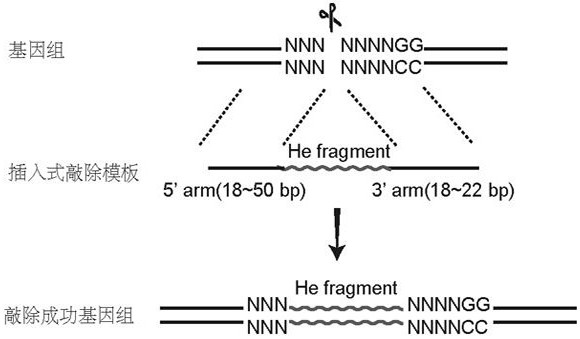
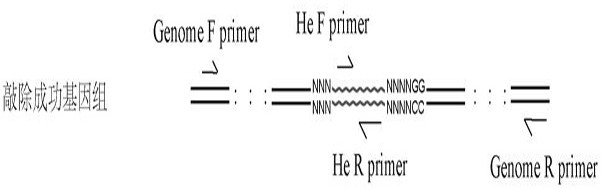
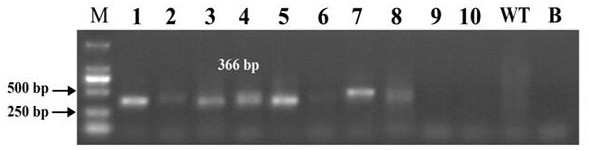
Method for realizing fixed-point insertion type knockout and identification in zebra fish genome
A genomic and insertional technology, applied in the field of fixed-point insertional knockout and rapid identification, can solve the problems of random mutation, difficult positive identification, and low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Example 1 Zebrafish Gnas gene-specific knockout
[0058] 1.1 Selection of Gnas gene sgRNA targeting sites
[0059] Exon 4 of the zebrafish Gnas gene (Gene ID: 557353) was selected for gene knockout. The sequence of exon 4 of the Gnas gene was analyzed for PAM sites on the CRISPOR website (http: / / crispor.tefor.net / crispor.py), and the PAM sites with higher scores were selected. The sequence information is as follows:
[0060] ATTGACTACATCCT (PAM) CAACTTAGCCAATCAAAAGG (sgRNA) ACTTTGAGTTC.
[0061] Gnas sgRNA sequence transcribed in vitro: GGCCUUUUGAUUGGCUAAGUUGGUUUUAGAGCUAGAAAUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCCGUUAUCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCACCGAGUCGGUGCUUUUCACAA.
[0062] 1.2 Design of single-stranded DNA template for Gnas gene insertion knockout
[0063] According to the sgRNA target site selected in 1.1, the insertion knockout donor was designed, and the sequence information of the Gnas gene insertion knockout single-stranded DNA template was obtained as follows:
[0064] Gnas donor:...
Embodiment 2
[0091] Example 2 Zebrafish izumo1 gene-specific knockout
[0092] 1.1 Selection of izumo1 gene sgRNA targeting sites
[0093] The exon 2 of the zebrafish izumo1 gene (Gene ID: 100329365) was selected for gene knockout. The sequence of exon 2 of the izumo1 gene was analyzed for PAM sites on the CRISPOR website (http: / / crispor.tefor.net / crispor.py), and the PAM sites with higher scores were selected. The sequence information is as follows:
[0094] CAAGAACAGAATACCA (PAM)GAGTGAATTCAAGAGGCATT (sgRNA)GG.
[0095] In vitro transcribed izumo1 sgRNA sequence:
[0096] GGAAUGCCUCUUGAAUUCACUCGUUUUAGAGCUAGAAAUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCCGUUAUUCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCACCGAGUCGGUGCUUUUCACAA.
[0097] 1.2 Design of single-stranded DNA template for insertional knockout of izumo1 gene
[0098] According to the sgRNA target site selected in 1.1, the insert knockout donor was designed, and the sequence information of the izumo1 gene insert knockout single-stranded DNA template was obtained as follows:...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com