Method and devicefor capturing and manipulating particles through a partially coherent light beam
A technology of coherent beams and particles, applied in the field of particle capture and manipulation, which can solve problems such as inability to achieve
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] This embodiment provides a device for trapping and manipulating particles with partially coherent light beams, including:
[0034] Special correlation structures, particle capture modules and imaging modules;
[0035] Partially coherent beams generated by the special correlation structure are incident on the particle capture module, and the partially coherent beams are strongly focused by the particle capture module, and the beams will form multiple stable optical potential wells with different properties near the focal point. The trap captures particles with different refractive indices at multiple positions simultaneously, and displays them on the imaging module, and at the same time manipulates the particles by modulating the partially coherent beam building blocks.
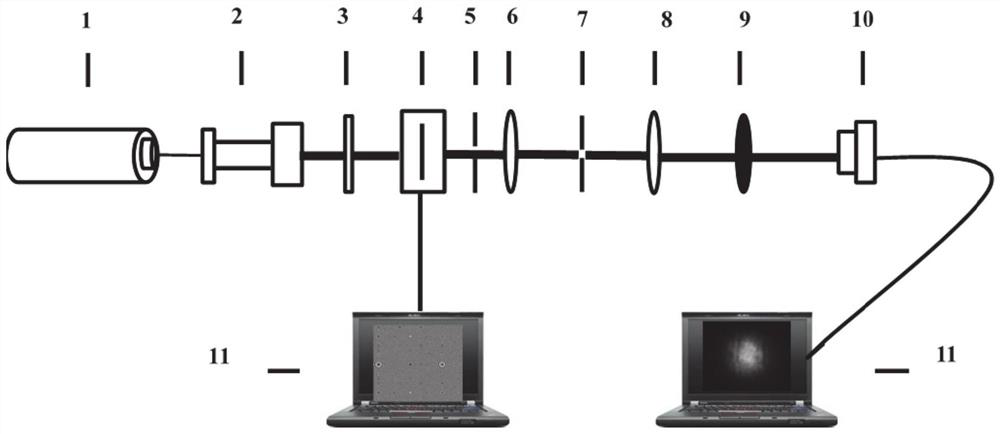
[0036] As one or more examples, such as figure 1 As shown, the special associated structure includes: sequentially setting a helium-neon laser, a beam expander, a linear polarizer, a spatial light modu...
Embodiment 2
[0040] This embodiment provides a method for trapping and manipulating particles with a partially coherent beam, including:
[0041] Using the above-mentioned device for trapping and manipulating particles with partially coherent beams, a beam of partially coherent light with a special correlation structure is strongly focused through a lens, and the beams will form multiple stable optical potential wells with different properties near the focus. The trap traps particles with different refractive indices at multiple locations simultaneously, and manipulates the particles by adjusting special correlation structures.
[0042] The specific theoretical process of the Laguerre non-uniform correlation (LNUC) beam is:
[0043] In the spatial frequency domain, scalar partially coherent beams are characterized by the cross spectral density function:
[0044] W(r 1 ,r 2 )=* (r 1 )E(r2 )> (1)
[0045] where E is the instantaneous electric field. are any two position coordinates on...
