Heat-conducting polymer composite material with multi-layer continuous network structure and preparation method
A technology of network structure and composite materials, which is applied in the field of heat-conducting polymer composite materials and its preparation, can solve the problems of single three-dimensional continuous heat-conducting network structure, heat transfer, and large average distance, and achieve simple and easy-to-obtain raw materials, high thermal conductivity, and average small distance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
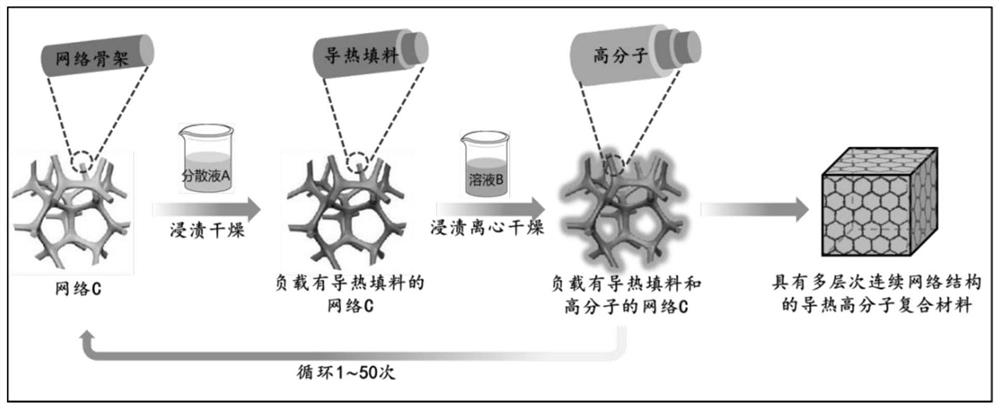
[0036] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for preparing a thermally conductive polymer composite with a multi-level continuous network structure comprises the following steps:
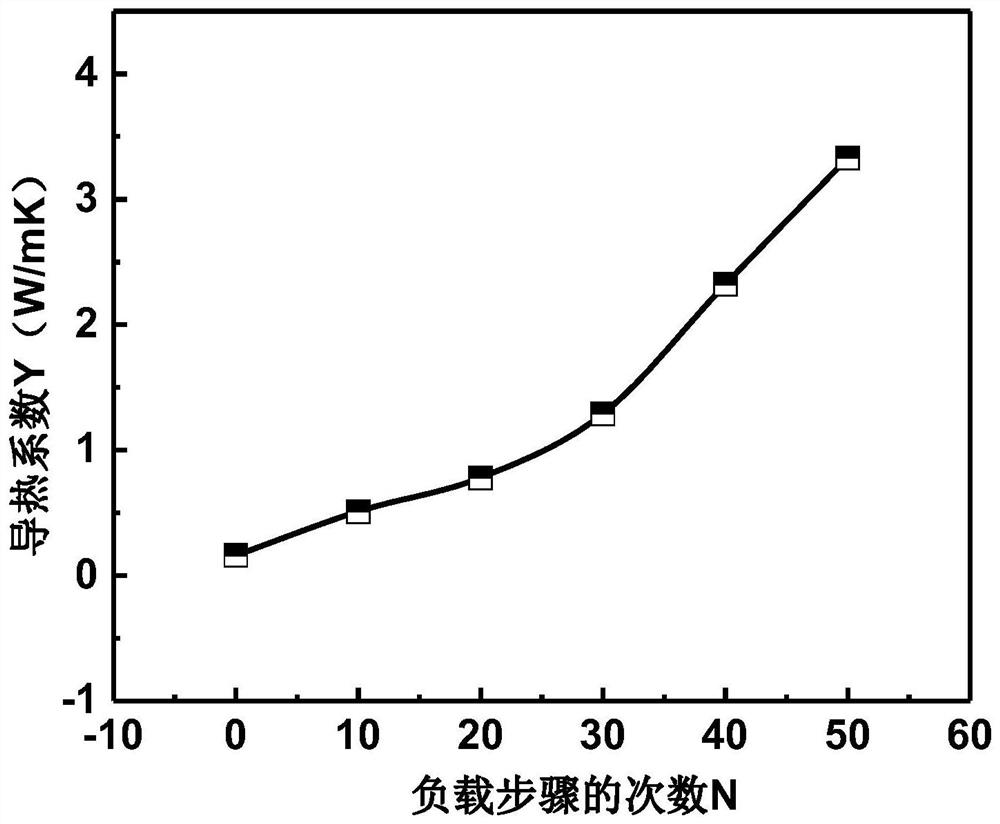
[0037]Prepare a network C, which is a polyurethane network with a pore diameter of 150 μm. Carry out the loading method on the network C 50 times, each loading method is: immerse in the dispersion A for 30 minutes, take it out and dry it at a temperature of 20°C for 0.5 hours to obtain the network C loaded with thermally conductive fillers, immerse the network C loaded with thermally conductive fillers solution B for 30 minutes, take it out and centrifuge at 2000r / min for 30 minutes, and dry at 20°C for 300 minutes to obtain a thermally conductive polymer composite material, wherein,
[0038] The preparation method of dispersion A is as follows: disperse the thermal conductive filler in liquid D to obtain a mixture, and use a cell pulverizer to ultrasonically treat the mixture for 60 minutes to obtai...
Embodiment 2
[0056] A method for preparing a thermally conductive polymer composite material with a multi-level continuous network structure, comprising the following steps:
[0057] Prepare a network C, which is a melamine network with a pore size of 100 μm. Carry out the loading method on the network C 50 times, each loading method is: immerse in the dispersion A for 1 minute, take it out and dry it at a temperature of 50°C for 1 hour to obtain the network C loaded with thermally conductive fillers, and immerse the network C loaded with thermally conductive fillers into the solution In B for 20 minutes, take it out and centrifuge at 1000r / min for 15 minutes, and dry at 50°C for 200 minutes to obtain a thermally conductive polymer composite material, wherein,
[0058] The preparation method of dispersion A is as follows: disperse the thermally conductive filler in liquid D to obtain a mixture, and use a cell pulverizer to ultrasonically treat the mixture for 5 minutes to obtain dispersion...
Embodiment 3
[0062] A method for preparing a thermally conductive polymer composite material with a multi-level continuous network structure, comprising the following steps:
[0063] Prepare a network C, which is a cellulose network with a pore size of 50 μm. Carry out the loading method on the network C 50 times, each loading method is: immerse in the dispersion A for 10 minutes, take it out and dry it at a temperature of 50°C for 3 hours to obtain the network C loaded with thermally conductive fillers, and immerse the network C loaded with thermally conductive fillers into the solution In B for 1min, take it out and centrifuge at 500r / min for 15min, and dry at 50°C for 30min to obtain a thermally conductive polymer composite material, wherein,
[0064] The preparation method of dispersion A is as follows: disperse the thermally conductive filler in liquid D to obtain a mixture, and use a cell pulverizer to ultrasonically treat the mixture for 30 minutes to obtain dispersion A. The power ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com