Anti-human CD73 antibody
An antibody and antibody drug technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of clinical treatment limitations, no specific targeting antibody for CD73, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0179] Antibody preparation
[0180] Any method suitable for producing monoclonal antibodies can be used to produce CD73 antibodies of the invention. For example, animals can be immunized with linked or naturally occurring CD73 protein or fragments thereof. Suitable immunization methods may be used, including adjuvants, immunostimulants, repeated booster immunizations, one or more routes may be used.
[0181] Any suitable form of CD73 can be used as an immunogen (antigen) for producing non-human antibodies specific to CD73 and screening the biological activity of the antibodies. Immunogens can be used alone or in combination with one or more immunogenicity enhancers known in the art. Immunogens can be purified from natural sources, or produced in genetically modified cells. The DNA encoding the immunogen can be genomic or non-genomic in origin (eg cDNA). DNA encoding the immunogen can be expressed using a suitable genetic vector, including but not limited to adenoviral vec...
Embodiment 1
[0223] Example 1 Preparation of anti-human CD73 monoclonal antibody
[0224] This example mainly describes the sequence of anti-human CD73 single chain antibody obtained by mouse immunization and phage display. Balb / C mice were immunized with recombinant human CD73 protein (C446, Novoprotein). After the first immunization, booster immunization was done every 14 days for a total of 4 immunizations. Mouse serum was collected for antibody titer evaluation. To evaluate the effective mice, take B cells, extract RNA for reverse transcription, and construct a phage display library. Pack the recombinant human CD73 protein at 1-5 μg / ml, add the displayed phages, and perform phage library screening. After the screening, the unwashed phages are collected and infected with host bacteria to obtain the first round of screening library. Follow this method Second and third rounds of screening. After the screening is completed, phage-ELISA identification is carried out, and those identified ...
Embodiment 2
[0233] Example 2 Affinity Detection of CQ137 Antibody
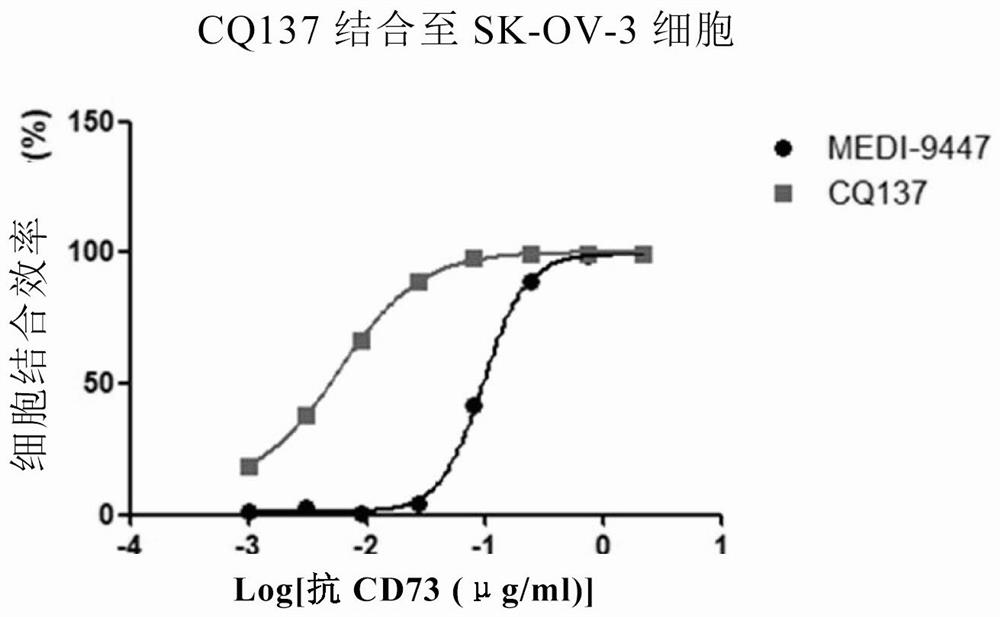
[0234] This example mainly describes the affinity detection between CQ137 and human and monkey recombinant CD73 protein, as well as the affinity detection with human CD73 positive cells (SK-OV-3, human ovarian adenocarcinoma cells) and monkey CD73 cell line (CHOK1-cynoCD73) affinity detection.
