Self-consistent driving sensor, functional device and electric excitation method for realizing driving sensing
An electrical excitation and sensor technology, applied in piezoelectric/electrostrictive or magnetostrictive motors, electrical components, generators/motors, etc., to solve the problems of heavy mass, complex structure, and low precision of movement control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
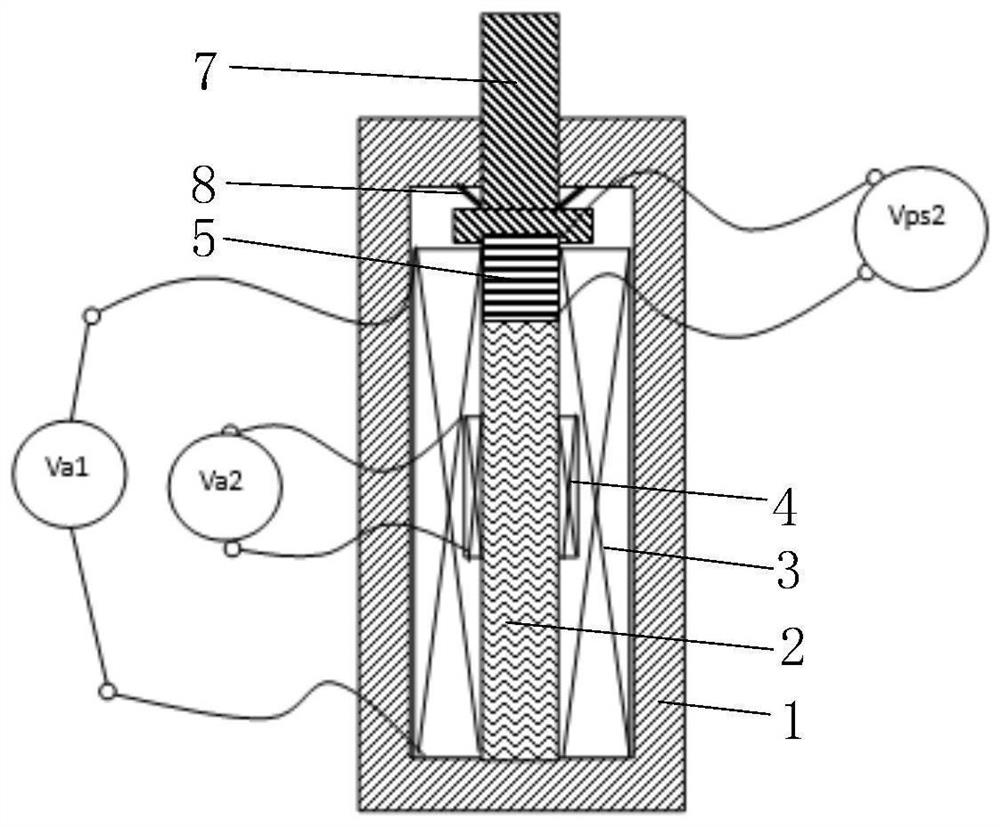
[0060]The present invention provides a self-consistent driving sensor, which includes a supporting shell 1, an electric excitation assembly, a driving body and a sensor, the electric excitation assembly and the driving body are installed on the supporting shell 1 and the electric excitation assembly Arranged along the circumferential direction of the driving body or connected to the end of the driving body, when the electric excitation component applies the first electric excitation, it can drive the driving body to produce a first deformation, thereby causing the sensor to produce a first The sensing signal, the first sensing signal is used to calibrate the reference value of the target detection quantity. When the electric excitation component applies a second electric excitation, it can drive the driving body to produce a second deformation, thereby causing the sensor to generate a second induction signal, and the second induction signal is used to obtain the measurement val...
Embodiment 2
[0077] This embodiment is a preferred example of Embodiment 1.
[0078] In this embodiment, a self-consistent driving sensor is provided, which can realize the driving function and realize the sensing function while realizing the driving, wherein the target detection quantity is displacement, such as figure 1 As shown, the electric excitation assembly includes a first coil 3 and a second coil 4, the sensor uses a first piezoelectric body 5, the driver uses a magnetostrictive body 2, and the first piezoelectric body 5 is connected to The magnetostrictive body 2 is arranged at the end of the magnetostrictive body 2, wherein, firstly, a first electric excitation V is applied to the second coil 4 a2 Afterwards, the first magnetic field is generated, wherein the first electric excitation adopts a high-frequency AC weak current, for example, the frequency is 10000 Hz, and the first magnetic field is a weak magnetic field, so that the magnetostrictive body 2 can produce a slight firs...
Embodiment 3
[0081] This embodiment is another preferred example of Embodiment 1.
