Patents
Literature
94 results about "Brassinosteroid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
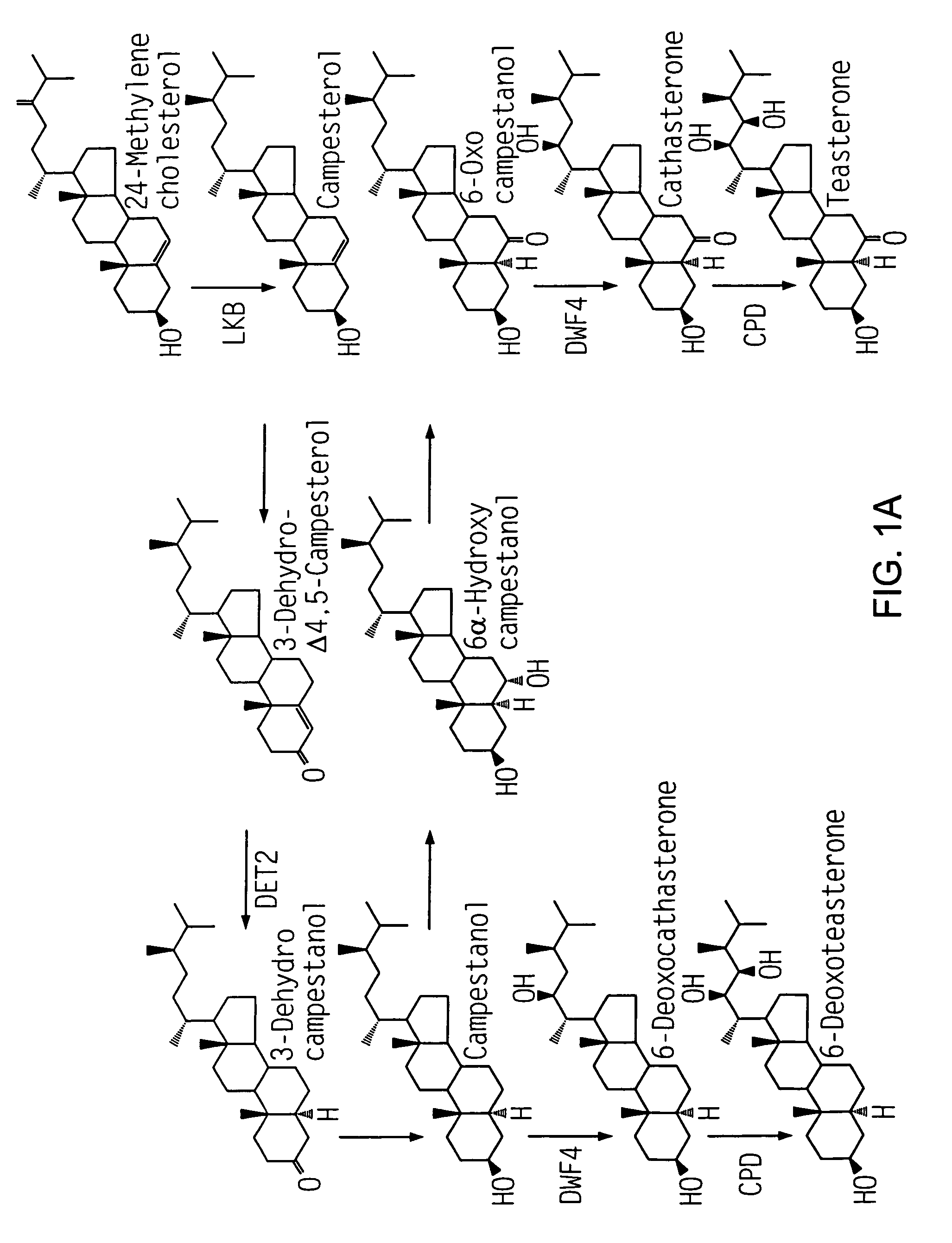
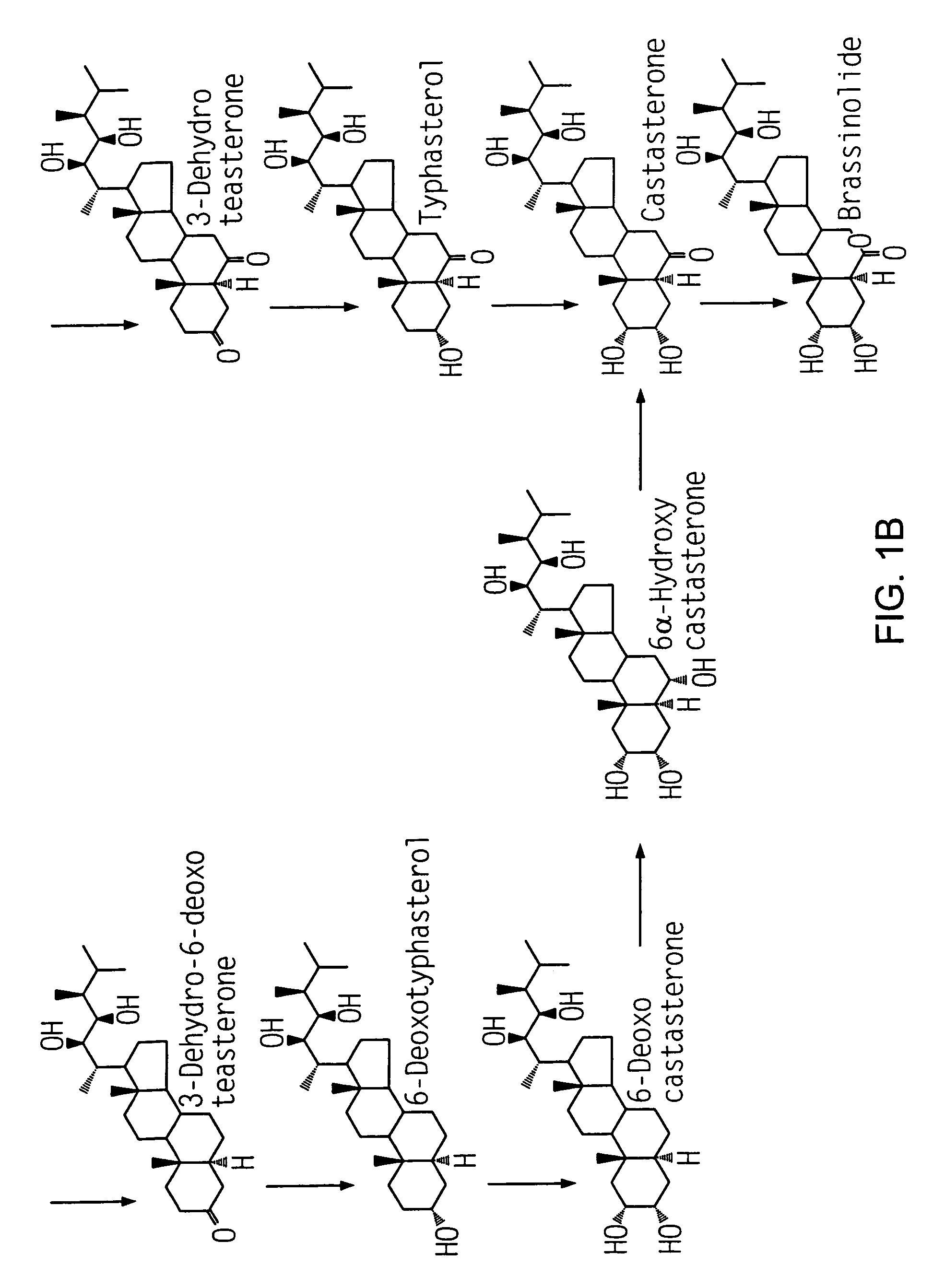
Brassinosteroids (BRs) are a class of polyhydroxysteroids that have been recognized as a sixth class of plant hormones and may have utility as an anticancer drug for endocrine-responsive cancers to induce apoptosis and inhibit growth. These brassinosteroids were first explored during the 70s, when Mitchell et al. reported promotion in stem elongation and cell division by the treatment of organic extracts of rapeseed (Brassica napus) pollen. Brassinolide was the first isolated brassinosteroid in 1979, when pollen from Brassica napus was shown to promote stem elongation and cell divisions, and the biologically active molecule was isolated. The yield of brassinosteroids from 230 kg of Brassica napus pollen was only 10 mg. Since their discovery, over 70 BR compounds have been isolated from plants.
Genes involved in brassinosteroid hormone action in plants
InactiveUS6921848B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesWild typeHormones regulation
The present invention provides a BZR1 gene and an altered gene, bzr1-D, involved in the brassinosteroid response pathway. The expression of BZR1 genes in transgenic plants causes such plants to become significantly larger and more robust than their wild-type counterparts, thus increasing plant yields.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
A multipurpose bactericial composition for farm crop
InactiveCN101156597APromote growthThe formula is scientific and reasonableBiocideFungicidesDiseaseAdipic acid
The invention provides a multi-purpose sterilizing combination for crops. The constituents has weight percentages that: constituent A is 1-50 percent, constituent B is 5-63 percent, constituent C is 0.1-5 percent, common carrier is 25-88 percent, and common assistant is 5.0-25 percent. The constituent A is any one of difenoconazole, prochloraz, prochloraz manganic salt, or metalaxyl-m. The constituent B is any one of basic copper sulfate, bluestone, copper hydroxide, copperchloride, cuprous oxide, copper acetate, cuaminosulfate, amber glue copper adipic acid, or copper rosinate. The constituent C is any one of diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate, sodium nitrophenolate, naphthyl acetic acid, gibberellins, or brassinosteroids lactone. The invention not only can multiply the expansion of the preventing spectrum on the crop disease, can delay the produce of the drug-resistance; can lower the dosage of each agent in the combination, can obviously improve the medical effect of the constituents when being used separately, can prevent and cure the disease, can facilitate the growth of the crop, and can increase the yield and the harvest of the crop.
Owner:湖南万家丰科技有限公司
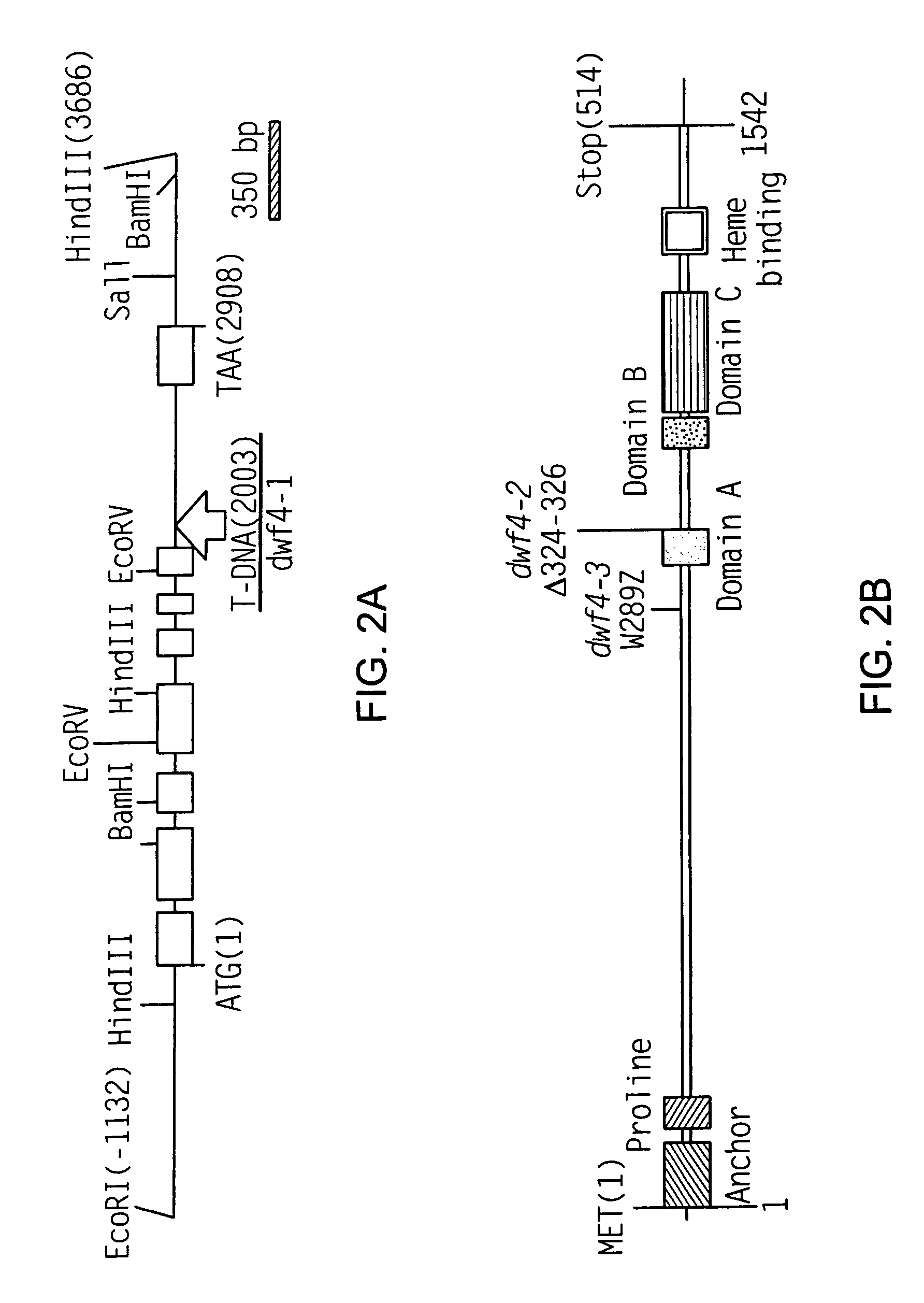
Dwf4 polynucleotides, polypeptides and uses thereof
The present invention relates to novel, polynucleotides isolated from dwarf plants. The dwf4 polynucleotides that encode all, or a portion of, a DWF4 polypeptide, a cytochrome P450 enzyme that mediates multiple steps in synthesis of brassinosteroids. The present invention also relates to isolated polynucleotides that encode regulatory regions of dwf4. Uses of the dwf4 polypeptides and polynucleotides are also disclosed.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Method for quickly producing astaxanthin from haematococcus pluvialis stimulated by brassinosteroids
InactiveCN101974599ALow costImprove accumulation efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationStress conditionsBetaxanthins
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
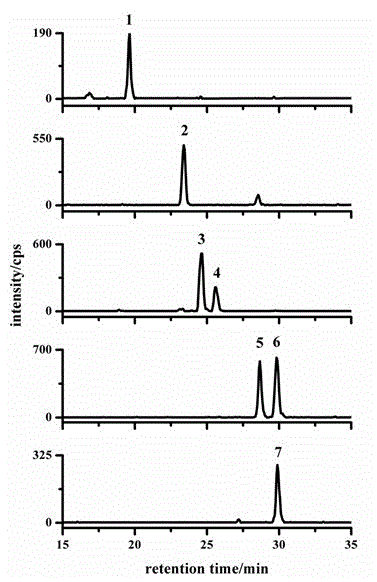
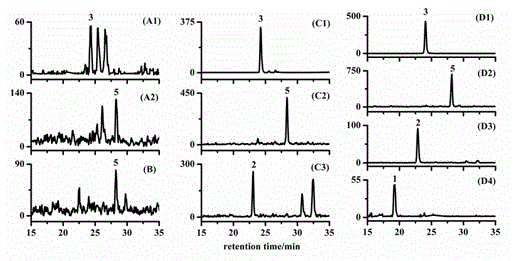
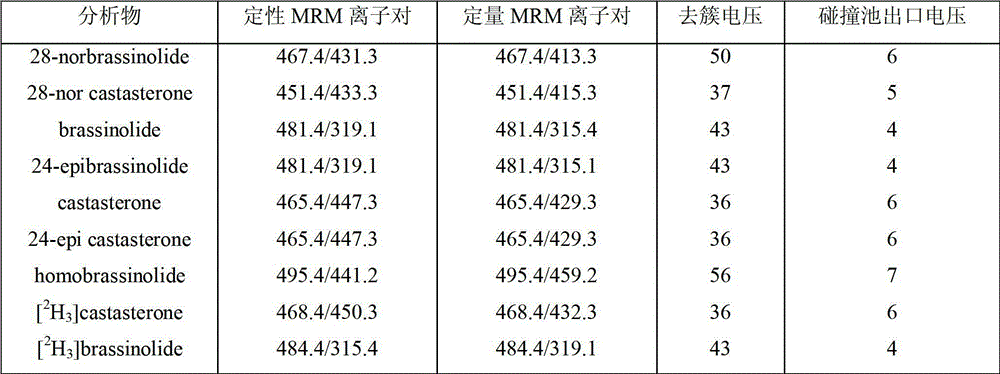
Method for quantitative detection of endogenous brassinosteroids in plant sample
