A q-learning-based trajectory planning method for concrete placing robot
A trajectory planning and robot technology, applied in the direction of instruments, manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in determining optimal performance indicators, poor construction conditions, and inability to cope with real-time changing factors on the construction site, so as to avoid multi-objective optimization Inverse calculation and data fitting process, improve autonomy, easy to change and test the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
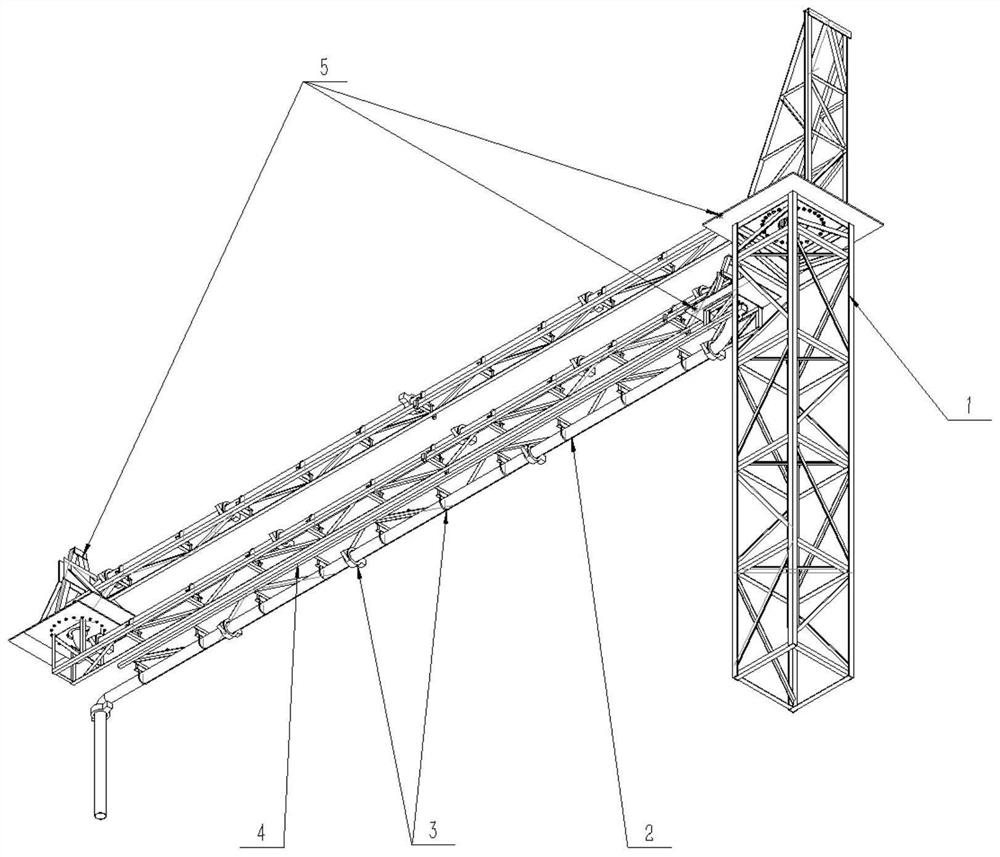
[0015] figure 1 It shows the overall structure of the designed intelligent redundant concrete placing robot, which is mainly composed of five modules, including column assembly (1), pipe assembly (2), pipe clamp (3), cantilever support (4), turntable assembly into (5). The design adopts three rotary joints, that is, three turntable assemblies (5), and for plane pouring with two degrees of freedom, the design has one redundant degree of freedom.