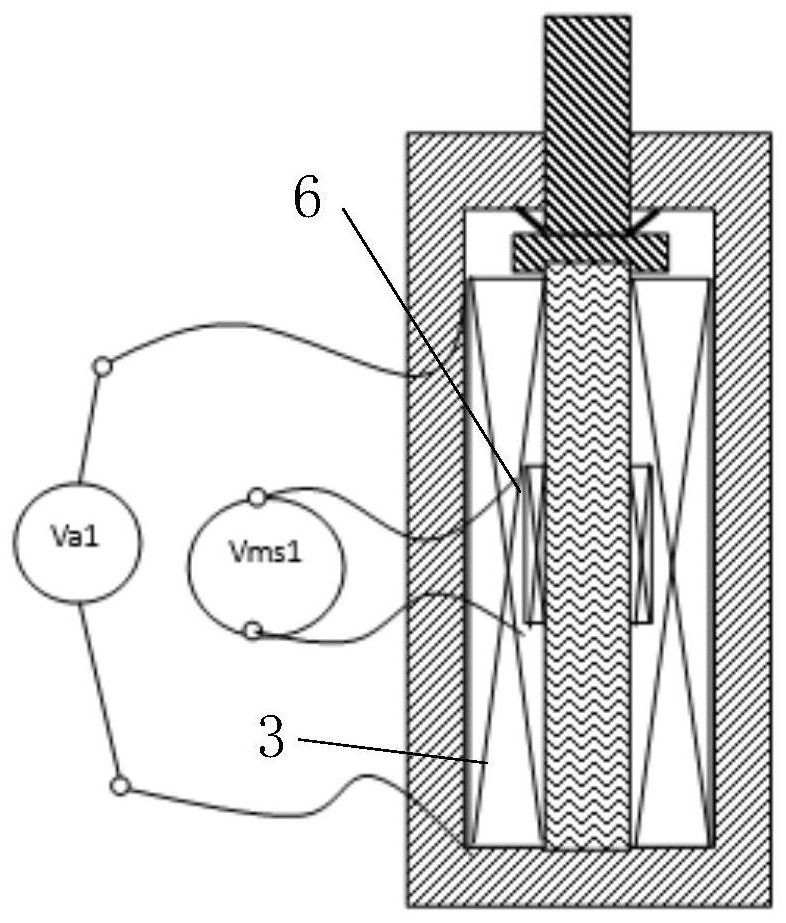
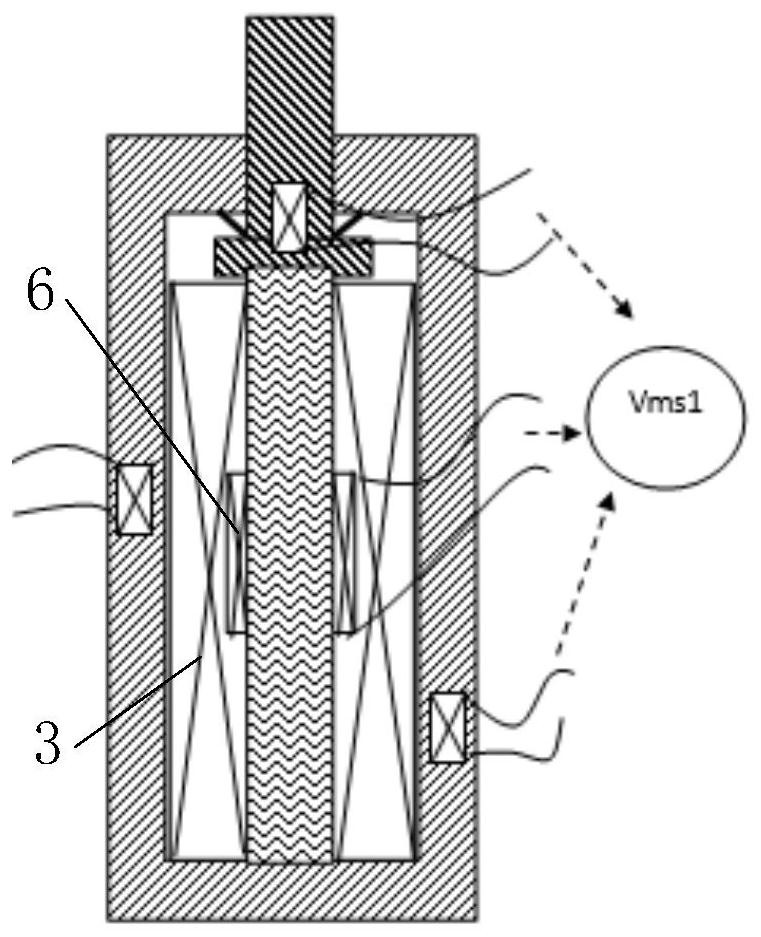
[0082] In this embodiment, a self-consistent driving sensor is provided, which can realize the driving function and realize the sensing function while realizing the driving, wherein the target detection quantity is displacement, such as figure 2 As shown, the electric excitation assembly includes a first coil 3, the sensor uses a third coil 6, the driver uses a magnetostrictive body 2, and the first coil 3 applies V a1 Electric excitation, specifically, the first electric excitation and the second electric excitation linearly superimposed on the frequency domain to generate the first magnetic field and the second magnetic field respectively, wherein the first electric excitation adopts high-frequency AC weak current, and the frequency is high frequency, for example 50000HZ, the first magnetic field is a weak magnetic field, and then the magnetostrictive body 2 can be made to produce a small first deformati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com