InactiveCN102980953AEfficient removalEfficient detectionComponent separationSolid phase extractionSolvent
The invention discloses a method for quantitative detection of endogenous brassinosteroids in a plant sample. According to the method, firstly the endogenous brassinosteroids are extracted by using a solvent, solid-phase extraction impurity removal is carried out by double-layer solid-phase extraction small columns, liquid-liquid extraction impurity removal is further carried out, and then, a high-performance liquid-electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry is adopted, so that the quantitative detection of the endogenous brassinosteroids is realized. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the operation is simple and fast, and the sample consumption is little; and meanwhile, most of plant matrixes are effectively removed, thus the quantitative detection of low-content endogenous brassinosteroids can be realized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
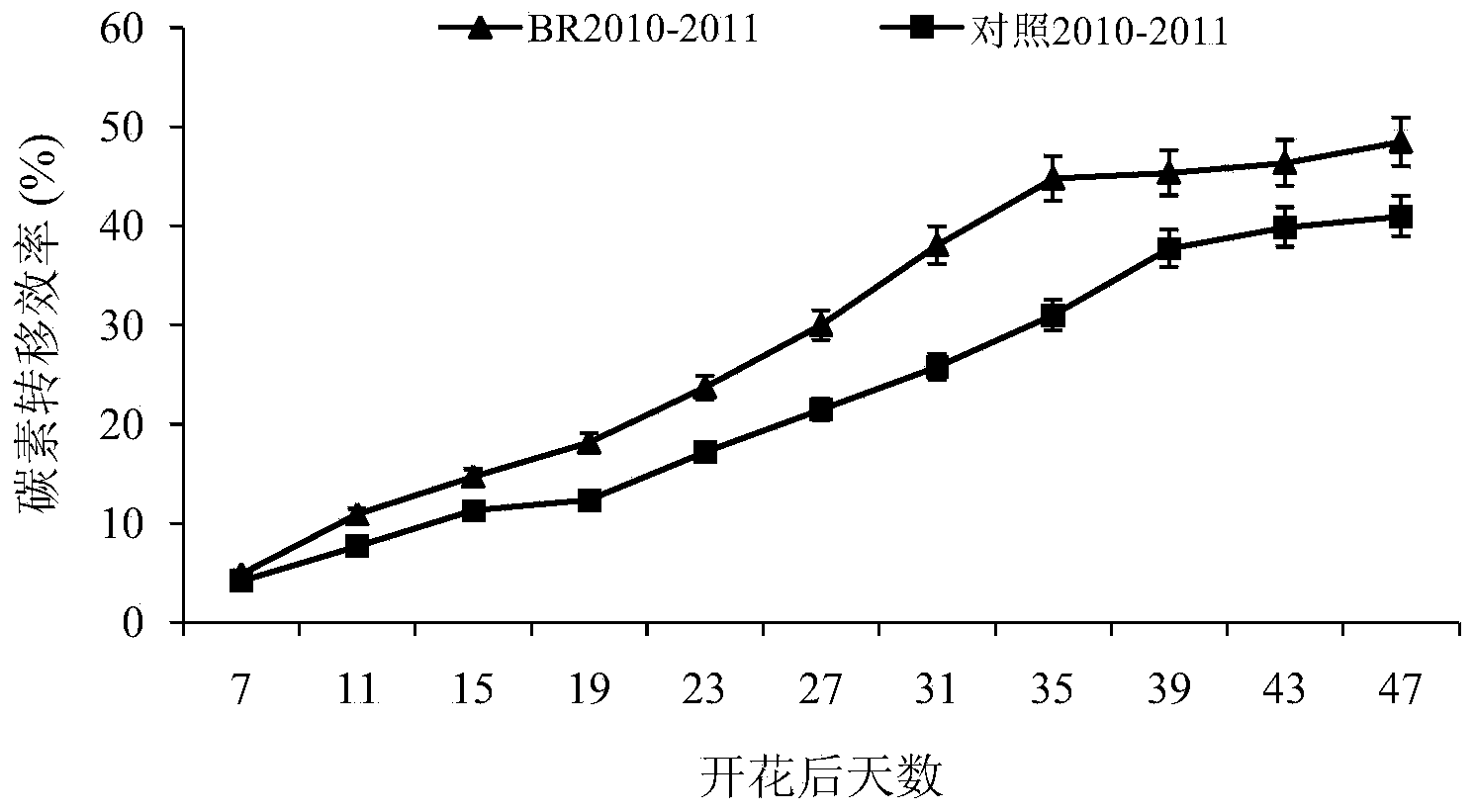
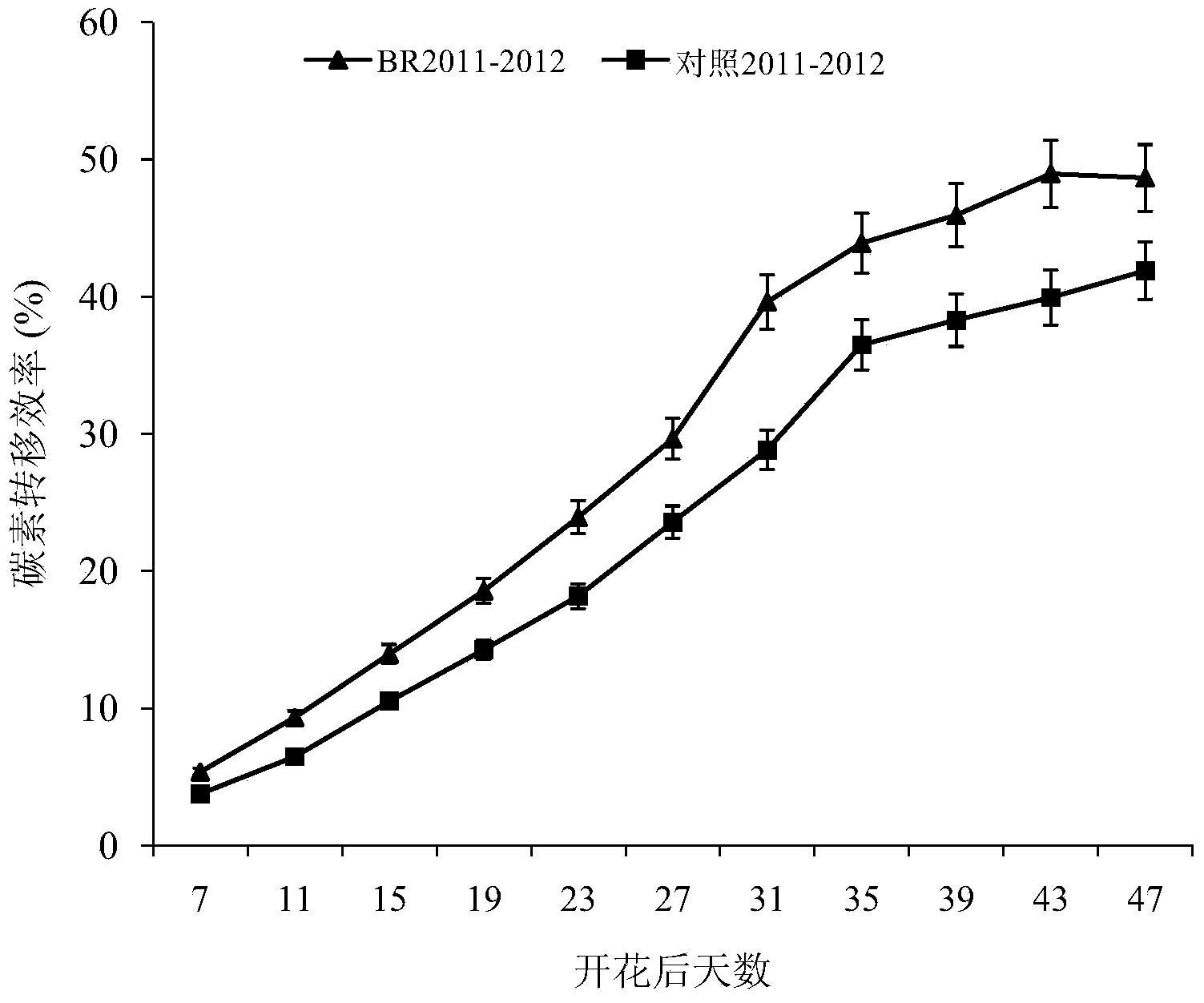
Method for promoting high production and early-maturing of rapes
InactiveCN103636397ADevelopment of High Yield Cultivation TheoryDevelop technologyHorticulture methodsPhosphatePotassium
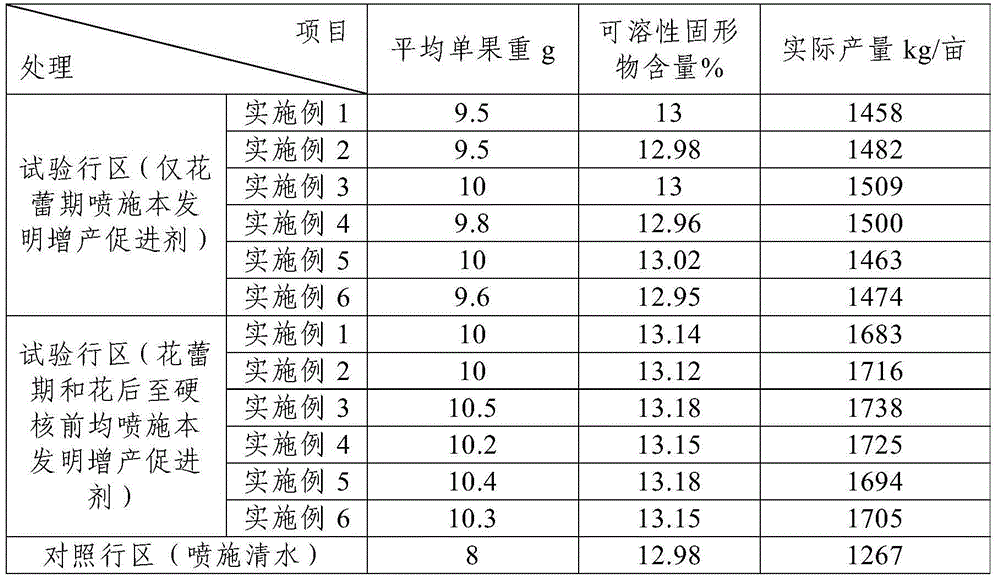
The invention discloses a method for promoting high production and early-maturing of rapes. The method comprises the following steps: A. construction of close planting high production colony of the rapes: selecting high-production, high-quality and early-maturing rape types, applying a nitrogen fertilizer in advance at the ratio of base fertilizer, seedling fertilizer to 12th lunar month fertilizer of 7:2:1; B. selection of exogenous plant growth substance type and dose: adopting a potting method, spraying 1 mg L<-1> Brassinosteroid (BR) at the blooming period to promote dry matter transshipment after blooming; C. application of exogenous plant growth regulator in field: adopting potassium dihydrogen phosphate, boric fertilizer and BR according to a certain mixing ratio; D. selection of rape harvest time: 21-35 days after blooming when the physiological maturity period is reached, wherein the harvested oil content is increased by 0.5-1.0 percent. The method is feasible, can increase the rape yield and quality, allows the rape to properly mature earlier for being harvested ahead of time, so as to effectively relieve the season contradiction, and can promote rape production and multiple cropping agricultural development in our country.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Diaper rash cream with nursing effect on baby skin and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107811950AImprove playbackPain reliefCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsMeadowfoam seed oilChlorhexidine diacetate
The invention discloses diaper rash cream and a preparation method thereof. The diaper rash cream is prepared from the main components of petrolatum, caprylic / capric triglyceride, avocado tree fruit fat, polyglyceryl-4 isostearate, meadowfoam seed oil, gallnut extract, microcrystalline wax, polydimethylsiloxane, Sorbitan olivate, Quaternium-18 Hectorite, propylene glycol, Chrysanthellum indicum extract, sodium dehydroacetate, butanediol, hydrolyzed rice protein, Anthemis nobilis flower extract, radix sophorae extract, fructus cnidii extract, Bisabolol, Ginger Root Extract, Hexyldecanol, Brassinosteroids, N-palmitoyl hydroxyproline cetyl ester, stearic acid, menthol, tocopheryl acetate, perfume, p-hydroxyacetophenone, caprylyl glycol, 1,2-hexanediol, chlorhexidine diacetate, disodium EDTA and water through synergistic interaction in an appropriate ratio by the scientific preparation method, and the produced diaper rash cream has good skin care and skin-firming effect and good affinity,can relieve skin pain, and has good stability.
