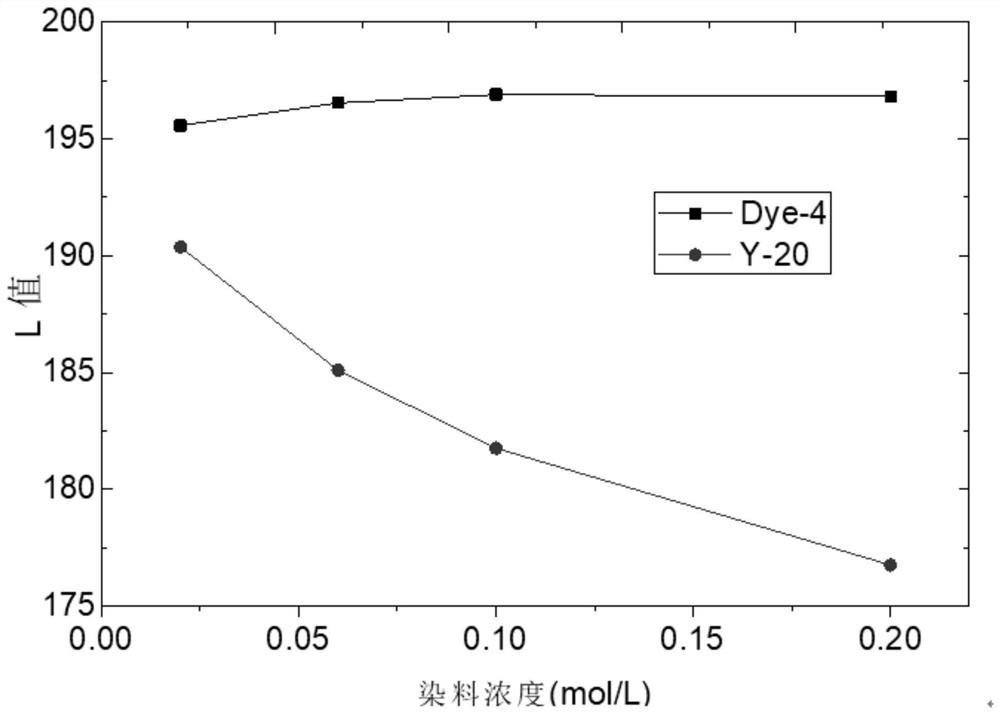
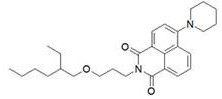
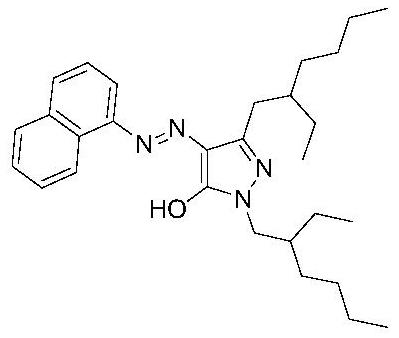
Naphthalimide organic dyes, electrowetting display inks and electrowetting displays
An electro-wetting display and electro-wetting display technology are applied in the fields of naphthalimide organic dyes, electro-wetting display inks and electro-wetting displays, and can solve the problem of improving energy consumption of display devices, low display contrast, and visual experience. Poor and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Weigh 2.0g (7.22mmol, 277g / mol) 4-bromo-1,8-naphthalene acid anhydride Put it into a 50ml round-bottomed flask, measure 40ml of absolute ethanol as a reaction solvent, and heat it up to 50 degrees Celsius. Weigh 3.7g (187g / mol, 0.02mol) 3-(2-ethylhexyloxy)propylamine The reaction was continued for 8h, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and 3.08g of colorless oily intermediate 1 was obtained by passing through the column. Yield 95.6%.
[0031] Weigh 1.5g (446g / mol, 0.00336mol) of Intermediate 1 Dissolve in 30ml ethylene glycol methyl ether, pipette 2ml piperidine The temperature was raised to 125°C and the reaction was continued for 12h. Pass the column to get 1.2g of yellow-green dye 1, (Dye-1), yield 80%.
[0032] NMR characterization data: 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ):δ=8.558-8.546(d,J=4.8Hz,1H),δ=8.485-8.471(d,J=5.6Hz,1H),δ=8.380-8.366(d,J=5.6Hz,1H), 7.669-7.643(t, J=10.4Hz, 1H), 7.167-7.151(d, J=6.4Hz, 1H), 4.272-4.243(t, J=11.6Hz, 2H), 3.550...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Weigh 2.0g (7.22mmol, 277g / mol) 4-bromo-1,8-naphthalene acid anhydride Put it into a 50ml round-bottomed flask, measure 40ml of diethylene glycol butyl ether as a reaction solvent, and heat it up to 120 degrees Celsius. Weigh 7.4g (187g / mol, 0.04mol) 3-(2-ethylhexyloxy)propylamine The reaction was continued for 8h, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and 4.2g of yellow-green dye 2 was obtained by passing through the column. (Dye-2), yield 75.6%.
[0035] NMR Spectrogram Characterization Data: 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ=8.567(m, 1H), 8.429(m, 1H), 8.067(m, 1H), 7.525(m, 1H), 6.640(m, 1H), 6.465(m, 1H), 4.264-4.253( d, J=4.4Hz, 2H), 3.703(s, 2H), 3.554-3.508(d, J=18.4Hz, 4H), 3.389(s, 2H), 3.287(s, 2H), 2.098(s, 2H) ), 2.031(s, 2H), 1.439(s, 2H), 1.266(m, 16H), 0.905(m, 12H). 13 C NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ):164.756,164.184,149.922, 134.612,130.996,129.829,126.327,124.327,123.064,120.318,103.753,74.764,73.747,71.247, 69.250,43.458,39.895,39.641,37.781,30....
Embodiment 3
[0037] Weigh 2.77g (0.01mmol, 277g / mol) 4-bromo-1,8-naphthalene acid anhydride Put it into a 50ml round-bottomed flask, measure 40ml of glacial acetic acid as the reaction solvent, and heat it up to 50 degrees Celsius. Weigh 4.47g (149g / mol, 0.03mol) p-n-butylaniline The temperature was raised to reflux for 12h, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and 2.5g of colorless oily intermediate 1 was obtained by passing through the column. Yield 62.5%.
[0038] Weigh 1.5g (408g / mol, 0.00367mol) of intermediate 1, dissolve it in 30ml ethylene glycol methyl ether, pipette 2ml piperidine was added to the above reaction solution, heated to reflux for 24h, passed through the column to obtain 1.2g of yellow dye 2, (Dye-3), 83% yield.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com