Storage device for blood routine examination waste liquid
A blood routine detection and storage device technology, applied in the field of medical waste treatment, can solve the problems of suspended solids generation, separation, environmental pollution, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing aging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
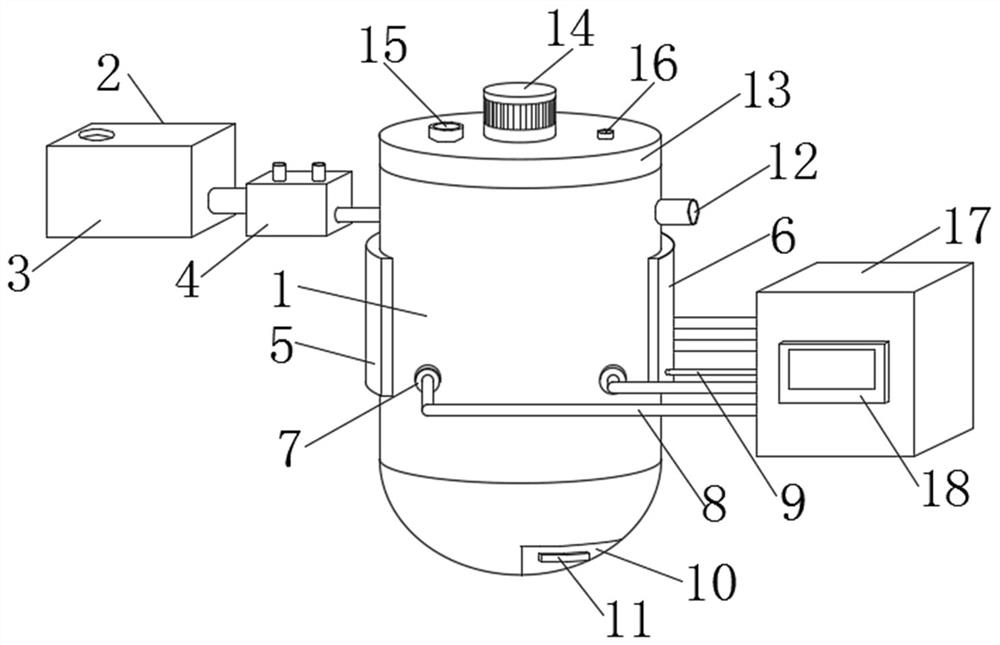
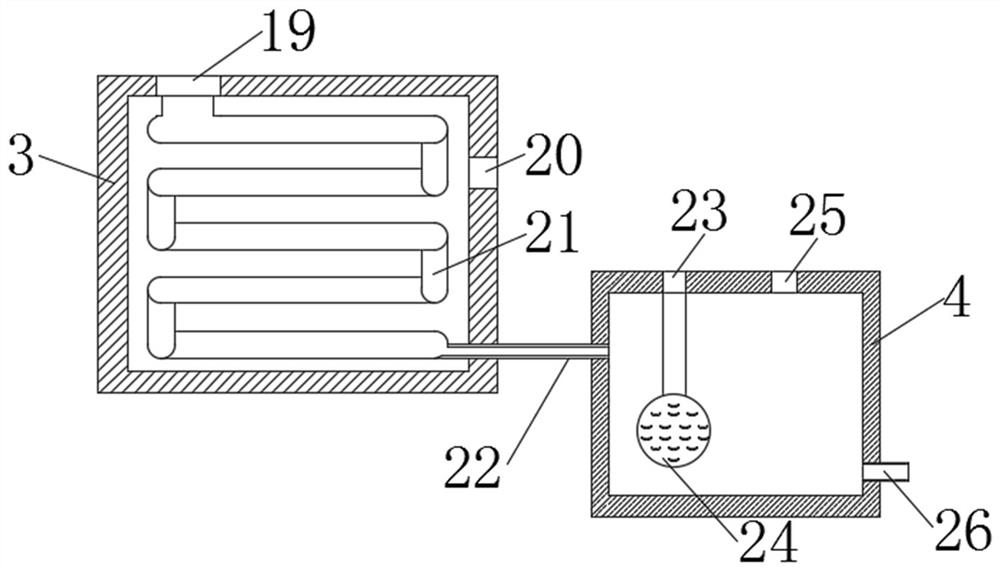
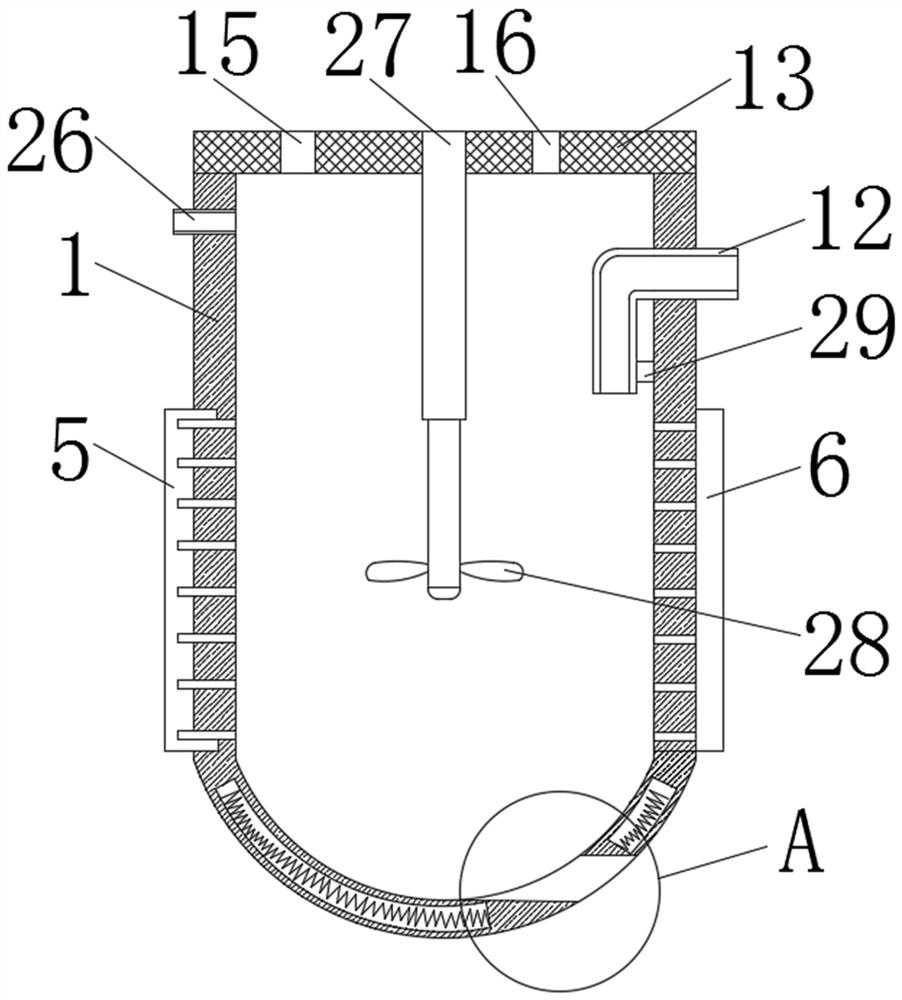
[0030] like Figure 1-6 As shown, a storage device for blood routine testing waste liquid includes a storage box (1) and a pretreatment mechanism (2). The left and right sides of the storage box (1) are respectively fixed with a laser transmitter (5) and a laser receiver. laser emitter (6), the laser emitted by the laser transmitter (5) can pass through the interior of the storage box (1) to irradiate the corresponding receiving area on the laser receiver (6), and the interior of the storage box (1) is evenly distributed and fixed with four A pH value measuring probe (7), a heating coil (30) is installed in the lower half of the storage box (1), the bottom of the storage box (1) is provided with a sediment discharge port (10), and the sediment discharge port ( The outer wall of 10) is fixedly connected with a fixed block (11), the top of the storage box (1) is equipped with a detachable sealing cover (13), the fixed block (11) can assist the sediment discharge port (10) to ope...
Embodiment 2
[0037] like Figure 1-6 As shown, a storage device for blood routine testing waste liquid includes a storage box (1) and a pretreatment mechanism (2). The left and right sides of the storage box (1) are respectively fixed with a laser transmitter (5) and a laser receiver. laser emitter (6), the laser emitted by the laser transmitter (5) can pass through the interior of the storage box (1) to irradiate the corresponding receiving area on the laser receiver (6), and the interior of the storage box (1) is evenly distributed and fixed with four A pH value measuring probe (7), a heating coil (30) is installed in the lower half of the storage box (1), the bottom of the storage box (1) is provided with a sediment discharge port (10), and the sediment discharge port ( The outer wall of 10) is fixedly connected with a fixed block (11), the top of the storage box (1) is equipped with a detachable sealing cover (13), the fixed block (11) can assist the sediment discharge port (10) to ope...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com