Owner:达威控股有限公司
Green efficient seed dressing agent and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN105104434ADisease controlPromote germinationPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBacillus thuringiensisBrassinosteroid
A green efficient seed dressing agent is provided by the present invention, and belongs to the technical field of pesticide. The green efficient seed dressing agent consists of pure natural plant extracts such as brassinosteroid, algaeinc and tea saponin, and bio-functional bacteria such as Bacillus subtilis, actinomycetes, Beauveria bassina, trichoderma and Bacillus thuringiensis. The seed dressing agent is green and environmentally friendly, and has good effects on improving the germination rate and emergence rate of seeds, and on insect killing and sterilization.
Owner:崔明华
Sample pretreatment method of endogenous brassinosteroids in plant sample
ActiveCN103207103AAchieve enrichment and purificationSimple methodPreparing sample for investigationPretreatment methodSolvent
The invention discloses a sample pretreatment method of the endogenous brassinosteroids in a plant sample. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, the endogenous brassinosteroids are extracted by a solvent; and then the impurities of the solution obtained in the previous step are further removed with boron-affinity material as an extraction medium, so that the sample pretreatment of the endogenous brassinosteroids is realized. The method has the advantages of simplicity, rapidness, solvent conservation and simplicity in operation. Besides, according to the method, high selectivity is shown in the aspect of removing endogenous impurities of plant extracting solution and enrichment and purification of low-content endogenous brassinosteroids can be realized.
Owner:武汉绿剑可瑞信科技有限公司
Application of brassinosteroids to drought resistance and afforestation
InactiveCN101536658AReduce cell membrane permeabilityReduce MDA contentClimate change adaptationAfforestationEcological environmentDeciduous species
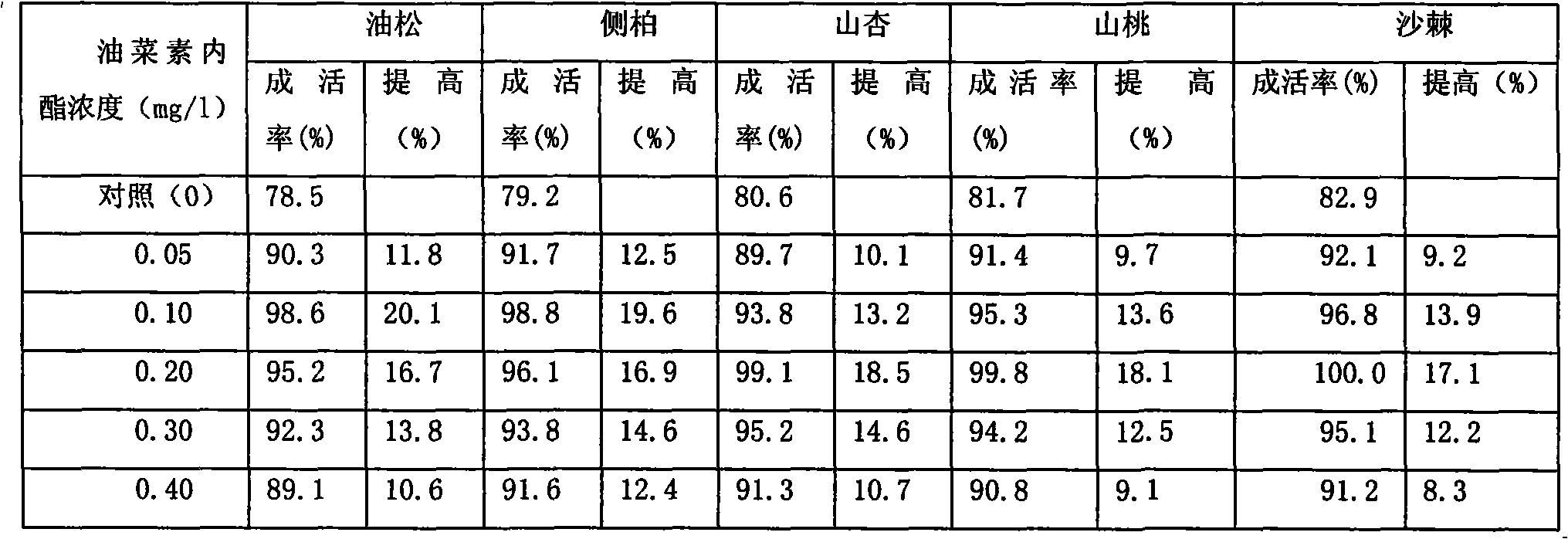
The invention relates to application of brassinosteroids to drought resistance and afforestation, which has simplicity, low cost, no soil pollution and quick effect and quite important and profound significance to accelerating vegetation to restore and reconstruct and improving the ecological environment. The invention comprises the following steps: (1) selecting the brassinosteroids with the weight percentage of 0.1 percent; (2) selecting an afforestation area; (3) selecting afforestation seasons from the last third of October to the last third of November in autumn and from the first third of March to the first third of April in spring; (4) selecting a land preparation method and specification: digging fish-scale pits on a sloping surface along a contour line, wherein the rows of the fish-scale pits are arrayed in a shape like the Chinese character 'pin', and the each fish-scale pit has a length of 60 cm, a width of 40 cm and a width of 40 cm; (5) determining afforestation tree species and seedling tree ages, wherein the afforestation tree species comprise pitch pines, biota orientalis, ansu apricots, prunus davidiana and hippophae rhamnoides, and annual seedling trees of the biota orientalis and other deciduous species are selected for the afforestation except that biennial seedling trees of the pitch pines are selected for the afforestation; (6) carrying out root-dip treatment of the brassinosteroids; and (7) planting the seedling trees.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Clone of gene PM1 for controlling paddy rice spike and application of gene PM1
InactiveCN103421820AIncrease productionTypical BR-deficient traitsOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringAgricultural sciencePlant genetic engineering
The invention belongs to the field of plant gene engineering and particularly relates to separated clone, function verification and application of a gene PM1 (Panicle Morphogenesis 1) for controlling the morphogenesis of paddy rice spike. External application of brassin steroid hormone (BR), PM1 gene expression analysis, construction of complementary carrier genetic transformation and other experiments testify that the cloned PM1 gene has the function of regulating and controlling the form of paddy rice spike. The PM1 gene and the coded protein can be used for genetic improvement of the paddy rice spike forms and grain shapes, and has an important production application value.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Yield-increase accelerant for preventing flower and fruit dropping of large cherry and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104823991APromote formationPromote floweringBiocidePlant growth regulatorsCell divisionFruit set
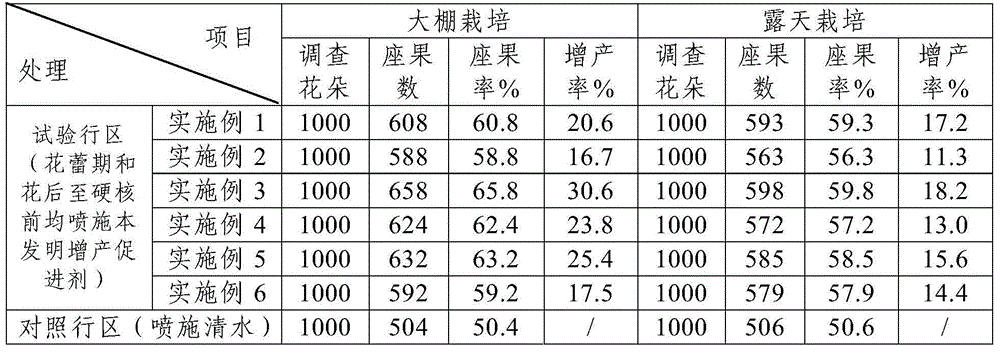
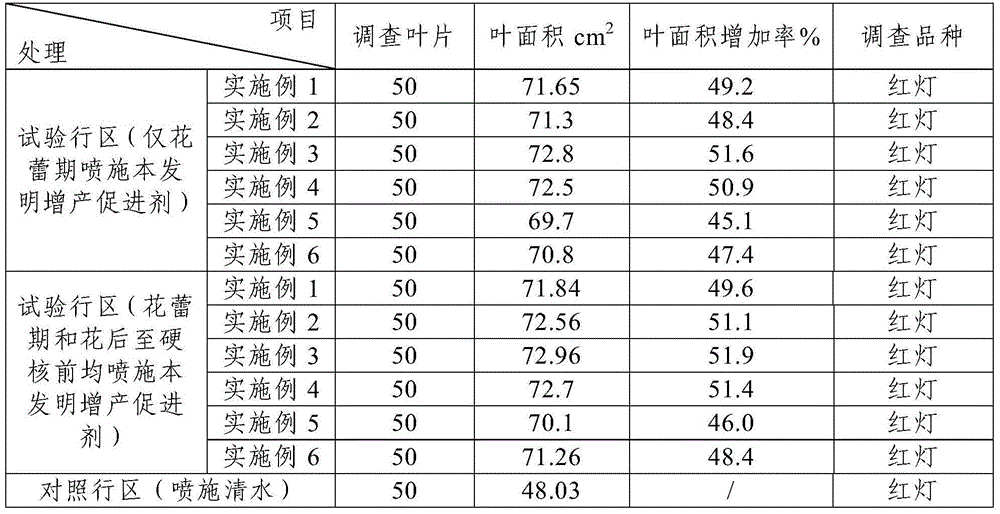
The invention discloses a yield-increase accelerant for preventing flower and fruit dropping of large cherry. The yield-increase accelerant is prepared from the following raw materials by the mass percentage: 0.2%-0.4% of phethalanilic acid, 0.1%-0.35% of 6-benzylaminopurine, 0.08%-0.2% of auxin, 2.8%-4.0% of brassinosteroid, 0.5%-2.5% of a penetrating agent, and the balance dimethylformamide. In addition, the invention also discloses a preparation method of the yield-increase accelerant. The yield-increase accelerant can promote pollination and fertilization of the large cherry, has flower and fruit retention effects, effectively prevents flower and fruit dropping of the large cherry, improves the fruit-setting ratio of the large cherry, induces cell division of large cherry fruits, improves the quality of the large cherry, increases the single fruit weight to the greatest extent, thereby improving the yield and achieving purposes of increasing yield, income and efficiency.
Owner:郭徐澄
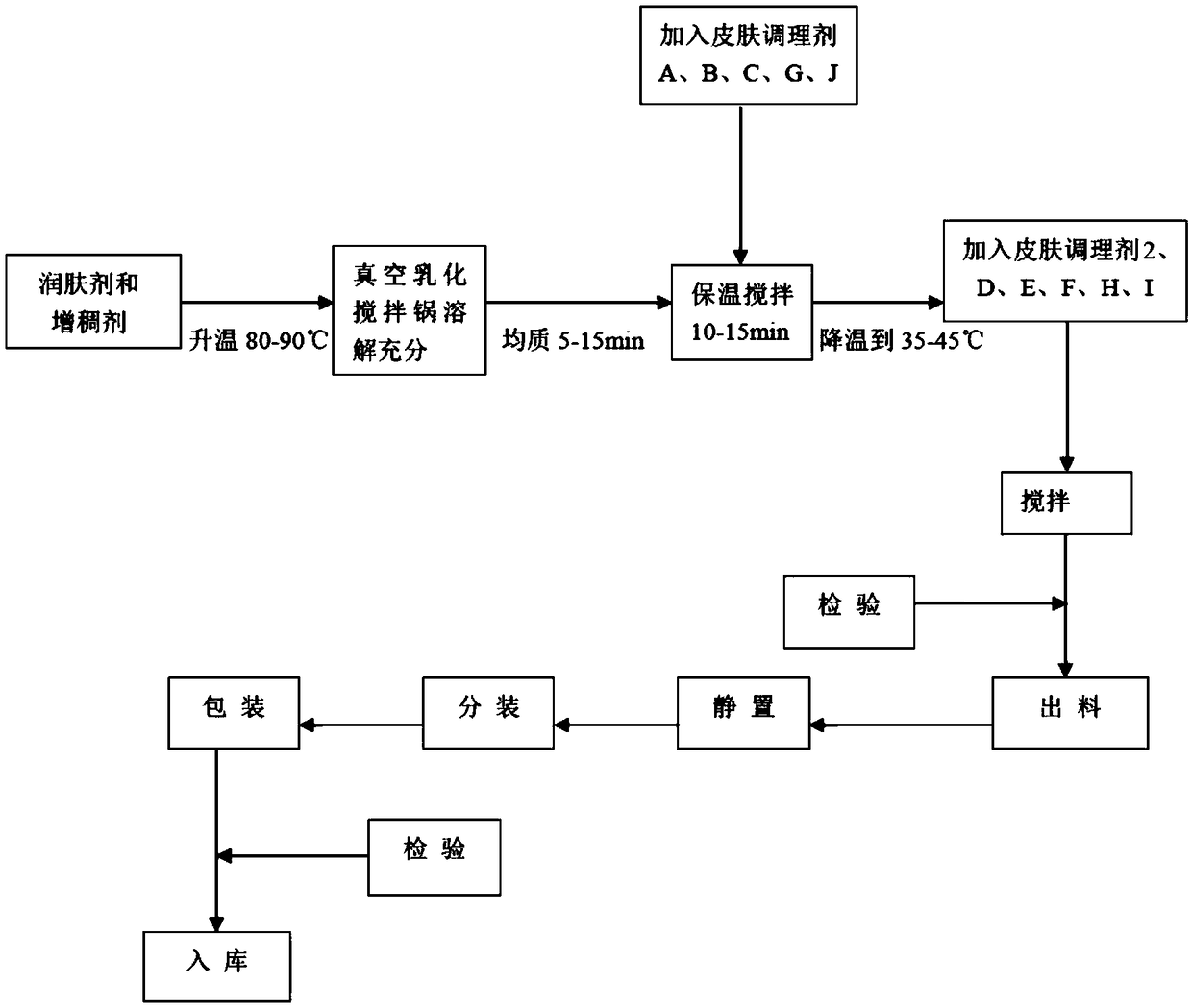
Skin-care product composition for repairing damaged cells and sensitive skin and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the field of skin-care products, and discloses a skin-care product composition for repairing damaged cells and sensitive skin and a preparation method thereof. The skin-care product composition comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 88-92% of an emollient, 6-10% of a skin conditioner, and 1-2% of a thickening agent, wherein the emollient comprises at least one of the following components: squalene, butyrospermum parkii fruit fat, and triethylhexanoin; the skin conditioner comprises a skin conditioner 1 and a skin conditioner 2; the skin conditioner 1 comprises at least one of brassinosteroid, cetostearyl alcohol, a radix arnebiae extract, allantoin, lavender oil, rose oil, bisabolol, a butyrospermum parkii fruit fat extract, spent grain wax,argan oil, a ginger extract, glycerinum, a flos chamomillae recutitae extract, and hydroxyphenylpropionamide benzoic acid; the skin conditioner 2 comprises at least one of butanediol, 1,2-pentanediol, a red-knees herb extract, and xanthan gum; and the thickening agent comprises at least one of the following components: polyethylene, vinyl polydimethyl siloxane / polymethylsiloxane silsesquioxane cross-linked polymer.
