Methods of diagnosing and treating based on site-specific tau phosphorylation
A technology of phosphorylation and phosphorylation, applied in chemical instruments and methods, disease diagnosis, specific peptides, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0130] Example 1 - Phosphorylation sites on tau protein in normal non-AD human brain
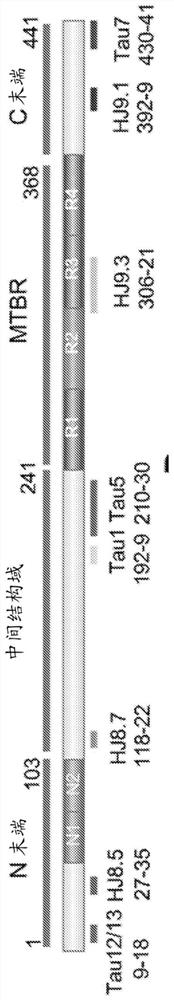
[0131] To determine the phosphorylation sites of normal soluble brain tau, extracts from healthy controls were purified by immunocapture using Tau-1 and HJ8.5 tau antibodies to concentrate both phosphorylated and unphosphorylated tau. Trypsin digestion of brain tau isoforms yielded 27 unmodified peptides of sufficient length and hydrophobicity to be detected by LC-MS (Barthélemy et al., 2016). Twenty-five peptides contained serine and / or threonine as potential phosphorylation sites. Several peptides contained multiple potential phosphorylation sites (4-9), which allowed consideration of different monophosphorylated peptides that might co-elute together during LC separation. Thereafter, the PRM screening method described above was applied to these peptides.
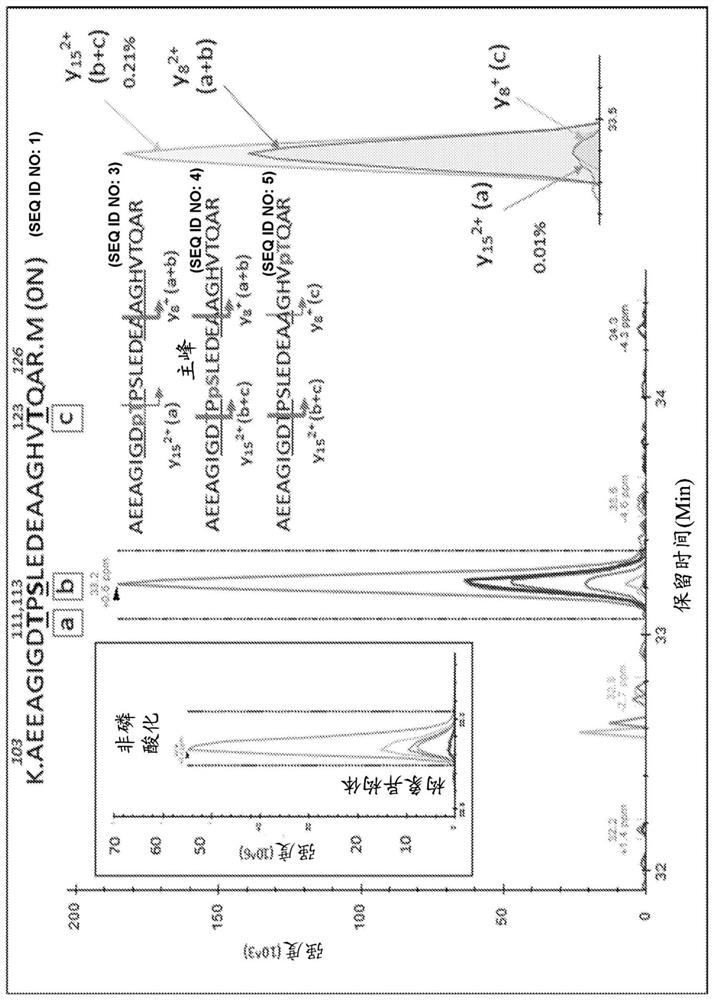
[0132]Analysis of the projection domain in the tau sequence (103-126) revealed that multiple p-tau peptides eluted as overlapping com...
Embodiment 2
[0140] Phosphorylation site on tau protein in embodiment 2-CSF
[0141] Compared to brain tau digests, CSF tau purification and digestion using tau-specific antibodies yielded detectable peptides primarily from the middle domain of the protein sequence (residues 150-221). Peptides are detectable to a lesser extent from the N-terminus, and little sequence is detectable from the microtubule-binding repeat (MTBR) domain or C-terminus of tau (Barthélemy et al., 2016; Sato et al., 2018). This difference in signal recovery may be caused by tau being truncated during release from neurons (Sato et al., 2018). Using current PRM methods, peptide recovery of this intermediate domain is sufficient to monitor the corresponding minor phosphorylated isoforms. In contrast, significant technical advances in MS methods are required to detect phosphorylated peptides in MTBR and C-terminal domains.
[0142] PRM screening of tau phosphopeptides from normal control CSF identified several phosphor...
Embodiment 3-
[0144] Example 3 - CSF p-tau abundance measurements highlight differences compared to p-tau abundance in the brain
[0145] In the brain, S404 was the most phosphorylated of the phosphorylation sites examined (pS404 / S404 = 110%, ie 52% of S404 was phosphorylated). Thus, more than half of brain tau was phosphorylated at S404 compared to other hyperphosphorylated sites at S202 and T181 (9.7% and 9.5%, respectively). 1.3% of S199 was phosphorylated, but this may be underestimated because the Tau1 antibody used for extraction was unable to bind its corresponding phosphorylated epitope (Liu et al., 1993). Phosphorylation at C-terminal sites other than S404 was found to be about 1%. At the N-terminus, T52, S68 / T69, T50 and S113 were also phosphorylated, with abundances ranging from about 0.5% to 2%. Other detected sites appeared to be phosphorylated at much lower levels (<0.5%).
[0146] In addition to pT205 and pS208 being uniquely detected in CSF tau but not in brain, the relat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com