Transgenic plants with increased yields
A gene and yield technology, applied in the field of transgenic plants with improved yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0187] Generation and screening of high-yielding plant lines
[0188] This example describes methods for generating mutant plant lines and screening for high-yielding plants. Mutant plants produced by the methods of this example may exhibit increased growth characteristics, such as increased plant height, plant weight, number of tillers, number of spikes, number of seeds, weight of seeds, size of seeds, leaf angle, number of primary branches , number of secondary branches and / or growth rate. As disclosed herein, modulation of genes associated with DP-E2F signaling (eg, overexpression of the PZR1 gene in rice) using the methods of this example can result in high-yielding plants.
[0189] Cloning and Plant Transformation Vectors used to generate Oryza sativa and Arabidopsis plants overexpressing rice OsDPB / PZR1 under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter were constructed as follows: RNA was extracted and cDNA was synthesized from 7-day-old rice seedlings with specific primers (T...
Embodiment 2
[0197] Method for conferring resistance to plant lines to the BR biosynthesis inhibitor propiconazole
[0198] This example describes methods for generating plants or plant lines resistant to herbicides that affect brassinosteroid signaling. The generation of plants that are resistant to herbicides can be used in methods for producing high yielding crop fields. For example, a crop field containing herbicide-resistant crop plants can be treated with herbicides to effectively remove a weed or weeds from the crop field, thereby allowing the crop plants to thrive and increasing the overall Yield.
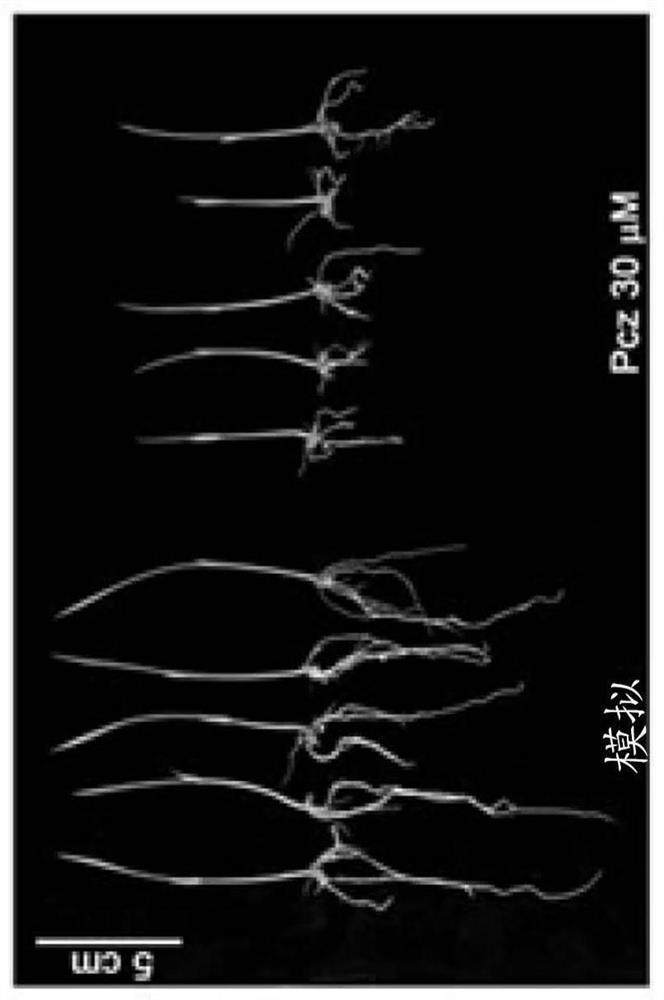
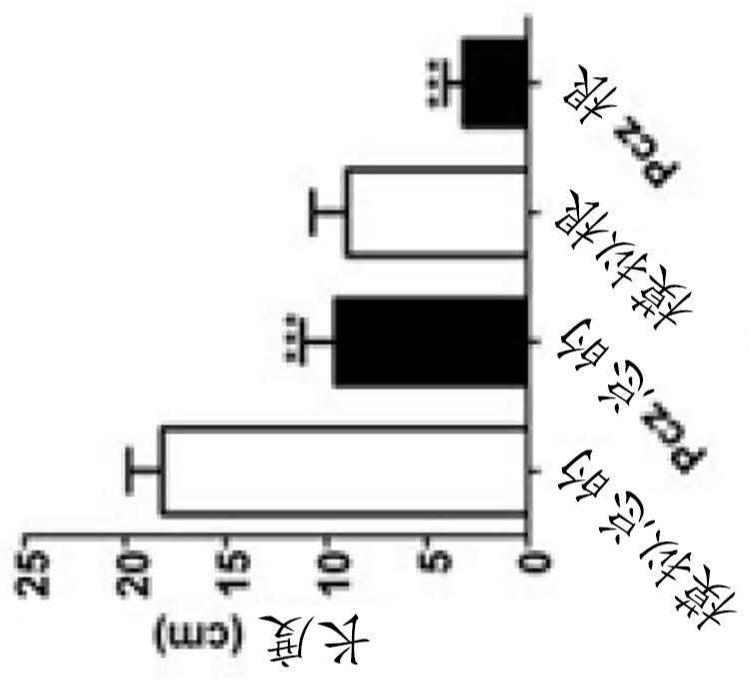
[0199] The response of rice to different concentrations of the inhibitor Pcz was studied to determine the optimal conditions for isolating Pcz-resistant mutants. Pcz affects rice plant growth and induces dwarfing in a dose-dependent manner ( Figure 8A with Figure 8B ). Treatment with 30 μM Pcz reduced the total size of wild-type seedlings by up to 47%, and the root response was eve...
Embodiment 3
[0203] Evaluation of Plant Architecture and Yield of Rice Plants
[0204] This example describes methods for evaluating plant architecture and yield in plants produced by genetic modification methods disclosed herein, such as those described in Example 1.
[0205] Examining the phenotypes of adult plants under field and greenhouse conditions, pzr1-D plants were found to have higher yields than wild-type plants ( Figure 2A to Figure 2I ). Total plant weight was 33% higher in the mutant than in the wild type, although their total height was not significantly different. The increase in weight could be explained by an increase in the number of tillers in the mutant, as well as an increase in the number of spikes per plant ( Figure 2A to Figure 2F ). Seed weight per plant increased from 30 g in the wild type to 50 g in the mutant, indicating an increase in yield of approximately 160%. The morphology of spikes was detected, and it was found that not only the number of spikes i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com