Owner:北京润熙怡和科技有限公司
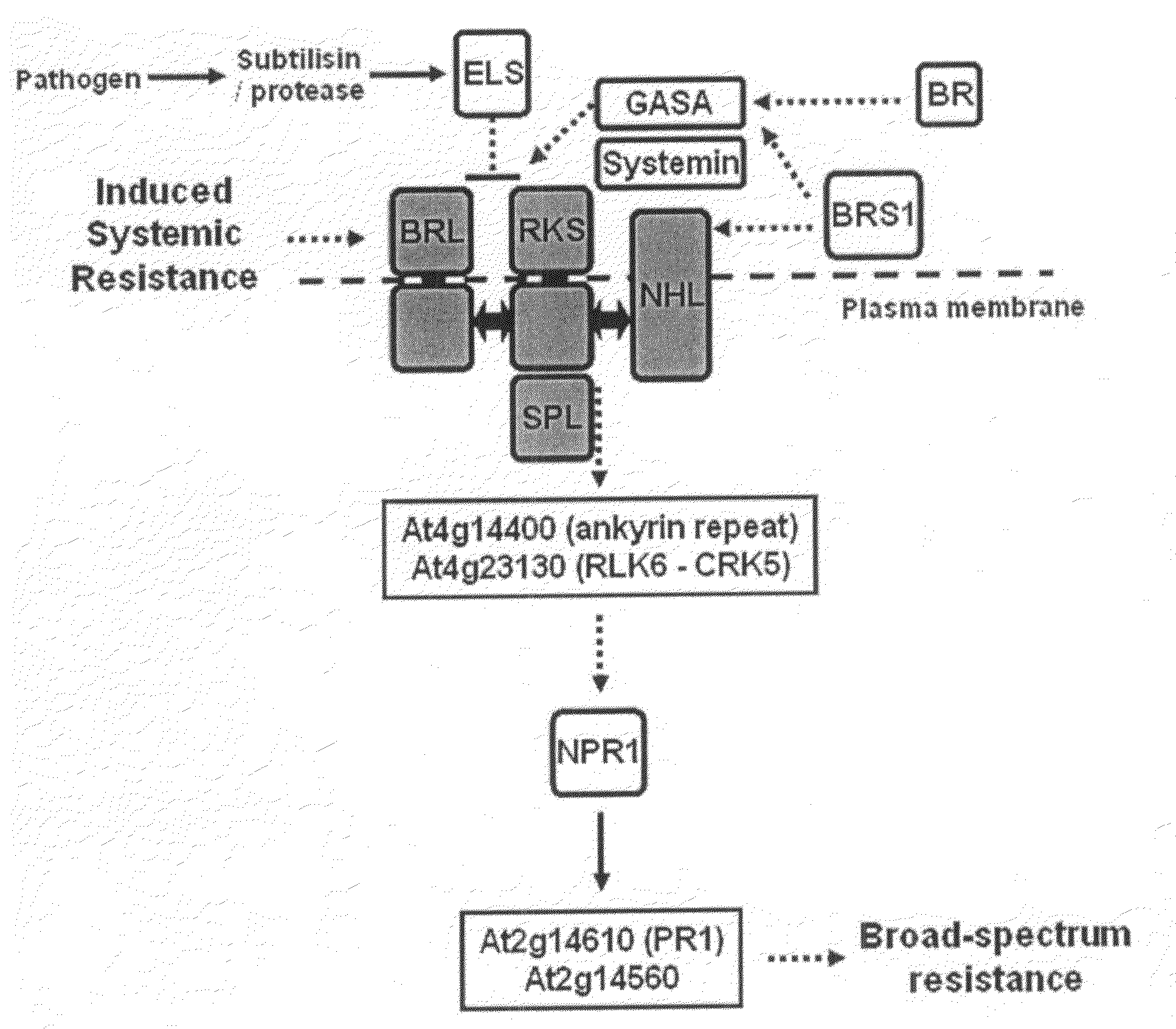
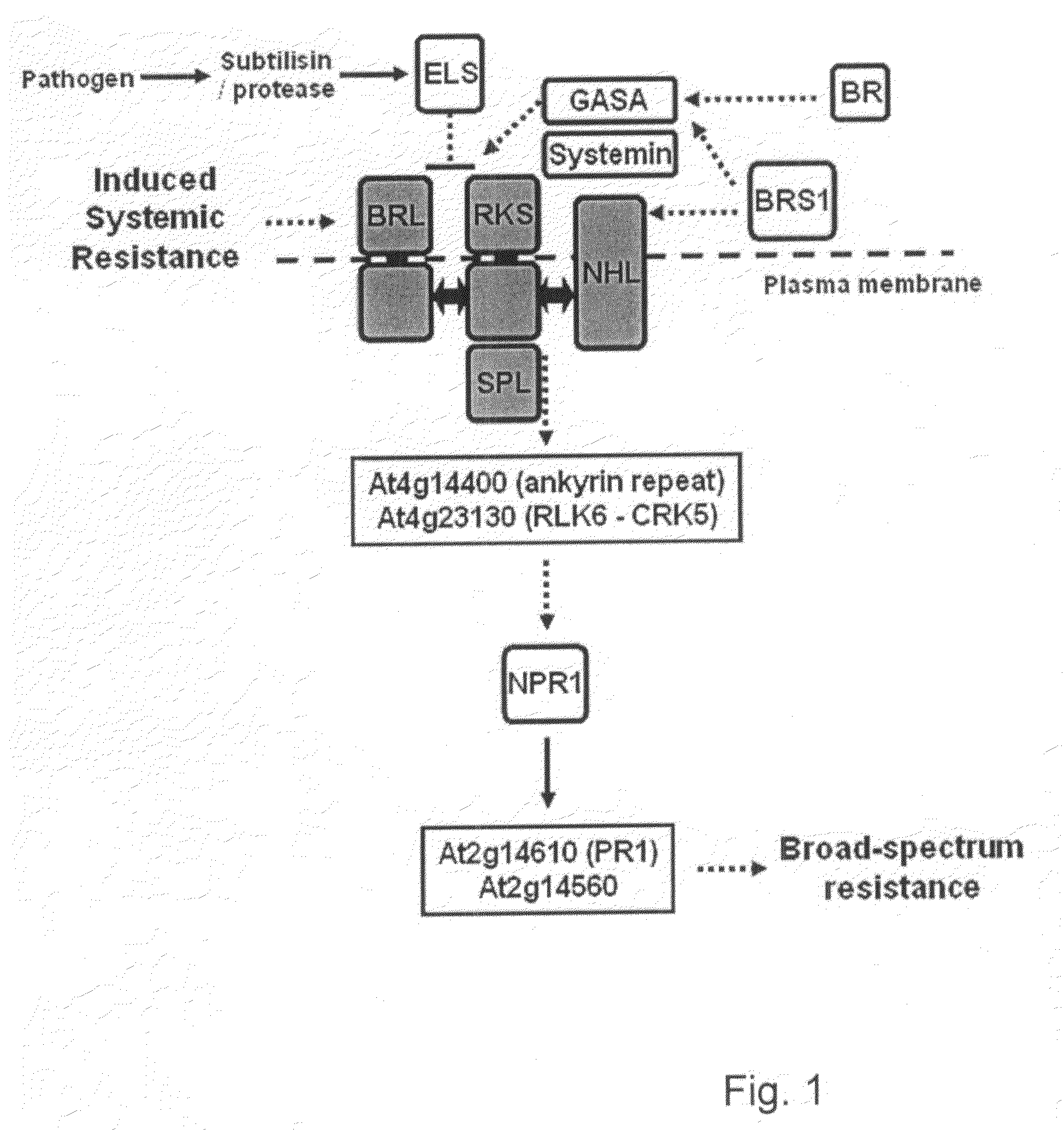
Novel method to increase pathogen resistance in plants
InactiveUS20080220971A1High sensitivityFacilitate cognitionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementWhole bodyA-DNA
The invention provides a method for enhancing resistance in plants by providing these plants with a gene construct comprising a DNA sequence coding for a receptor for a systemic signal compound, wherein such a systemic signal compound is one or more of the group consisting of salicylic acid, jasmonic acid and brassinosteroids. The resistance can the be induced by contacting said plants with said signal compound. Preferably, the receptor is an RKS receptor, salicylic acid receptor or jasmonic acid receptor. Also combinations and / or chimaeric receptors can be applied.
Owner:EXPRESSIVE RES
Metabolic inhibitors against brassinosteroids
A brassinosteroid metabolism inhibitor, which comprises as an active ingredient a compound represented by the following formula (I) or (II): wherein R1 and R2 independently represent hydrogen atom or a lower alkyl group, R3 represents a hydrogen atom, a lower alkyl group, or a lower alkoxyalkyl group, R4 represents a phenyl group which may be substituted, X represents a single bond or —CH2—, R11 represents a lower alkyl group, a lower alkenyl group or a phenyl group which may be substituted, R12 represents a lower alkyl group or a phenyl group which may be substituted, and R13 represents a phenyl group which may be substituted, or a salt thereof.
Owner:RIKEN
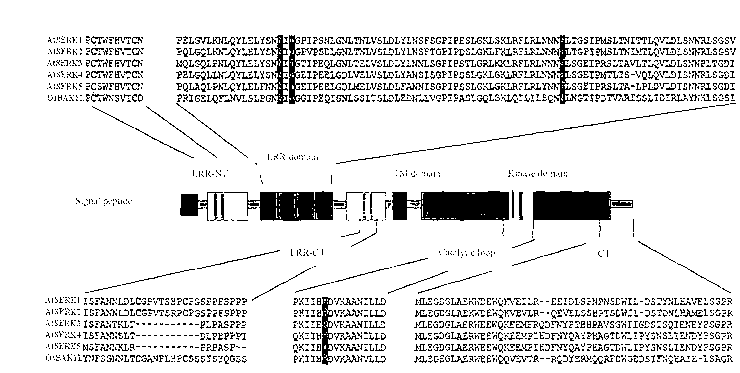
Receptor kinase albuminoid of rice brassinosteroid and coding genes and applications thereof
The invention discloses a receptor kinase albuminoid of rice brassinosteroid and coding genes and applications thereof. Proteins related to the disease resistance of plants as provided in the invention have proteins which contain one of following amino acid residue sequences: 1) sequence of SEQ ID No1 in the sequence table; 2) proteins related to the disease resistance of plants and containing a SEQ ID No: 1 amino acid residue sequence in the sequence table with replacement, deletion and addition of 1-10 amino acid residues. After being inoculated with pathogenic bacteria, proteins in the invention can induce the up-regulation expression in plants which carry non-host resistance genes and can increase the plant disease resistance.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
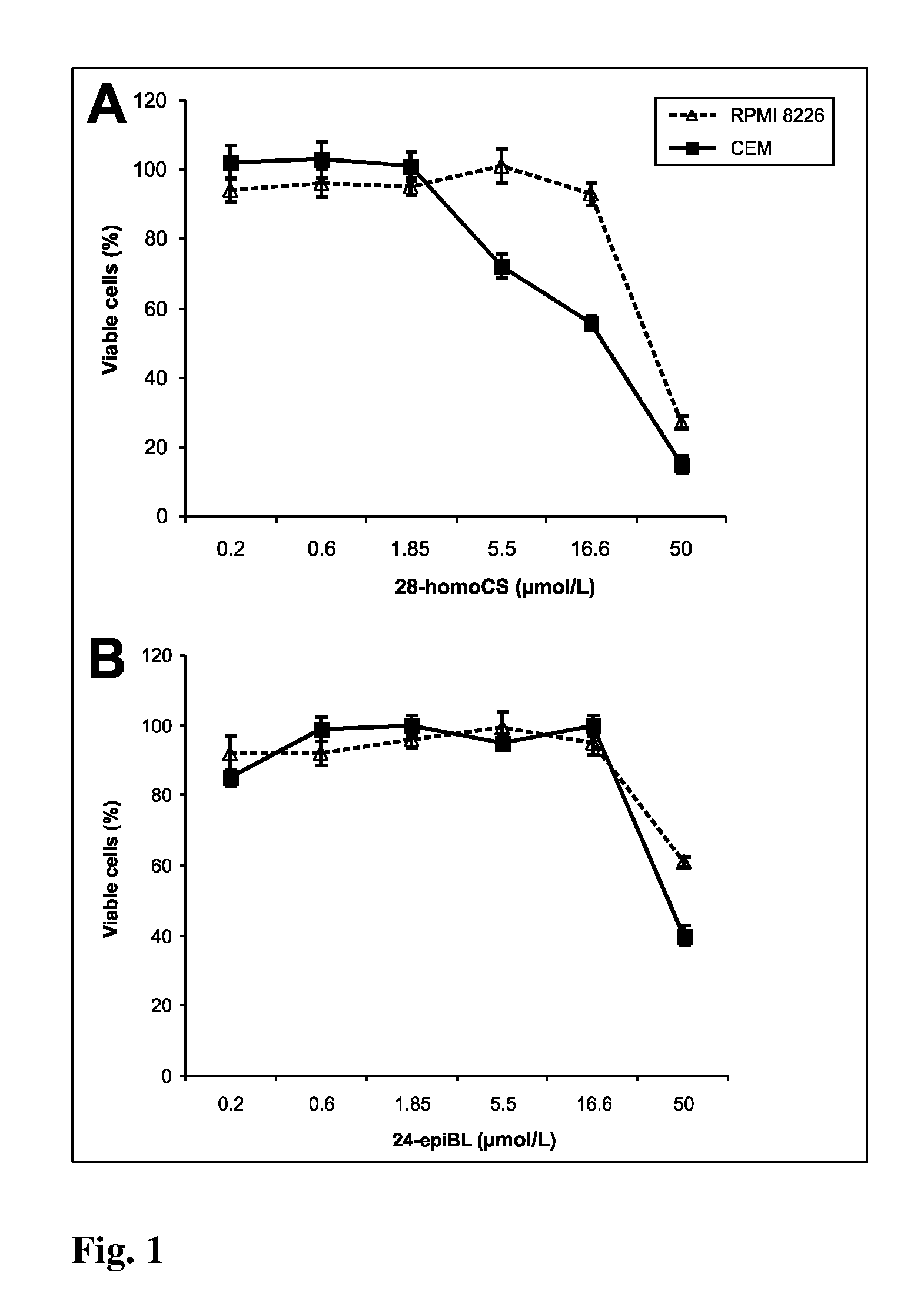
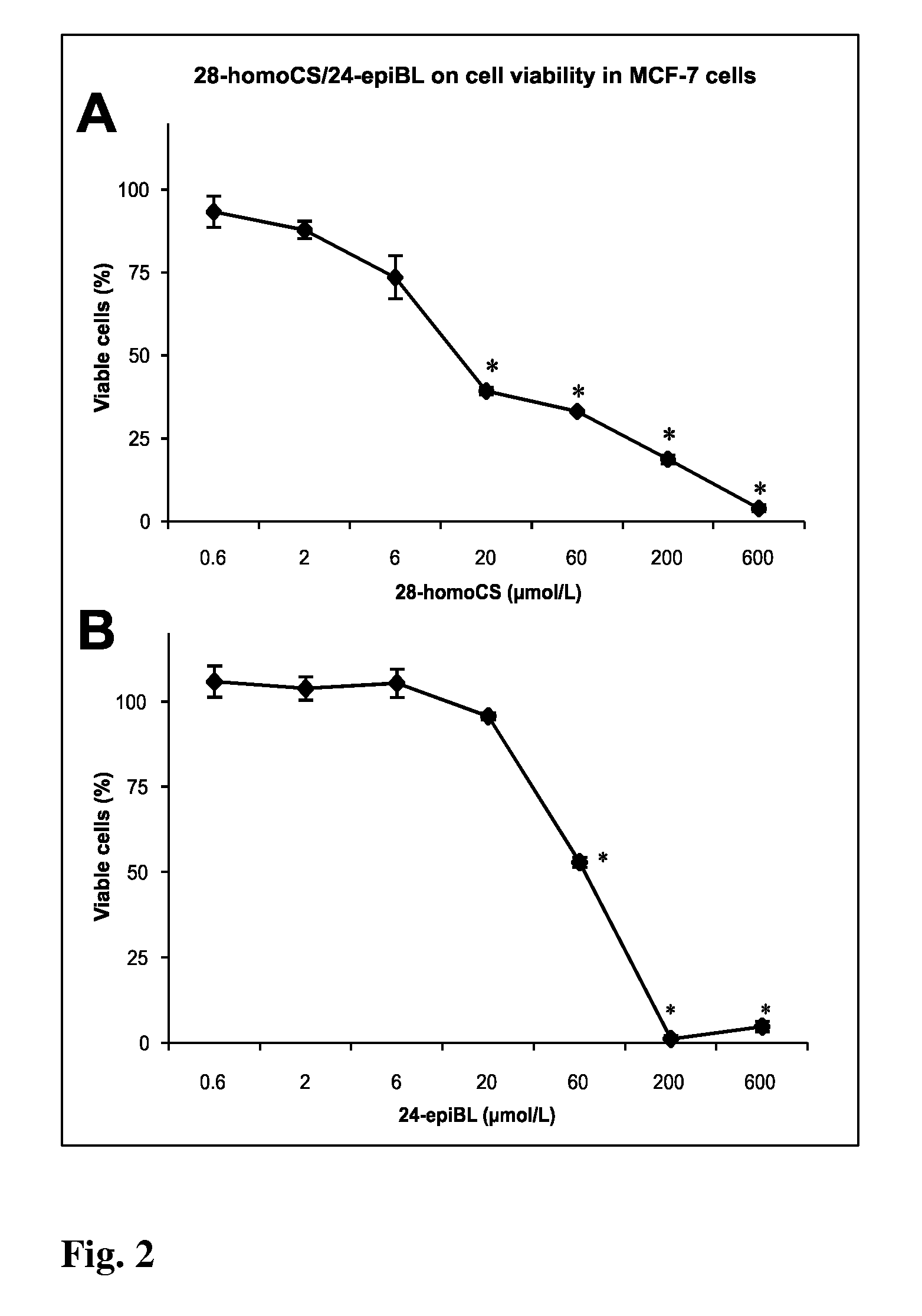
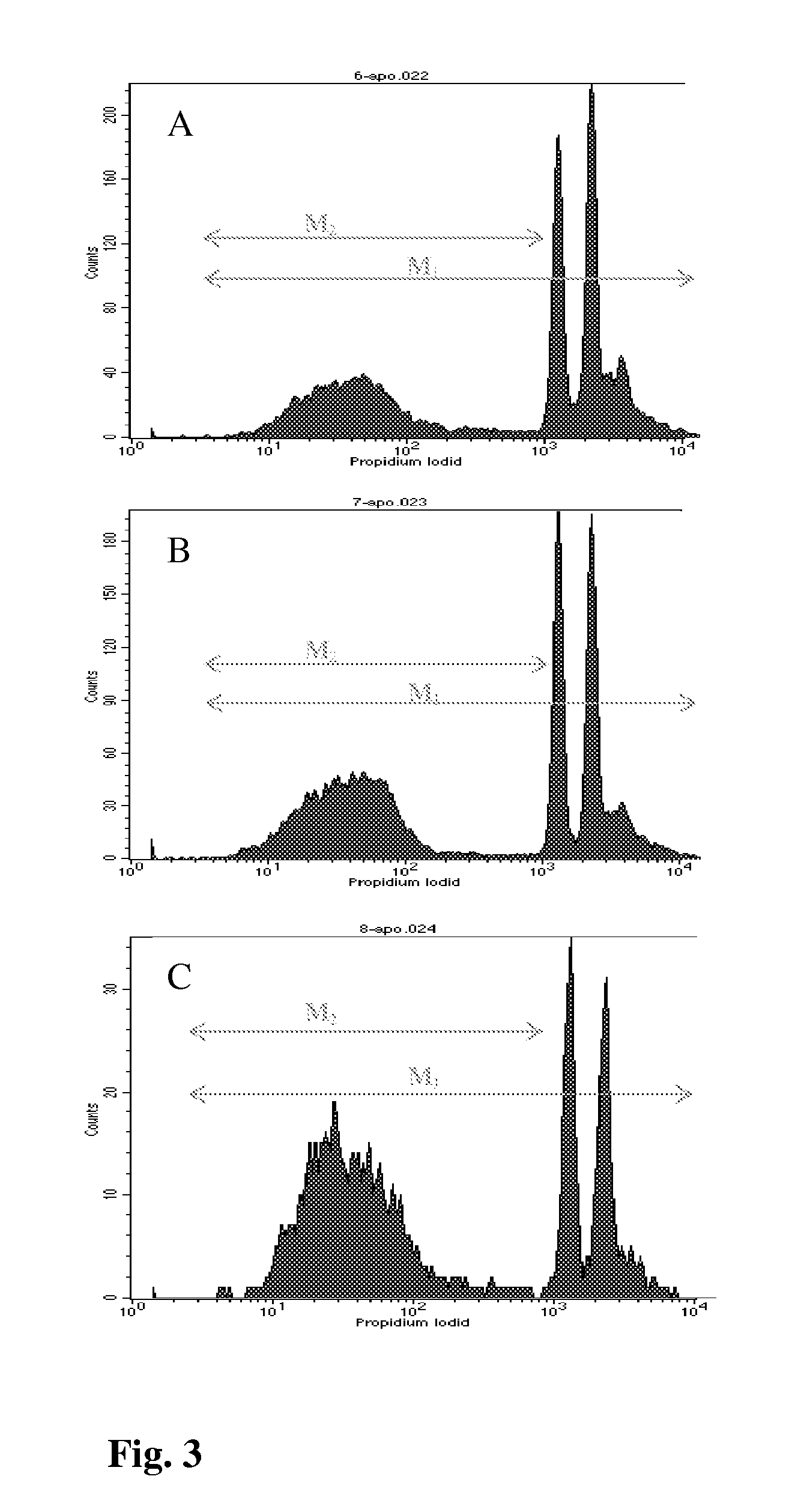
Natural brassinosteroids for use for treating hyperproliferation, treating proliferative diseases and reducing adverse effects of steroid dysfunction in mammals, pharmaceutical composition and its use
InactiveUS20100204460A1Improve water-binding capacityPromote absorptionGlycoside steroidsAntineoplastic agentsProstate cancer cellMammal
The present invention relates to natural brassinosteroids of general formula (I), wherein R is CH2 or O—CH2 group, R2 is hydrogen or hydroxyl, R3 is hydroxyl, R24 is alkyl or alkenyl, which are selected from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, methylen, ethylen and propylen, and R25 is alkyl selected from the group consisting of methyl and ethyl, and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use for treating hyperproliferation, treating proliferative diseases and reducing adverse effects of steroid dysfunction in mammals. The present invention also provides methods capable to arrest of the cell cycle by natural brassinosteroids resulting in apoptotic changes in cancer cells. More specifically, the present invention relates to use for treatment of the adverse effects of hyperproliferation on mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo, especially treatment of hyperproliferative diseases in mammals by administering compositions containing natural brassinosteroids. This invention also describes new use for treating consisting in a new therapeutic way for modifying cell viability of human breast and prostate cancer cells.
