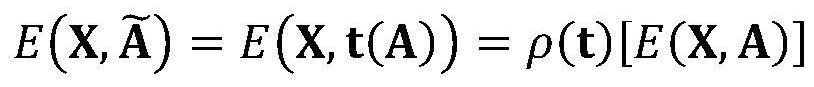Unsupervised graph topology transformation covariant representation learning method and device
A topological transformation, unsupervised technique, applied in the field of unsupervised learning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
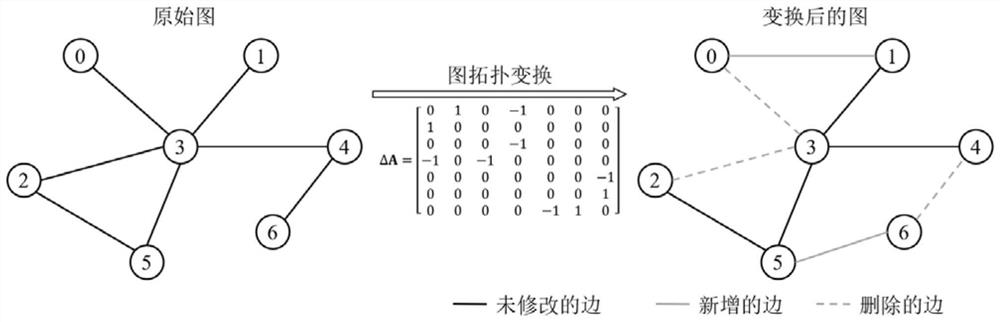
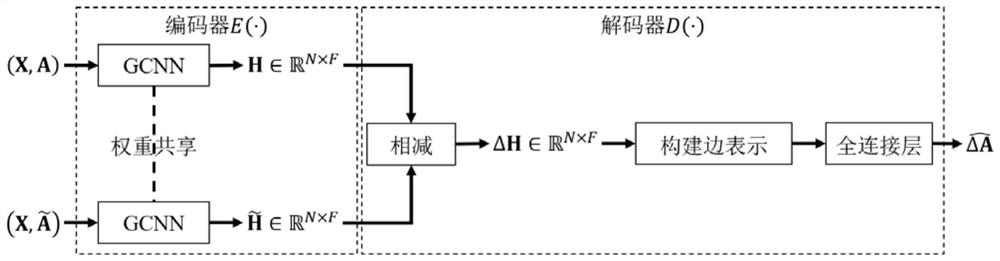
[0040] The present invention will be described in further detail below through specific embodiments and accompanying drawings. Before introducing the main steps of the method of the present invention, first introduce the basic concept of graph and graph topology transformation.
[0041] (1) Graph and graph signal:
[0042] Define an undirected graph, is the set of vertices on the graph, N is the number of vertices on the graph; ε is the set of edges. Graph signals refer to data residing on the vertices of graphs, such as social networks, transportation networks, sensor networks, and neuronal networks, represented as matrices The i-th row of the matrix represents a C-dimensional feature on vertex i. To represent the connectivity between nodes, we define the adjacency matrix as The matrix is a real symmetric matrix. if a i,j =1, it means that vertices i and j are connected; if a i,j = 0, it means that vertices i and j are not connected.
[0043] (2) Graph topolo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com