Desalting method of amino acid chelating agent
An amino acid, chelating agent technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, semi-permeable membrane separation, etc., can solve problems such as increasing synthesis and post-processing costs, losing products, and reducing yields
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
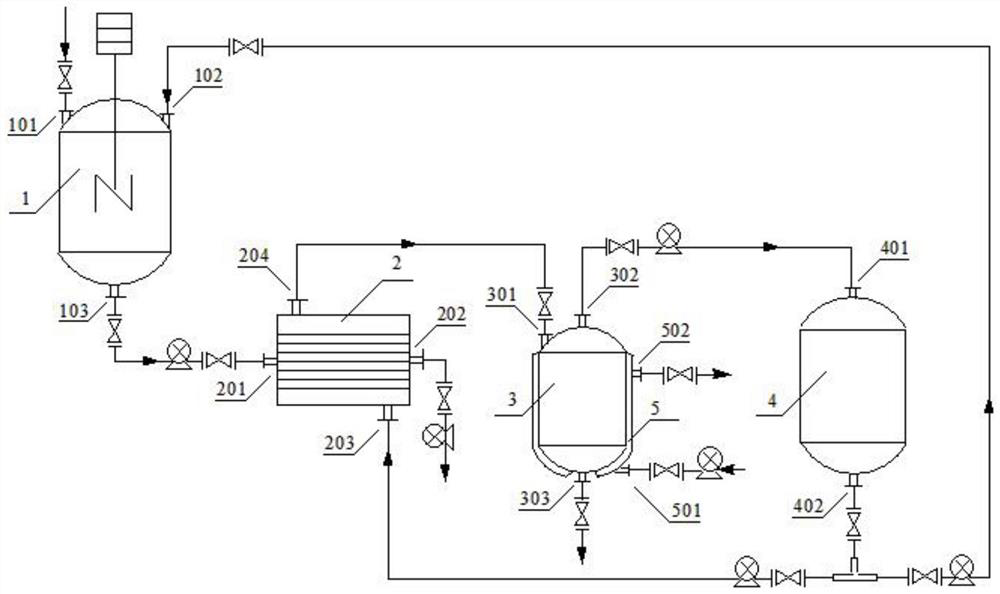
[0047] Step 1: adding pure water to dilute the amino acid chelating agent mother liquor that has been reacted into an aqueous solution with a chelating agent content of 20%;
[0048] Step 2: Transfer the aqueous solution obtained in step 1 into the ultrafiltration membrane module to make ultrafiltrate, use flowing pure water as the filtered water acceptor, close the outlet of the ultrafiltration membrane group, and use a pressure pump to pump pure water from the inlet into the ultrafiltration In the membrane group, the working pressure of the ultrafiltration membrane is controlled at 1.5MPa;
[0049] Step 3: After the ultrafiltration membrane runs for 11.5 hours, detect that the chloride ion content in the solution in the ultrafiltration membrane group is reduced to 0.78%, open the outlet of the ultrafiltration membrane group, transfer the internal solution into the concentration kettle for concentration and dilution treatment, and obtain the required content of chelating agen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com