Owner:ASTAV ORGANICKU ACHEM A BIOCHEM ACAD VED CR V V I +1
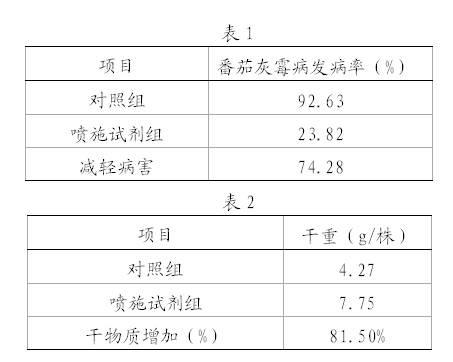
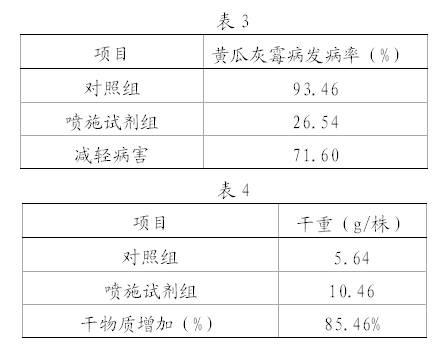
Preparation for controlling Botrytis cinerea and preparation and application method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of pesticides, in particular to a preparation for controlling Botrytis cinerea of crops like tomatoes, cucumbers and the like. The preparation comprises the following components: Brassinosteroids, magnesium sulfate, ferrisulphas, boric acid, composite amino acid, alcohol and Tween 80. The preparation has the advantages of simple preparation, convenience in use, low cost and no side and toxic effects, can obviously relieve the attack degree of the Botrytis cinerea of the crops like the tomatoes, the cucumbers and the like by at least 70 percent and can also obviously enhance the resistance of the crops and improve the quality of the crops after being used.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel rosin increasing agent for pinus massoniana
The invention provides a novel rosin increasing agent for pinus massoniana based on systematical research on the influence of plant mineral nutrients, plant growth regulators and pH on the rosin production of the pinus massoniana in order to improve the efficiency of rosin harvesting, ensure the supply of raw materials for rosin industry and promote healthy development of the rosin industry. The rosin increasing agent provided by the invention can significantly improve rosin production and rosin secretion of the pinus massoniana, and the rosin increasing period is two months or more. The rosinincreasing agent is composed of one or more of a plant growth regulator naphthalene acetic acid, brassinosteroid, and plant essential mineral nutrient elements Mg, Zn, Fe, Cu, B, Na, Cl and S.
Owner:梧州市林业技术推广站 +2
High-efficiency slow-release fertilizer used for fragrant fruit lotus root and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106518295AFull of nutritionFertilizer effect time is longAnimal corpse fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserOysterAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a high-efficiency slow-release fertilizer used for fragrant fruit lotus root. The fertilizer contains the following ingredients: oyster shell, sulphited castor oil, cane sugar, white carbon black, serpentine powders, rice hull ash, grapevine powder, plant deodorizing bacteria, saccharomycetes, ganoderma lucidum, butanedioic acid, nitrogen humate, black pepper extract, grape seed extract, Brassinosteroid, aproper amount of hydrogen peroxide, a proper amount of ammonia water, etc. By fermentation of serpentine powders, rice hull ash and grapevine powder in cooperation with nutrients, a coated slow-release fertilizer is prepared. The fertilizer itself is rich in organic matter and mineral elements, has rich nutrients, and has no peculiar smell. With the adoption of a coating layer capable of oxygen supply and dynamic regulation of pores, the fertilizer has long time of fertilizer efficiency, can release organic matter for a long time, and can promote metabolism of lotus root, promote growth and development of lotus root and inhibit infectious microbes in the growth environment. By the use of the fertilizer, quality of lotus root is guaranteed, oxidation resistance and brittleness are enhanced, and high-efficiency cultivation is realized. The fertilizer can be widely applied and promoted.