Embodiment approach
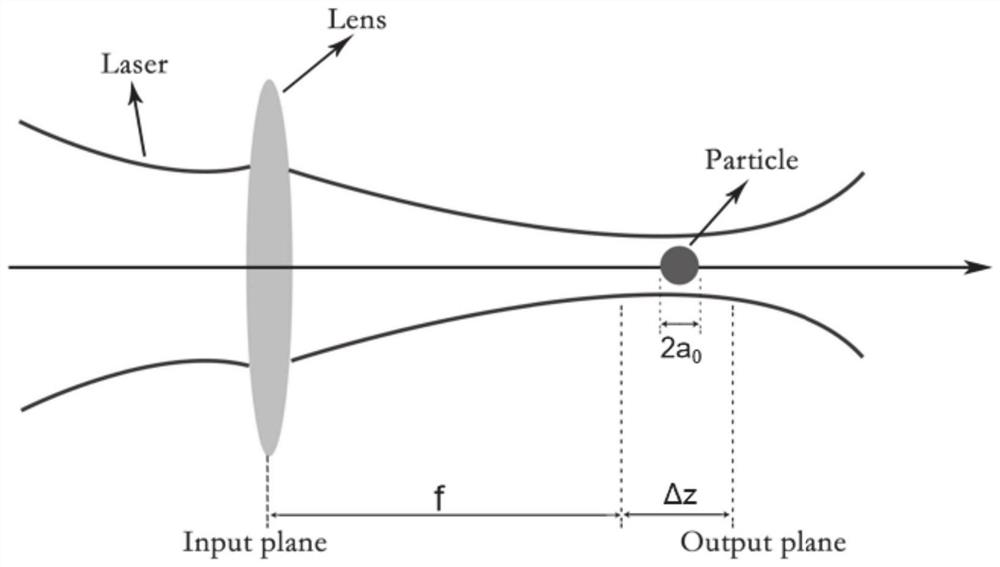
[0080] Specific implementation plan: based on the above theoretical basis analysis, such as figure 2 As shown, the Laguerre non-uniform correlated beam with a beam waist width of 3 cm is selected, and it is strongly focused through a lens with a focal length of 5 mm, and the Rayleigh particles with a refractive index of 1.59 and a radius of 50 nm are processed in an environment with a refractive index of 1.33. capture and manipulation.
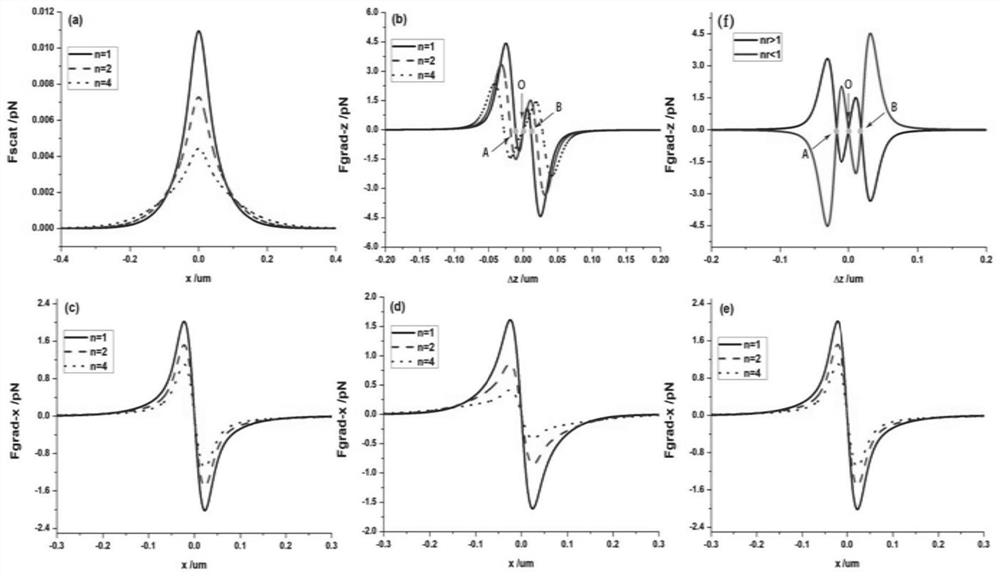
[0081] like image 3 and Figure 4 As shown, the scattering force and gradient force of the strongly focused Laguerre non-uniform correlated beam are much greater than the Brownian force generated by thermal motion, and the influence of Brownian force on the particles can be completely ignored, so the particles can be stably trapped. At the same time according to figure 2 (b) and figure 2 (f) It can be seen that there are three stable trapping points on the optical axis. At point A and point B, particles with a refractive index larger t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com