 3
[0185] Example 3: Process for the Preparation of Alpha-Lipoic Acid Compositions in Oil
[0186] Alpha lipoic acid (AL) in powder form was sieved through a 1 mm sieve to remove larger particles. A small amount of oil is preheated to 45°C and mixed with the powder to form a homogeneous liquid paste. The added oil may be fish oil, microbial / algae oil or vegetable oil, such as rapeseed oil or soybean oil, or a mixture of oils. Add more oil until desired consistency is achieved. Oil acts as a carrier. The AL composition can be sprayed while stirring to prevent AL settling. This composition was used to coat the feedstuffs described in Examples 1 and 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com