Owner:高鹏
Resistance to abiotic stress in plants
InactiveUS8119855B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationPlant cellBrassinosteroid
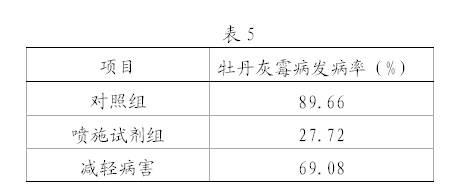
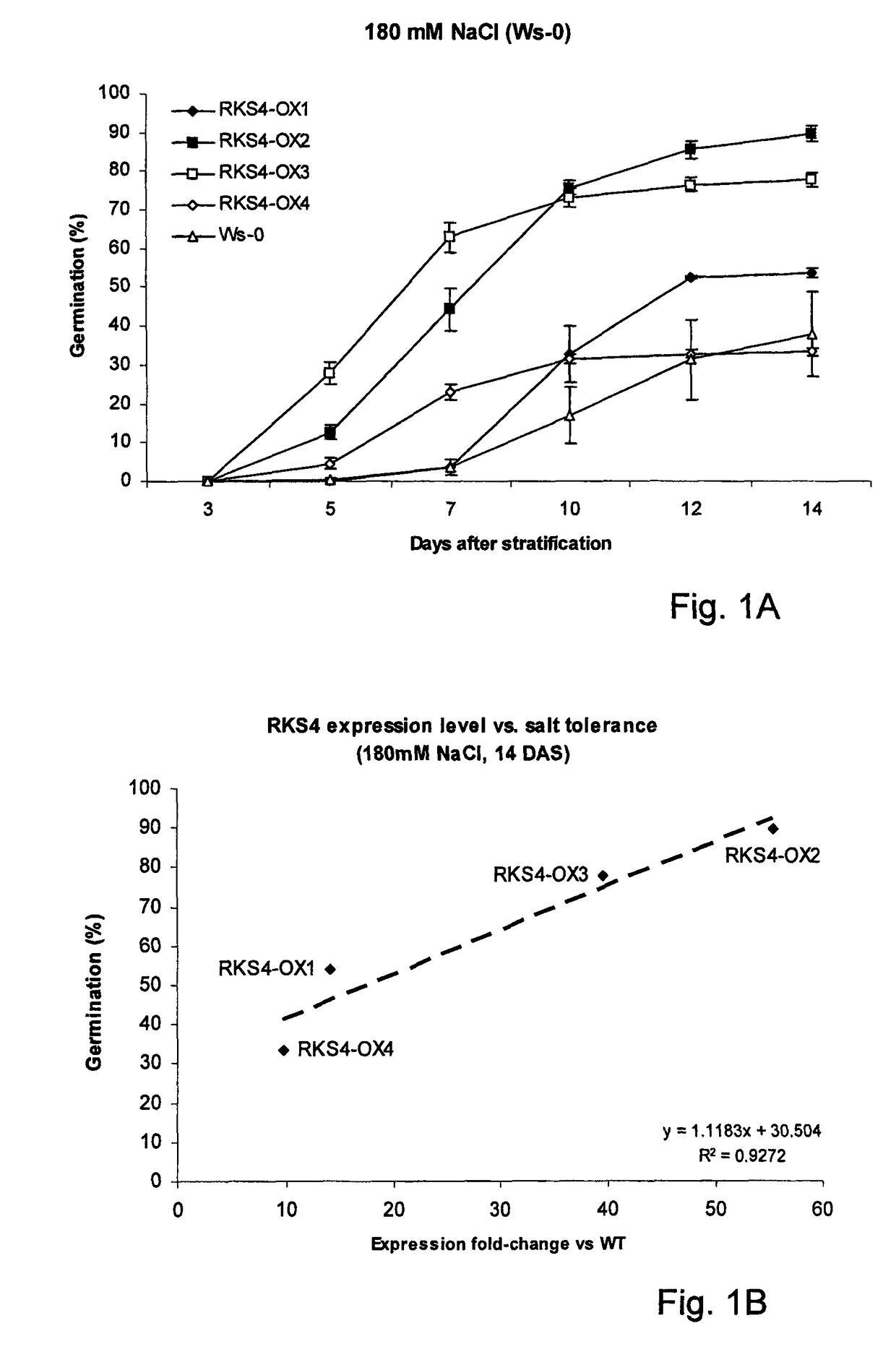
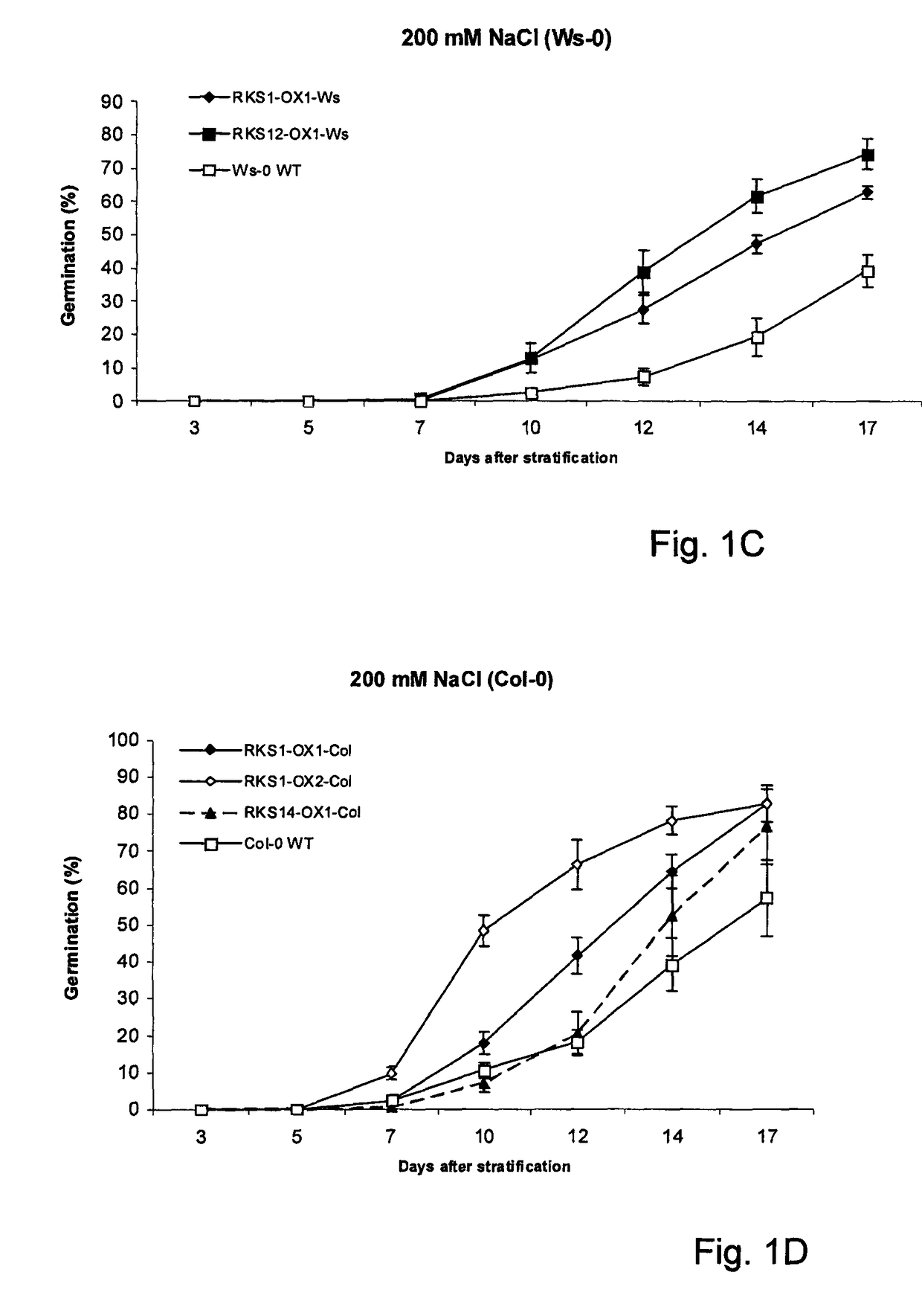
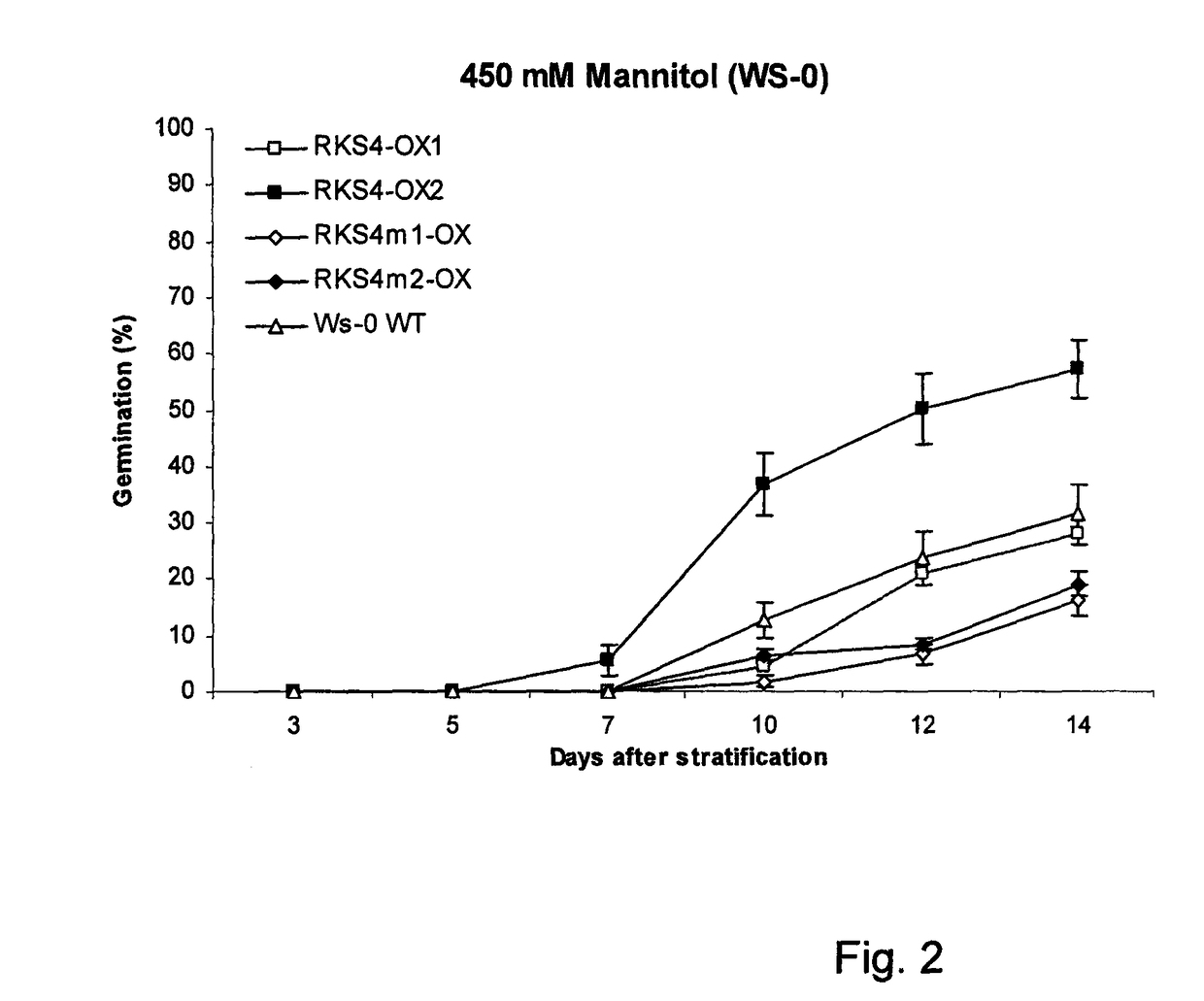
The invention relates to a method for conferring tolerance to abiotic stress to plants or plant cells. This is done by introducing a gene coding for an RKS protein, especially a gene coding for an RKS subgroup II protein, more specifically RKS1, RKS4 or truncated RKS4, or a gene from RKS subgroup III, more preferably RKS12. The effect of overexpression of the RKS gene may be enhanced by additionally treating the plant with a brassinosteroid compound.
Owner:EXPRESSIVE RES
Preparation for accelerating degradation of pesticides in plants
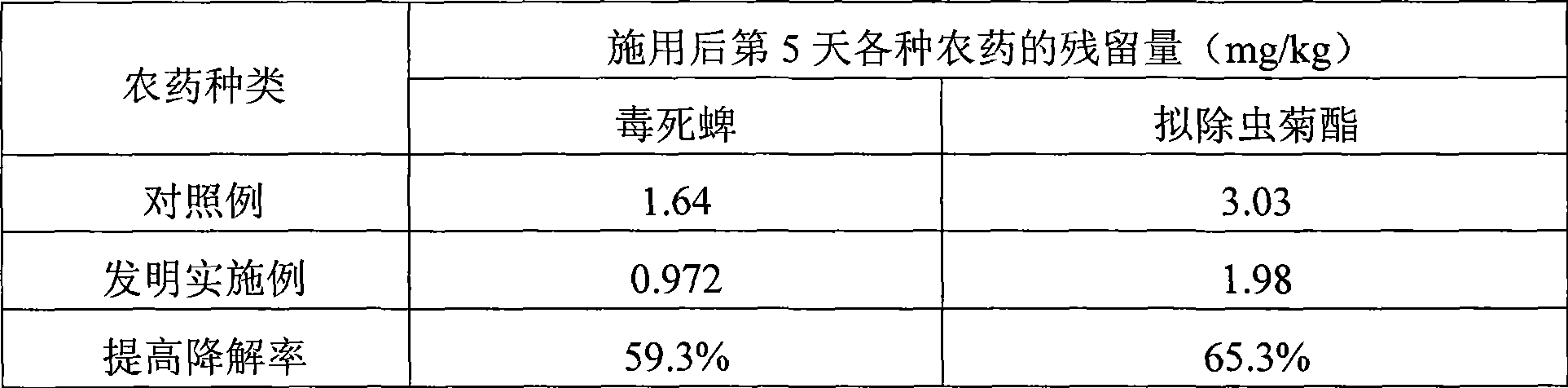
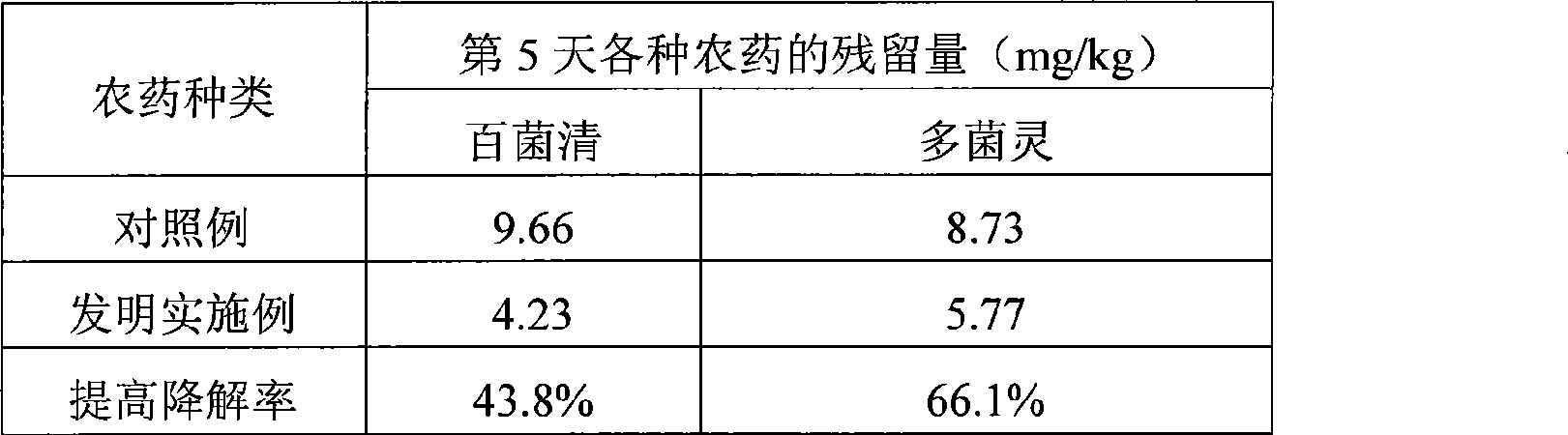
The invention discloses a preparation for accelerating the degradation of pesticides in plants. Each 100ml of preparation comprises 5-20mg of brassinosteroids, 0.1-1.0g of abscisic acid, 3-50ml of alcohol with 95% of mass concentration and 2-10ml of tween 60 with 98% of mass concentration, and the rest is water. The preparation of the invention has the advantages of simple fabrication, convenient use, low cost and no side effects. Furthermore, the preparation can remarkably reduce 30%-70% of residues of pesticide in the plants, and reduces the safe interval period in using pesticides for about 3-5 days, meanwhile, the preparation can also improve the resistibility of the plants remarkably, and reduce the usage amount of pesticides. Thus, the preparation is applicable for crops such as vegetables, fruit trees, flowers, tea leaves and the like, and is suitable for popularization and application in vast rural areas of our country.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Dendrobium officinale seed tissue culture medium
InactiveCN105746361APromote divisionImprove scalabilityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureDiseaseBud
The invention relates to the technical field of tissues, in particular to a dendrobium officinale seed tissue culture medium.The culture medium is formed by mixing mother liquor I, mother liquor II, mother liquor III, mother liquor IV, mother liquor V and mother liquor VI, and the volume ratio of the mother liquor I to the mother liquor II to the mother liquor III to the mother liquor IV to the mother liquor V and the mother liquor VI is (3-5): (1-2): (1-2): (1-2): (2-3): (0.03-0.05); the mother liquor VI is composed of, by weight, 5-10 mg / L of metalaxyl, 30-50 mg / L of compound sodium nitrophenolate, 30-80 mg / L of forchior fennron, 15-55 mg / L of microcystin, 30-80 mg / L of brassinosteroid.The dendrobium officinale seed tissue culture medium has the advantages that dendrobium officinale seed cell division can be quickly promoted, the germination time can be accelerated, it can be guaranteed that seedlings grow healthily and are free of diseases, colors are glossy dark green, bud flesh is satiate in thickness, and the bud ratio reaches 100%, and the preparation technology is easy to operate and convenient to popularize.
