Method for biologically preventing and controlling cryptocaryon irritans infection by using tilapia mossambica
A technology that stimulates Cryptocaryon and biological prevention and control. It is applied in application, fish farming, climate change adaptation, etc. It can solve problems such as inability to prevent and control, stimulate Cryptocaryon strangulation, and outbreaks of infection, and achieve prevention and control. The effect of secondary superinfection, reduction of infection, and improvement of survival rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 Sensitivity determination of red tilapia to the infection of Cryptocaryon irritant
[0038] 1. Experimental method
[0039] To evaluate the sensitivity of red tilapia to Cryptocaryon stimuli infection, red tilapia (3.94±0.53g) were artificially infected with Cryptocaryon stimuli, and compared with pompano ovata (13.07±2.37g). A total of 3 groups of experiments were set up:
[0040] The first group was 30 pomfrets raised alone as the control group 1;
[0041] The second group is 6 red tilapias raised alone, as the control group 2;
[0042] The third group is the polyculture of pomfret and red tilapia, including 30 pomfret and 6 tilapia.
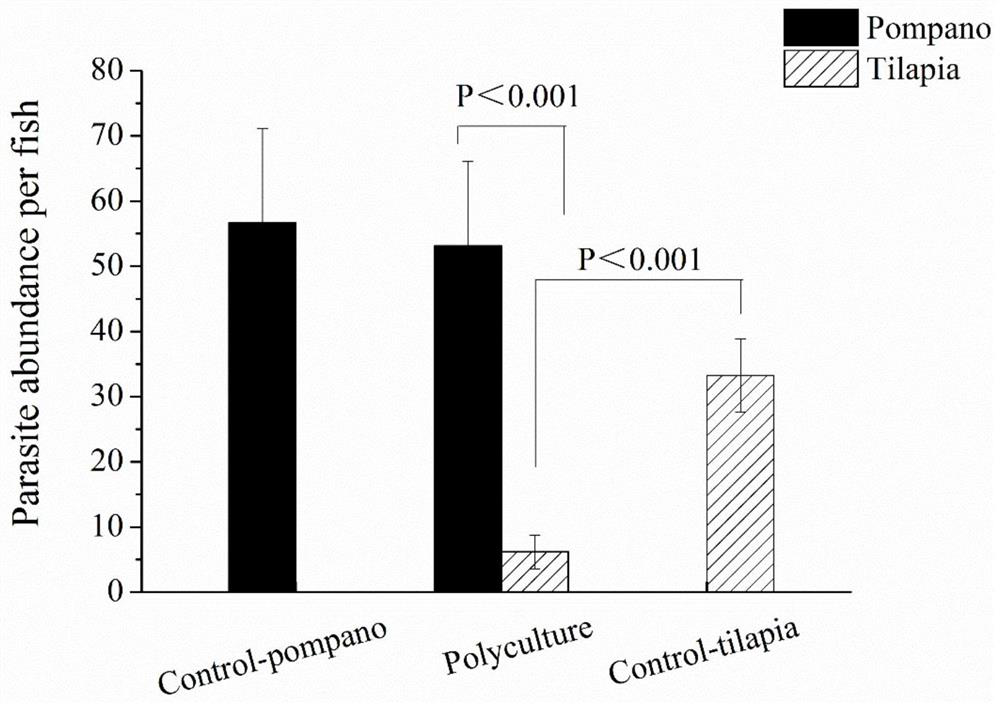
[0043] Each group of 3 parallel, were temporarily raised in 9 water tanks. Each water tank was filled with 100 liters of seawater, and 3000 Cryptocaryon stimuli larvae were added within 2 hours of incubation, and infected for 2 hours; then the fish of the 3 groups after infection were transferred to clean water tanks. On ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2 Determination of the effect of red tilapia feeding on stimulation of Cryptocaryon cyst
[0047] 1. Experimental method
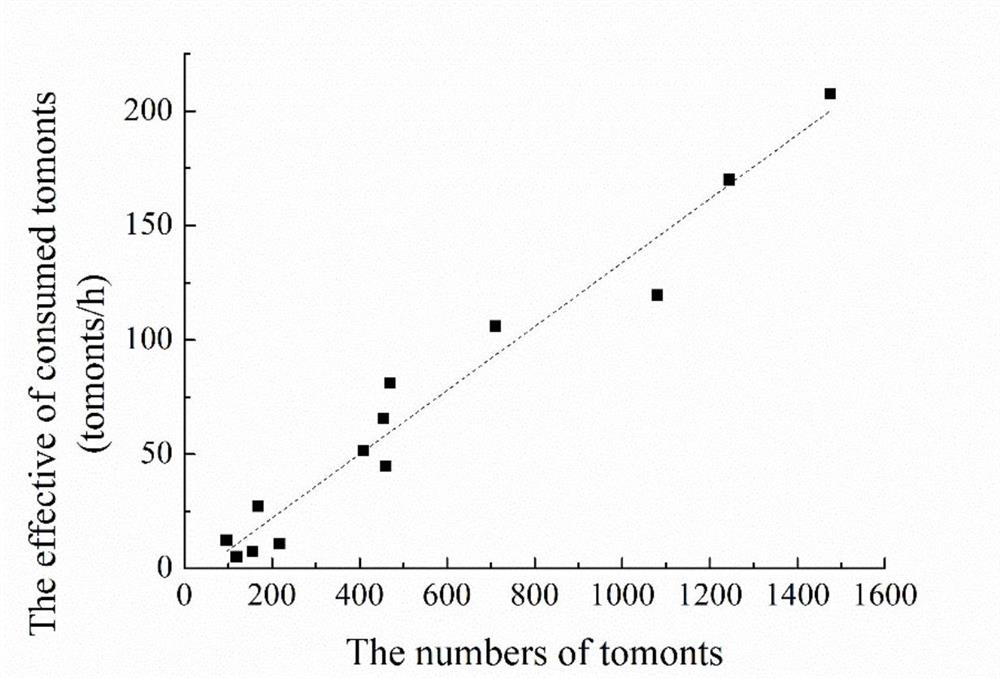
[0048] (1) Determination of cyst consumption rate of red tilapia feeding stimulation Cryptocaryonia
