Colorectal cancer screening kit based on excrement sample
A colorectal cancer, kit technology, applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, biological tests, and microbial determination/inspection, can solve problems such as defects in the diagnosis of colorectal cancer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0185] Embodiment 1: experimental method
[0186] 1. DNA extraction of stool samples and quantification of human DNA
[0187] The collected stool samples were immediately preserved in STE buffer solution (500 mM Tris-HCl, 10 mM NaCl, 100 mM EDTA). Each time with 3.2 grams of feces, using Stool DNA Kit (Omega) was used to extract DNA. 10 ng / μl human cell genomic DNA NA12878 was serially diluted 10 times (10, 1, 0.1, 0.01, 0.001 ng / μl), and the extracted fecal DNA was diluted 1000 times with water. KAPA SYBR FAST Master Mix was used for qPCR quantification, and the hLine gene was used as the detection site to measure the concentration and content of human DNA in feces extracted DNA.
[0188] 2. Fecal occult blood test
[0189] The q-FOB sample collection tube (Epitope Diagnostics, 30210) was used to randomly collect a small amount of fecal samples three times, and the results of fecal occult blood were detected with Xiaokang Bao fecal occult blood test strips (colloidal g...
Embodiment 2
[0208] Example 2: Low detection efficiency of fecal occult blood for colorectal adenoma
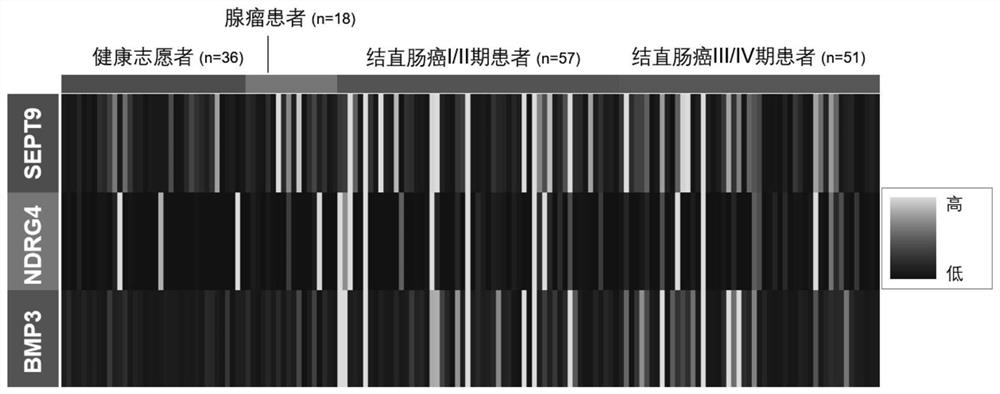
[0209] A total of 36 healthy volunteers, 18 colorectal adenoma patients, 57 colorectal cancer stage I and II patients and 51 colorectal cancer stage III and IV patients were collected in this experiment. According to the experimental method of Example 1, the collected samples were extracted from feces DNA and tested for fecal occult blood. The results are as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0210] No positive fecal occult blood was found in healthy volunteers, 2 patients with adenoma had positive test results (11.1%), and 41 samples of colorectal cancer stage I and II patients had positive test results (71.9%). A total of 34 samples (66.7%) of rectal cancer stage III and IV patients were positive. The results show that the detection efficiency of fecal occult blood detection for colorectal adenoma and adenocarcinoma is only about 66-72%, and there are undetected false negatives for both ade...
Embodiment 3
[0211] Example 3: Stool DNA Accumulation of More Mutations in Patients with Colorectal Adenomas and Adenocarcinomas
[0212] A total of 36 healthy volunteers, 18 colorectal adenoma patients, 57 colorectal cancer stage I and II patients and 51 colorectal cancer stage III and IV patients were collected in this experiment. According to the experimental method of Example 1, the collected samples were extracted from feces DNA, and DNA mutation detection was done, and the results figure 2 shown.
[0213] A sequencing library was constructed using the target region primer library to detect mutations at specific sites of KRAS, BRAF and PI3KCA. The sequence obtained from the sequencing library was compared with the target sequence, and the mutation frequency of the sequence in the measured region was analyzed, and 0.1% was selected as the lowest detection limit. The trial found that colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas had more DNA mutations than samples from healthy volunteers...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com