Owner:LINGYUN LONGEVITY IMMORTAL GRASS BIOTECH SCI DEV
Method of increasing growth of lateral roots of Malus hupehensis
InactiveCN106577217APromote growthIncrease vitalityPlant growth regulatorsBiocideInsect diseaseGreenhouse
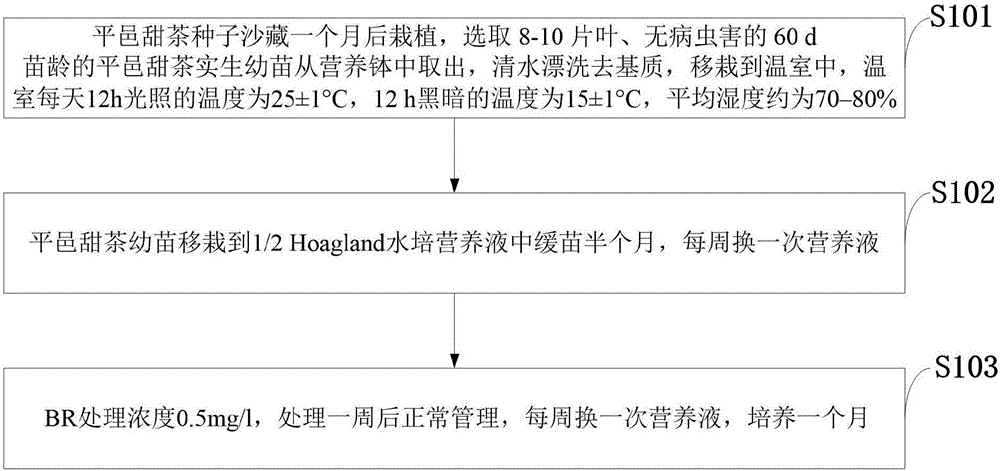
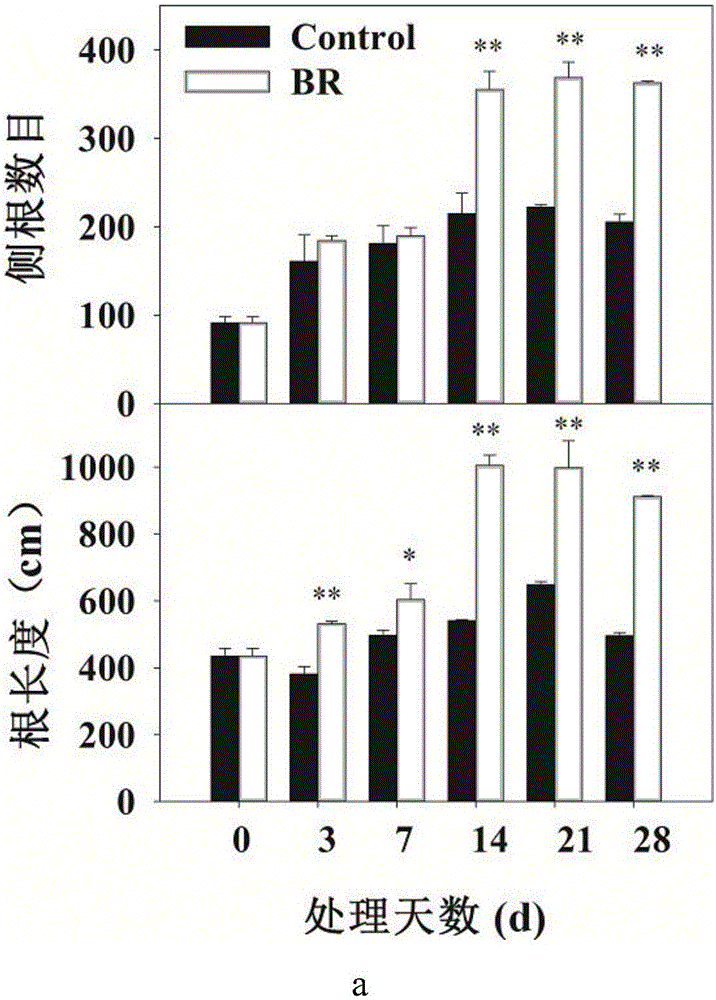
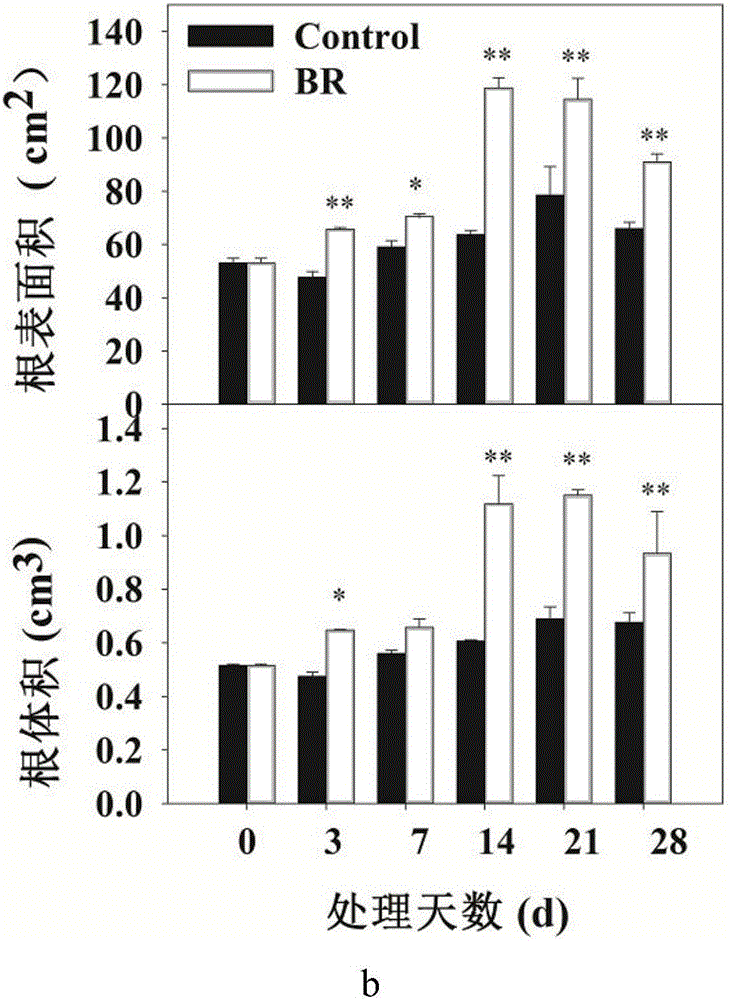
The invention discloses a method of increasing growth of lateral roots of Malus hupehensis. The method of increasing growth of lateral roots of Malus hupehensis includes the steps: after storing seeds of Malus hupehensis in sand for one month, planting the seeds of Malus hupehensis in a nutrition pot; selecting 8-10 leaves and 60-days old and insect-disease-free seedlings of Malus hupehensis, and taking the seedlings of Malus hupehensis away from the nutrition pot, rinsing the matrix by means of clean water, and transplanting the seedlings of Malus hupehensis to a greenhouse; transplanting the seedlings of Malus hupehensis to 1 / 2Hoagland water planting nutrient solution for seedling recovering for half a month, and exchanging the nutrient solution once a week; and performing BR (brassinosteroid) processing, wherein the BR processing concentration is 0.5mg / l, normally managing after one week of processing, exchanging the nutrient solution once a week, and cultivating for one month. For the method of increasing growth of lateral roots of Malus hupehensis, the BR processing increases the number of roots, the length of roots, the surface area of roots, the volume of roots, the height of plants, and the thickness of stems of the seedlings of Malus hupehensis. In a word, the RB processing is conductive to growth of lateral roots, and especially increases growth of fine roots. The method of increasing growth of lateral roots of Malus hupehensis can provide certain theoretical basis for growth of lateral roots of apple, and has important meaning for guiding practical production.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Rapid and efficient detection method of brassinosteroid
InactiveCN105116060ASimple extraction processHigh extraction rateComponent separationFiltrationDerivatization
The present invention provides a rapid and efficient detection method of brassinosteroid. The rapid and efficient detection method comprises: adopting fresh grape fruits as a material, rapidly grinding into powder with liquid nitrogen, adding 80-95% methanol, isotope internal standard 2H3 brassinosteroid and 2H3 brassin sterone, carrying out low temperature ultrasonic extraction, standing for 2-5h, filtering, taking the filtration residue, adding 80-95% methanol, leaching for 1-2 h, filtering, merging the two filtrates, carrying out physical adsorption to remove the water, sequentially loading onto a C18 column, a sephadex LH-20 column and a silica column, eluting with methanol to obtain an enriched sample liquid, adding phenylboronic acid, carrying out a derivatization reaction, cooling, concentrating to achieve a dry state, redissolving with acetonitrile so as to be used for liquid chromatography determination, selecting acetonitrile and water as the mobile phase, and collecting the target peak, wherein a volume ratio of the acetonitrile to water is (6:4)-(9:1), and the elution way is isocratic elution. The method of the present invention has characteristics of rapidness, efficiency, stable baseline and good brassinosteroid separation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANLI UNIV
Chinese cabbage activating protein 2/ethylene responsive factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factor gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102747091AImprove resistance to bacterial wiltPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringActivating protein 2Nicotiana tabacum
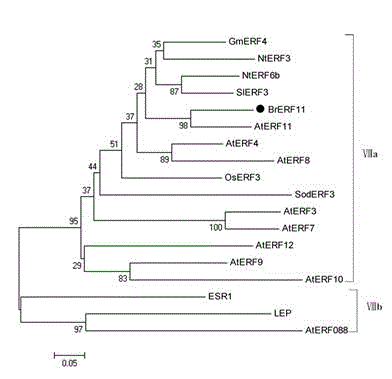
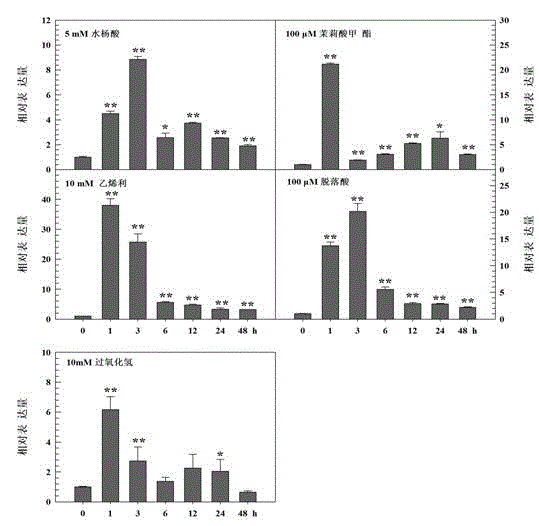
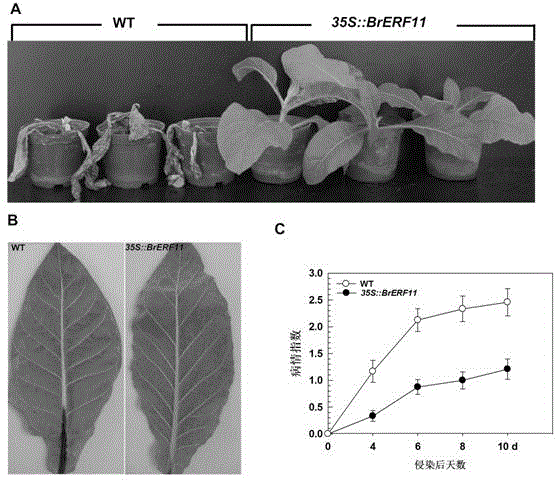
