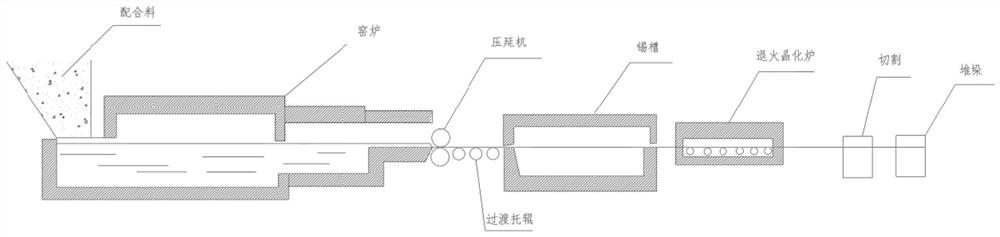
Microcrystalline glass plate production process
A production process and technology for glass plates, applied in glass forming, glass pressing, glass manufacturing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of narrow plate width, low production efficiency, small output, etc., and achieve excellent product quality, low production efficiency, and production high cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] A kind of glass-ceramic plate production process, concrete steps are as follows:
[0055] (1) Preparation of glass batch materials;
[0056] The glass batch material is composed of basic glass, crystal nucleus agent and clarifying agent;
[0057] The parts by weight of each component in the base glass are: Li 2 O 3.7 parts, Al 2 o 3 22 parts, SiO 2 60.3 parts, 0.7 parts of MgO, 2.2 parts of ZnO, 1.8 parts of CaO, 1 part of BaO, R 2 O 1 copy;
[0058] The parts by weight of each component in the crystal nucleating agent are: SnO 2 0.5 parts, ZrO 2 2 parts, TiO 2 1.8 parts, P 2 o 5 2 copies;
[0059] The parts by weight of each component in the clarifying agent are: Sb 2 o 3 0.5 part, NaCl 0.5 part;
[0060] (2) Preparation of molten glass:
[0061] Place the glass batch material in an oxy-fuel combustion glass furnace, melt it at a temperature of 1610°C to form a glass solution, and then cool it down to 1400°C through a forehearth to obtain the molt...
Embodiment 2
[0077] A kind of glass-ceramic plate production process, concrete steps are as follows:
[0078] (1) Preparation of glass batch materials;
[0079] The glass batch material is composed of basic glass, crystal nucleus agent and clarifying agent;
[0080] The parts by weight of each component in the base glass are: Li 2 O 3.9 parts, Al 2 o 3 20.5 parts, SiO 2 66 parts, MgO 0.3 parts, ZnO 0.4 parts, CaO 2.5 parts, BaO 0.6 parts, R 2 O 1 copy;
[0081] The parts by weight of each component in the crystal nucleating agent are: SnO 2 0.5 parts, ZrO 2 1 part, TiO 2 1.8 parts, P 2 o 5 0.5 copies;
[0082] The parts by weight of each component in the clarifying agent are: Sb 2 o 3 0.5 part, NaCl 0.6 part;
[0083] (2) Preparation of molten glass:
[0084] Place the glass batch material in an oxy-fuel combustion glass furnace, melt it at a temperature of 1610°C to form a glass solution, and then cool it down to 1430°C through a forehearth to obtain the molten glass...
Embodiment 3
[0090] A kind of glass-ceramic plate production process, concrete steps are as follows:
[0091] (1) Preparation of glass batch materials;
[0092] The glass batch material is composed of basic glass, crystal nucleus agent and clarifying agent;
[0093] The parts by weight of each component in the base glass are: Li 2 O 3.3 parts, Al 2 o 3 21.5 parts, SiO 2 69.2 parts, MgO 0.5 parts, ZnO 0.4 parts, CaO 0.6 parts, BaO 0.2 parts, R 2 O 0.5 parts;
[0094] The parts by weight of each component in the crystal nucleating agent are: SnO 2 0.2 parts, ZrO 2 1 part, TiO 2 1.3 parts, P 2 o 5 0.5 copies;
[0095] The parts by weight of each component in the clarifying agent are: Sb 2 o 3 0.5 part, NaCl 0.3 part;
[0096] (2) Preparation of molten glass:
[0097] Place the glass batch material in an oxy-fuel combustion glass furnace, melt it at a temperature of 1630°C to form a glass solution, and then cool it down to 1440°C through a forehearth to obtain the molten ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface smoothness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com