Q-switched holmium laser
A holmium laser and laser technology, applied in the field of Q-switched holmium lasers, can solve the problems of increasing resonator loss, loss, and cluttered pulse signals, and achieve the effect of compact structure and stable Q-switched pulse output
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
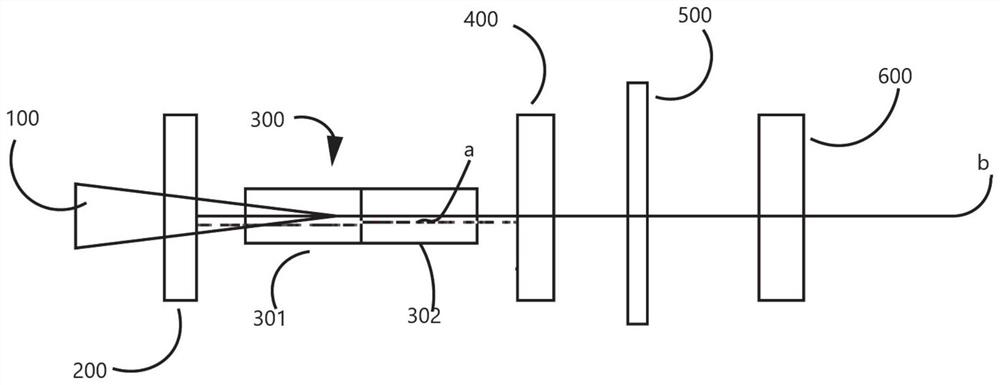
[0089] figure 1 For the structural representation of the Q-switched holmium laser provided by this embodiment, below in conjunction with figure 1 This embodiment will be described.
[0090] Such as figure 1 As shown, the Q-switched holmium laser sequentially includes a pump source 100 , a front cavity mirror 200 , a Tm / Ho composite gain medium 300 , a filter device 400 , a Q-switched element 500 and a rear cavity mirror 600 along the optical path. The Tm / Ho composite gain medium 300 includes a Tm-doped part 301 and a Ho-doped part 302, and is wrapped by indium foil and fixed in a cooling copper block (not shown in the figure) with built-in micro-channels. The Q-switching element 500 is interposed between the filter device 400 and the rear cavity mirror 600 .
[0091] The rear end surface of the front cavity mirror 200 is coated with a first reflective film with a reflectivity greater than 99.7% to the Tm laser a, and the front surface of the transparent insulator of the fil...
Embodiment 2
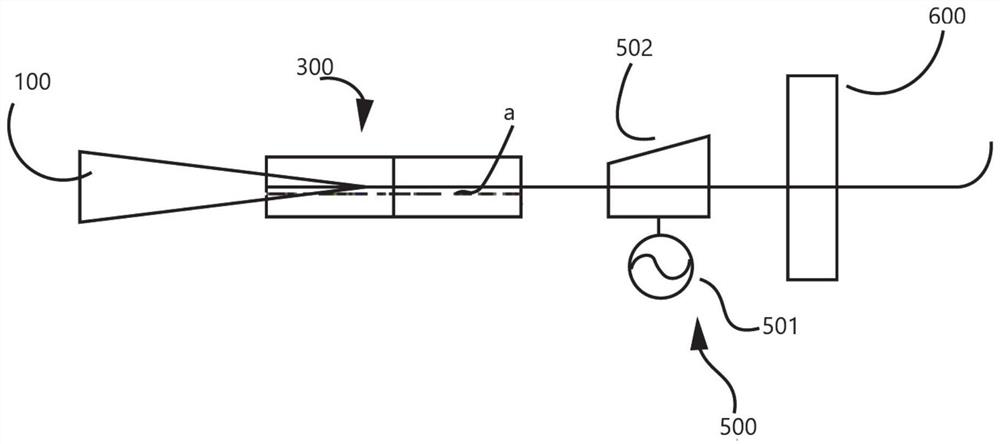
[0100] figure 2 For the structural representation of the Q-switched holmium laser provided by this embodiment, below in conjunction with figure 2 This embodiment will be described.
[0101] In specific implementation, such as figure 2 As shown, the functional film layer (i.e. the first reflective film) of the filter device 400 in Embodiment 1 is plated on the rear end surface of the composite gain medium 300, and the functional film layer (the first reflective film) of the front cavity mirror 200 in Embodiment 1 is coated A reflective film and a second reflective film) are plated on the front face of the composite gain medium 300, and then the composite gain medium 300 becomes a resonant cavity (i.e., a filter resonator) that confines the Tm laser a, and the composite gain medium 300 also becomes the laser resonant cavity At one end, the second reflective film is coated on the front end of the rear cavity mirror 600, and the rear cavity mirror 600 becomes the other end of...
Embodiment 3
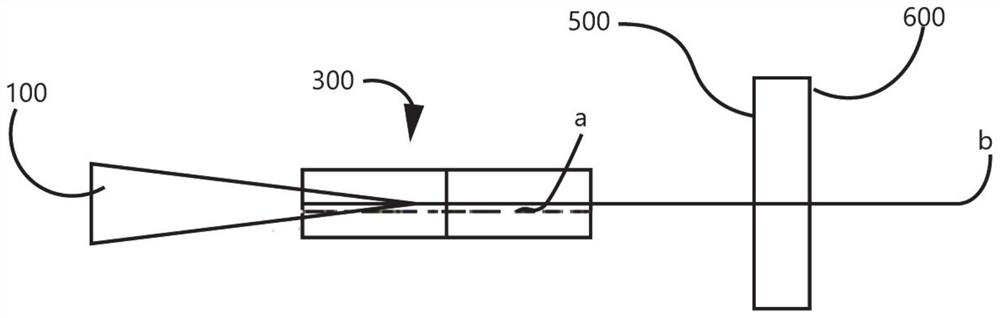
[0103] image 3 For the structural representation of the Q-switched holmium laser provided by this embodiment, below in conjunction with image 3 This embodiment will be described.
[0104] The Q-switching element 500 can be a saturable absorber or a saturable absorber based on a one-dimensional or two-dimensional material, and the MoSe 2 Uniformly coat the front end of the rear cavity mirror 600, and the front and rear end surfaces of the composite gain medium 300 act as the front cavity mirror and the filter device in Embodiment 1, respectively, and confine the Tm laser a in the composite gain medium 300 to the Ho-doped part Perform uniform pumping (similar to the composite gain medium in Example 2), and then realize pulsed Ho laser output. image 3 The structure is conducive to the figure 2 On the basis of the structure, the structure and size of the laser are further simplified, and the pulsed Ho laser output is realized under conventional LD pumping.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| reflectance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| reflectance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| reflectance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com