[0049] Cyst precursors were collected from Pompano ovata heavily infested with Cryptocaryon irritant using glass plates with a diameter of 20 cm. Count the collected cyst precursors (N 1 ), the range of the number of cysts is controlled at 96-1475 / plate. Then the plate was transferred to a 120L circular water tank, and 50L seawater was added to the water tank, and one red tilapia (4.45±1.06g) was added to each water tank, and oxygen exposure was continued. Let the red tilapia ingest the cysts within 5 hours, finally take out the plate, and count the number of remaining cysts (N 2 ), calculate the consumption rate of red tilapia to cyst: cyst consumption rate=(N 1 -N 2 ) / 5.
[0050] (2) Determination of the degree of infection of pomfr...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3 Using red tilapia polyculture to carry out biological control of Cryptocaryon stimuli
[0058] 1. Experimental method
[0059] 1. Seawater domestication of red tilapia
[0060] Taking red tilapia as an example, 50 red tilapias (4.46±0.78g, bred for 2 weeks) are temporarily raised in each breeding tank, and the breeding density is 100 fish / m 3 ;The water temperature is 26-32°C, continuous oxygen exposure, static water culture; transfer the red tilapia to seawater with a salinity of 12‰ for 2 days, and then increase the seawater salinity to 24‰ at a rate of 6‰ / 2d, Finally, increase the seawater salinity to 28‰. Feed 3% of the fish body weight every day, 1.5% each time, and feed twice a day (8:00, 16:00).
[0061] 2. Polyculture experiment of red tilapia and pomfret
[0062] Taking pomfret ovata as the infection object, the indoor simulation experiment was carried out. The specific experimental process is as follows:
[0063] (1) Temporary culture of experim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com