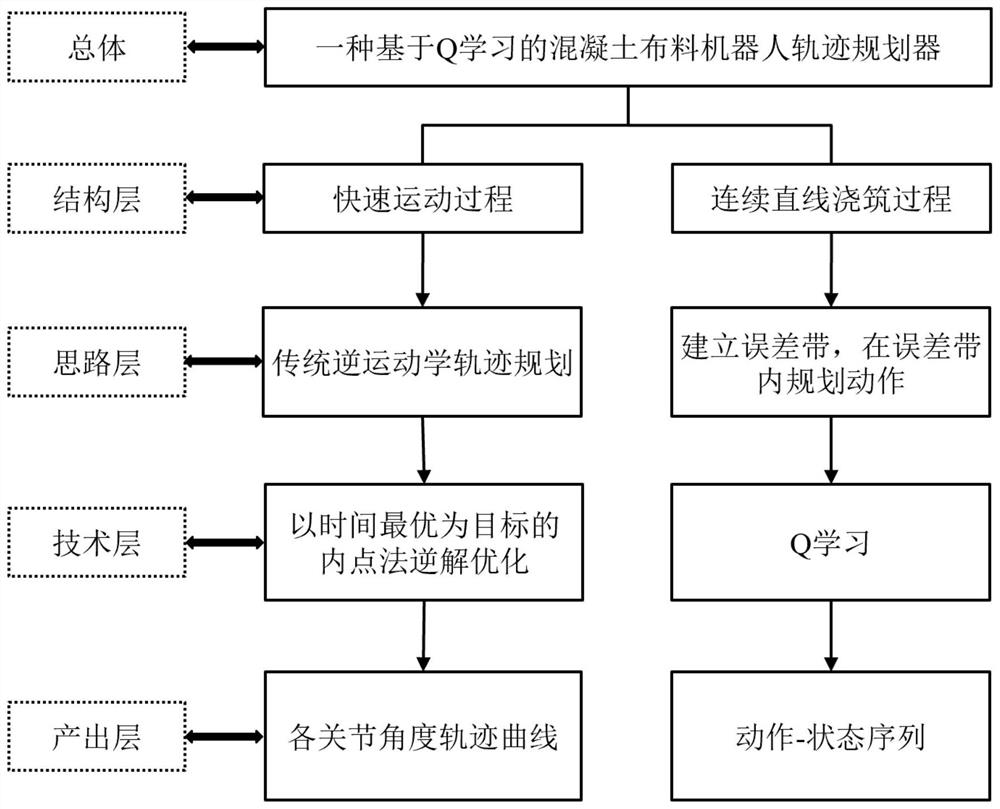
[0016] figure 2 It is the overall structure of the trajectory planner, including the planning method summary of the fast moving part and the continuous concrete pouring part.
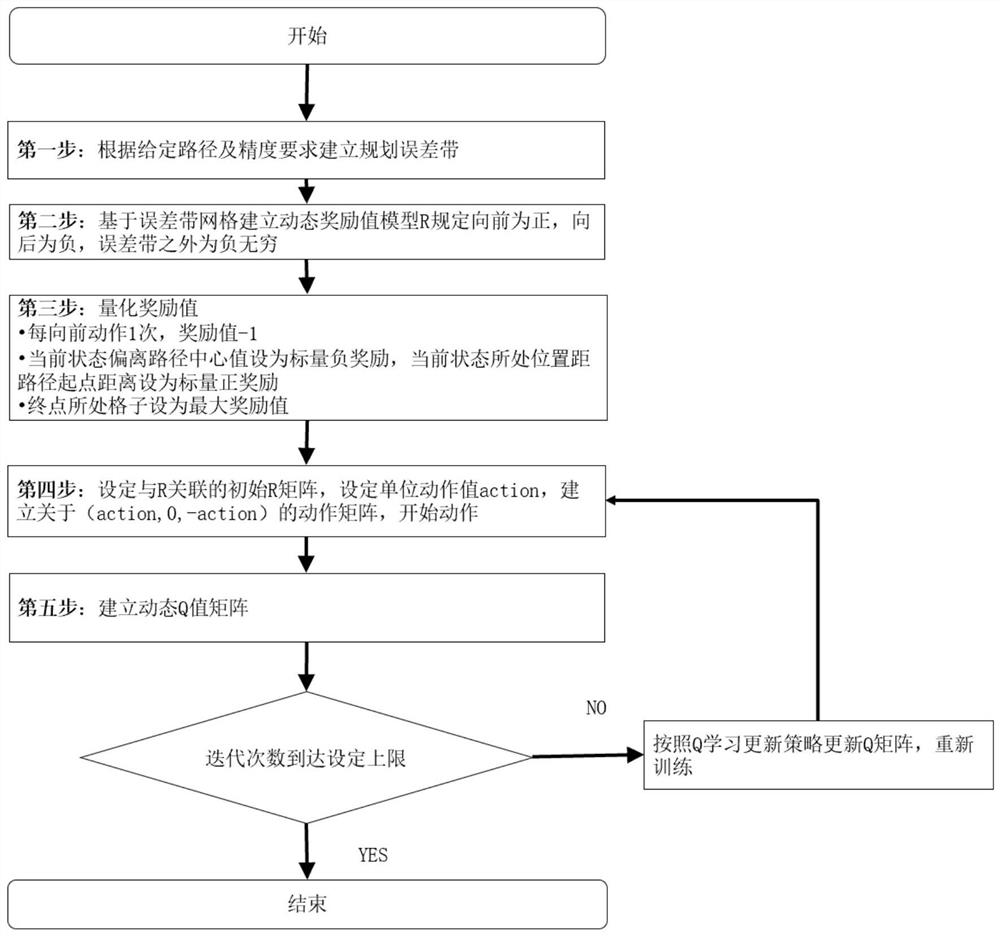
[0017] image 3 A detailed description of the thought layer and technical layer of the track planning part of the continuous pouring process of concrete, this part uses the Q learning method, image 3 Its application method and process are sorted out and summarized.
[0018] exist figure 2 In the paper, an overall design framework of trajectory planning...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com