[0235] (1) Affinity with human CD73 protein
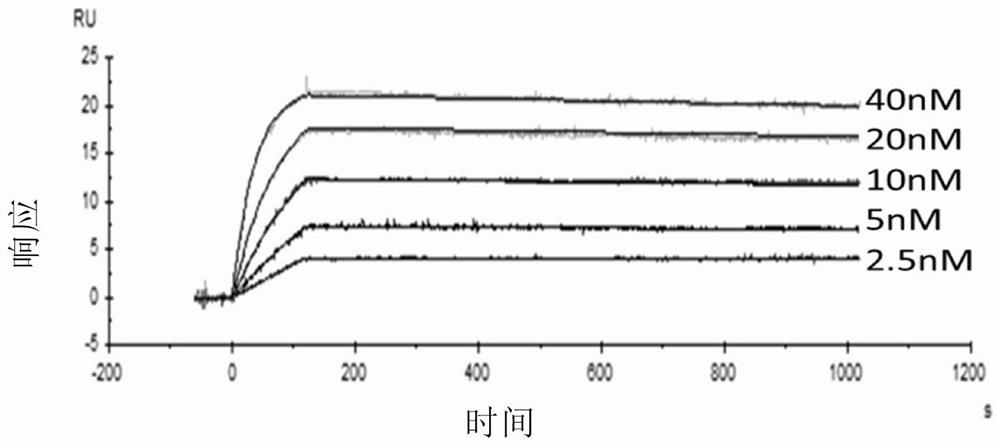
[0236] Use Biacore to measure the affinity between CQ137 and recombinant hCD73 protein, immobilize CQ137, and dilute the CD73 protein with a two-fold gradient (2.5nM-40nM). The obtained affinity diagram is shown in figure 1 .
[0237] The affinity data are shown in Table 1:
[0238] Table 1. CQ137 affinity
[0239]
[0240] The results showed that the measured affinity between CQ137 and rhCD73 was 8.653×10 -11 M.
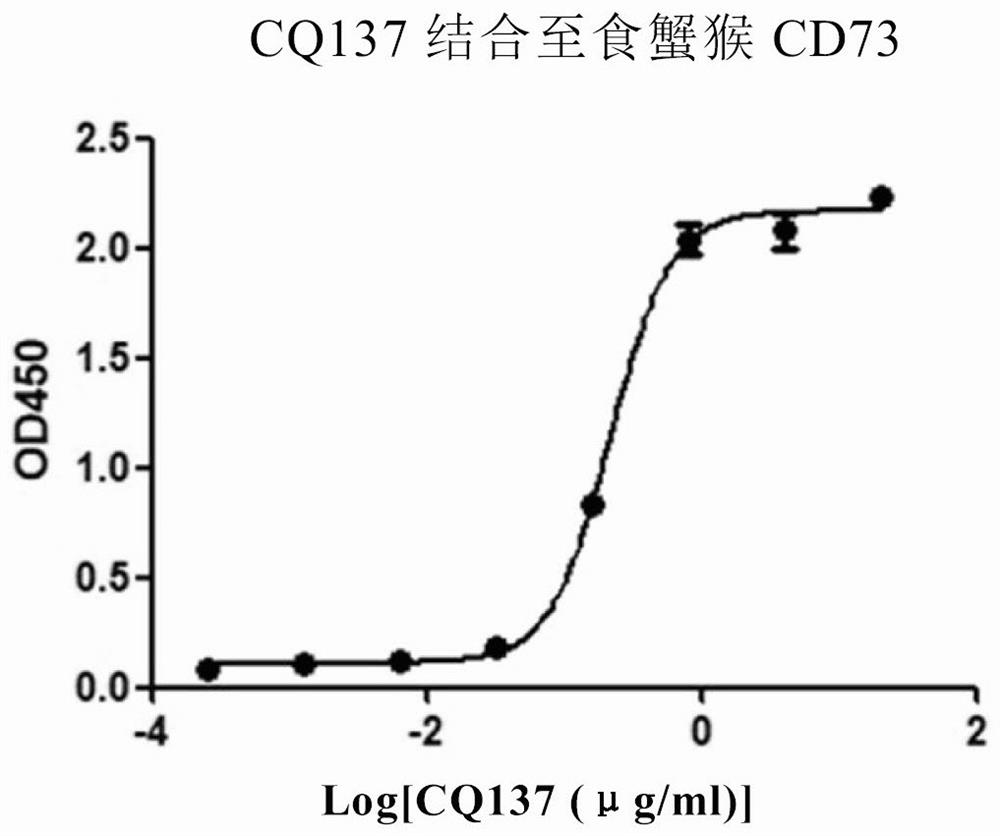
[0241] (2) Affinity with monkey CD73 protein
[0242]Pack the recombinant monkey CD73 protein at 3 μg / ml, add CQ137 in gradient dilution, and use the ELISA method ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com