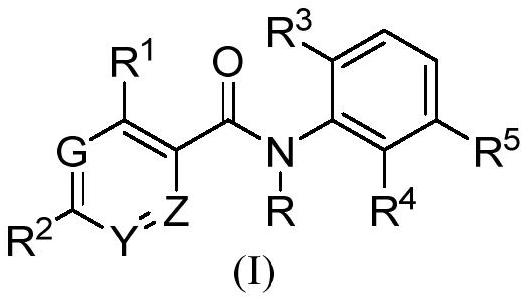
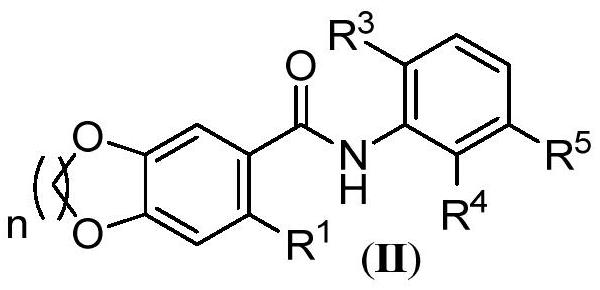
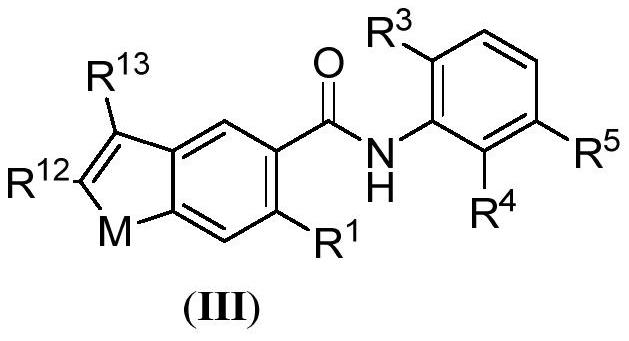
Benzamide derivatives as cgas-sting pathway agonists
A phenyl, hydrate technology, applied in the field of benzamide derivatives as CGAS-STING pathway agonists, can solve problems such as failure, in vivo biological activity and pharmacological properties to be determined
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0522] Preparation of compounds may involve protection and deprotection of various chemical groups. The need for protection and deprotection and selection of appropriate protecting groups can be readily determined by those skilled in the art. The chemistry of protecting groups can be found, for example, in Greene et al., "Protecting Groups in Organic Synthesis", 2nd Ed. (Wiley & Sons, 1991). The entire disclosure thereof is hereby incorporated by reference for all purposes.
[0523] The reactions or methods described in the present invention can be carried out in suitable solvents which can be readily selected by those skilled in the art of organic synthesis. Suitable solvents are generally substantially nonreactive with the reactants, intermediates and / or products at the temperatures at which the reactions are carried out, ie, temperatures that may range from the solvent's freezing temperature to the solvent's boiling temperature. A given reaction can be carried out in one ...
Embodiment 1
[0540]Example 1: N-(naphthalene-1-yl)benzo[d][1,3]dioxazole-5-carboxamide: pipecolic acid (0.0829g, 0.499mmol), 1-aminonaphthalene (0.080 g, 0.5586mmol) and (2-(1H-benzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate) (HBTU, 0.2068g, 0.5453mmol) were dissolved in N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF, 1 mL) and treated with N,N-diisopropylethylamine (0.26 mL). The mixture was stirred at 22°C for 18 hours. Ethyl acetate (20 mL) was added to dilute the mixture, and the mixture was washed with HCl (5 mL, 1 M, twice), saturated NaHCO 3 The solution was washed with saturated brine and the mixture was concentrated under vacuum and purified using normal phase chromatography (12g Isco silica gel column, ethyl acetate-hexane, 0-30%) to give a white solid (0.0562g, 38.65%). 1 H NMR (300MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ8.05-8.02(m, 2H), 7.91-7.89(m, 2H), 7.74(d, J=7.5Hz, 1H), 7.55-7.48(m, 5H), 6.94(d, J=9Hz , 1H), 6.09(s, 2H, OCH 2 O). C 18 h 13 NO 3 MS calculated for, 291.09; observed, (M+H) ...
Embodiment 2
[0542] Example 2: N-(naphthalene-1-yl)-2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-carboxamide: 1,4-benzyldioxane-6 -Carboxylic acid (0.0860g, 0.4773mmol), 1-aminonaphthalene (0.0752g, 0.525mmol) and (2-(1H-benzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyl Urea (hexafluorophosphate) (HBTU, 0.1991 g, 0.525 mmol) was dissolved in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF, 1 mL) and treated with N,N-diisopropylethylamine (0.25 mL). The mixture was stirred at 22°C for 18 hours. Ethyl acetate (20 mL) was added to dilute the mixture, and the mixture was washed with HCl (5 mL, 1 M, twice), saturated NaHCO 3 The solution was washed with saturated brine, then concentrated in vacuo, and subjected to normal phase chromatography (12 g Isco silica gel column, ethyl acetate-hexane, ) to give a white solid (0.0737g, 50.58%). 1 H NMR (300MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ8.10-8.05(m, 2H), 7.90-7.89(m, 2H), 7.73(d, J=6Hz, 1H), 7.54-7.52(m, 5H), 7.00-6.98(m, 1H) , 4.34(s, 4H, OCH 2 CH 2 O). C 19 h 15 NO 3 MS calculated for, 305.11; obse...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com