The invention relates to a Chinese cabbage AP2 / ERF transcription factor gene and applications thereof and belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. A complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA) sequence of the gene is represented as SEQIDNo.1. The Chinese cabbage AP2 / ERF transcription factor gene is applied in nightshade tobacco bacterial wilt-resisting genetic engineering. When transgenic tobacco is compared with wild tobacco, the overexpression of a Chinese cabbage brassinosteroid ethylene responsive factor 11 (BrERF11) gene in the tobacco can significantly improve the bacterial wilt-resisting ability of the transgenic tobacco, so that the Chinese cabbage AP2 / ERF transcription factor gene has an important application value in the plant bacterial wilt-resisting genetic engineering and can promote the development of the tobacco bacterial wilt-resisting genetic engineering greatly.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
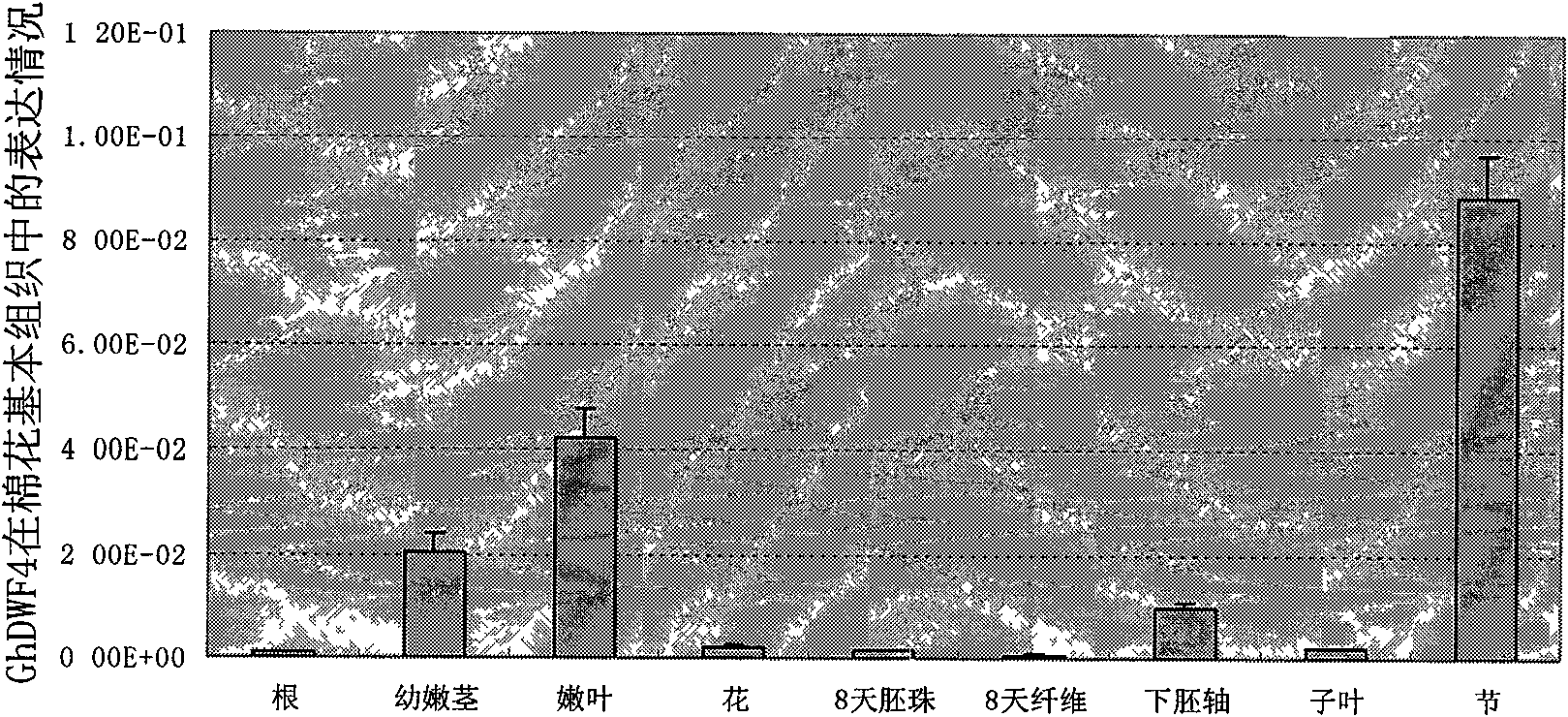
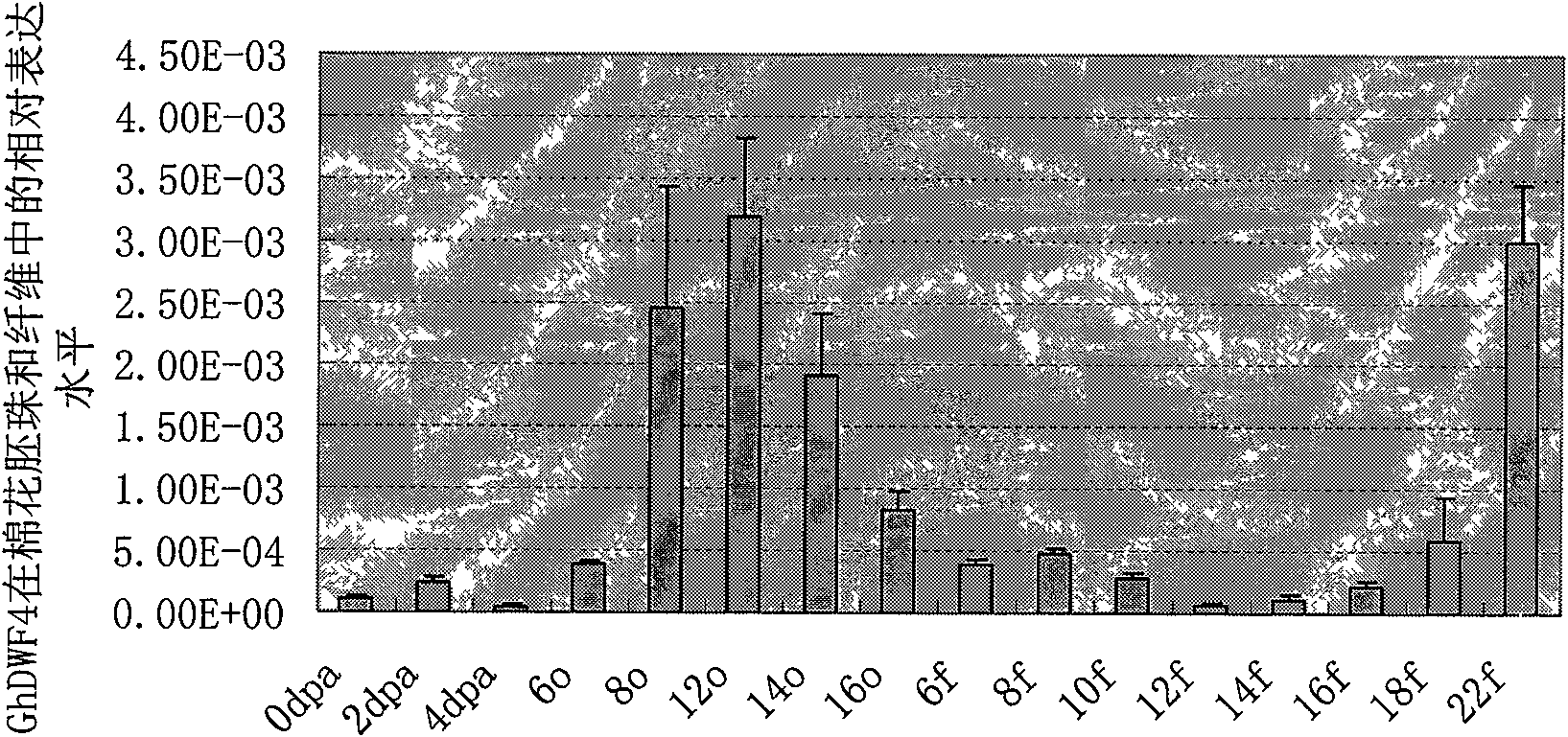
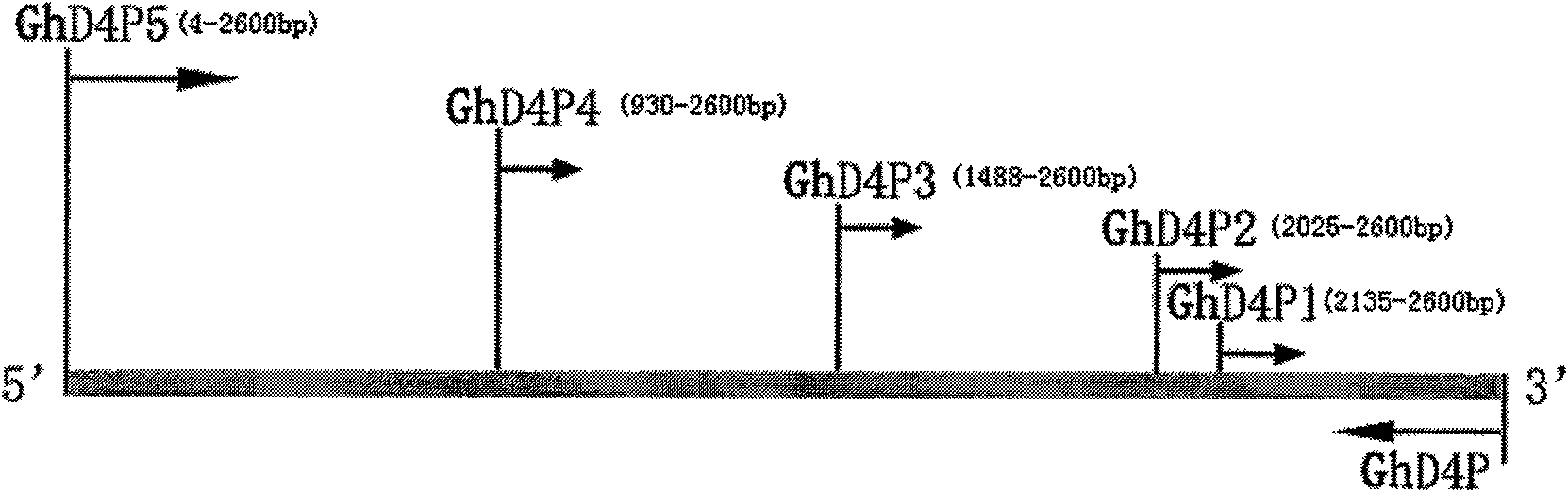
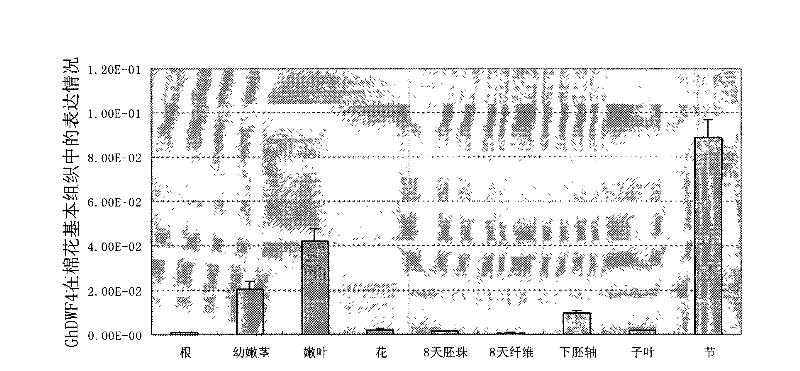
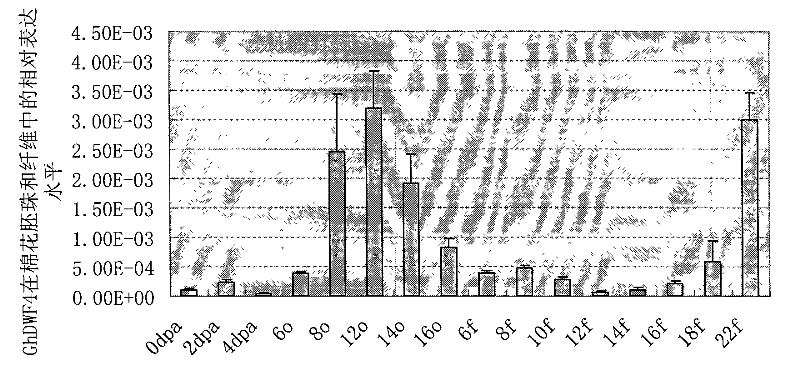
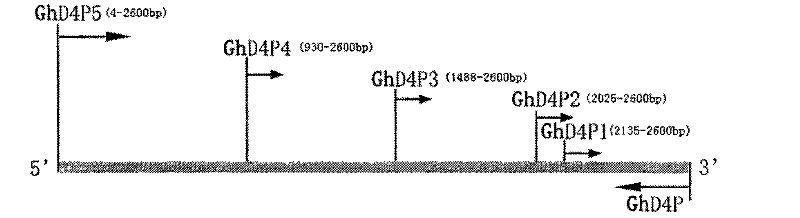
Promoter of cotton brassinosteroids synthetase GhDWF4 gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a sequence or a segment of a promoter of a cotton brassinosteroids synthetase GhDWF4 gene. The promoter contains 2600 bases and can be used for adjusting and controlling a target gene to express in a special tissue organ in a plant body so as to further adjust and control the growth of the tissue organ and obtain good agronomic traits.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Fertilizer for potted flower and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107417339APromote growthPromote healthy growthCalcareous fertilisersAnimal corpse fertilisersPolyvinyl alcoholMushroom
The invention discloses a fertilizer for a potted flower. The fertilizer comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 25-35 parts of urea, 8-12 parts of potassium nitrate, 15-20 parts of zinc ammonium phosphate, 20-25 parts of potassium phosphate, 1-2 parts of calcium sulfate, 3-5 parts of magnesium humate, 1-1.5 parts of potassium silicate, 0.1-0.2 part of copper chloride, 0.03-0.05 part of sodium borate, 15-20 parts of mushroom dreg, 10-15 parts of sugar residue, 18-22 parts of peanut vine, 20-25 parts of damaged flower branch, 15-20 parts of bean cake, 10-15 parts of shell powder, 0.5-1 part of brassinosteroid, 0.1-0.3 part of indoleacetic acid, 3-4 parts of saccharomycetes and 45-55 parts of coating material, wherein the coating material comprises the following raw materials: bentonite and modified polyvinyl alcohol. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the fertilizer for the potted flower.
Owner:天长市天兴园林绿化工程有限公司
Promoter of Cotton Brassinolide Synthase ghdwf4 Gene and Its Application
The invention discloses a promoter sequence of a cotton brassinolide synthase GhDWF4 gene or a fragment thereof. The promoters are 2600bp long, and they can be used to regulate the expression of target genes in special tissues and organs of plants, and then regulate the growth and development of the tissues and organs to obtain excellent agronomic traits.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Special fertilizer for tea-oil trees and preparation method of special fertilizer
InactiveCN108546214APromote absorptionBiocideExcrement fertilisersCamellia oleiferaPlant cultivation
The invention discloses a special fertilizer for tea-oil trees and a preparation method of the special fertilizer, belonging to the technical field of plant cultivation. The special fertilizer contains the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50-60 parts of corn straws, 20-26 parts of corn stigma, 10-14 parts of brewer's grain, 7-9 parts of furfural residue, 5-7 parts of fermented rapeseedcakes, 10-13 parts of humic acid, 2-4 parts of brassinosteroid, 5-7 parts of perlite, 2-4 parts of bamboo charcoal powder and 15-20 parts of animal urine and excrement. According to the special fertilizer for the tea-oil trees, the utilization rate of soil to the fertilizer can be increased, and pathogenic insects and pathogenic bacteria in the soil can be killed, so that the growth of the tea-oiltrees is accelerated.
Owner:安徽滋申生态农林综合开发有限公司
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com