Biological evaluation method capable of quantitatively characterizing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon adsorption capacity of modified biochar in water body
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and quantitative characterization technology is applied in the field of biological evaluation for quantitatively characterizing the ability of modified biochar to adsorb polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, which can solve the problem that biological evaluation indicators have not yet appeared.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1: The lowest total lethal concentration LC 100 Determination test
[0046] In order to measure the lowest total lethal concentration LC of four kinds of PAHs mixtures in the 48h acute toxicity test of Daphnia magna 100 , respectively pipette 0.375mL, 0.563mL, 0.844mL, 1.266mL, 1.898mL of the aforementioned four kinds of PAHs mixture saturation test solutions to a 250mL volumetric flask, add ISO standard dilution water to constant volume, and obtain concentrations of 0.15%, 0.23%, 0.34% , 0.51%, and 0.76% five test liquids, with ISO standard dilution water as blank control.
[0047] The test adopts the static method, and the control group and the test group are set for 4 repetitions, with 5 Daphnia magna and 50 mL of the test solution for each repetition. The test exposure time was 48h. The daphnia to be tested were randomly selected, and the test solution was added after reaching the test temperature, and the adding process was completed within 30 minutes. ...
Embodiment 2
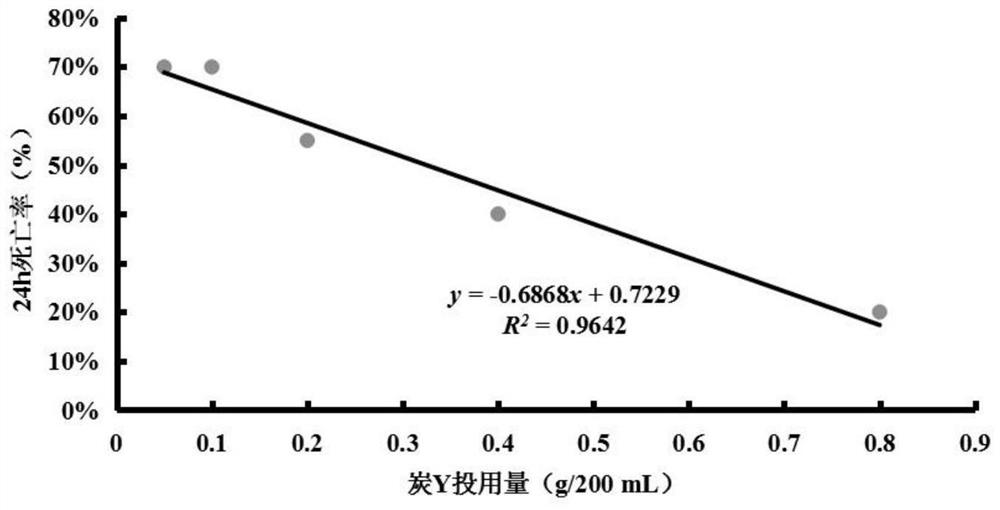
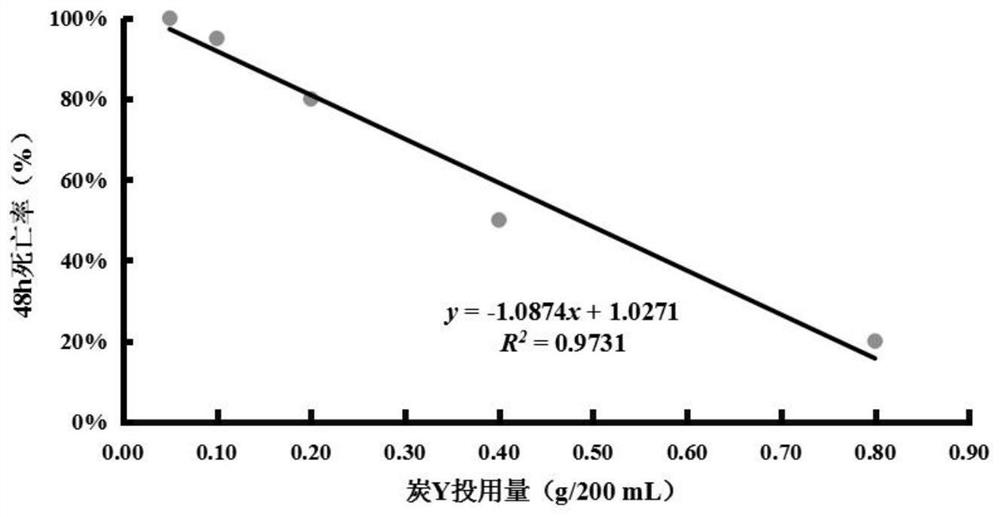
[0057] Example 2: Acute Toxicity Test of Daphnia magna under Charcoal Y Adsorption of PAHs
[0058] Pipette 1.266mL of the saturated test solution of the four kinds of PAHs mixtures into six 250mL volumetric flasks, and obtain the PAHs solution at the lowest total lethal concentration of 0.51mg / L after constant volume with ISO standard dilution water. Transfer the solution to five 250mL Erlenmeyer flasks with stoppers, then weigh 0.05g, 0.10g, 0.20g, 0.40g, and 0.80g of carbon Y into the above-mentioned Erlenmeyer flasks, and mix them in a shaker at 20°C at 150r / min Adsorbed for 24 hours, the filtrate filtered through a 0.45 μm pore size filter membrane was used as the test solution, and 200 mL of PAHs solution was measured from the sixth volumetric flask as a blank control.
[0059] The test adopts the static method, and the control group and the test group are set for 4 repetitions, with 5 Daphnia magna and 50 mL of the test solution for each repetition. The test exposure t...
Embodiment 3
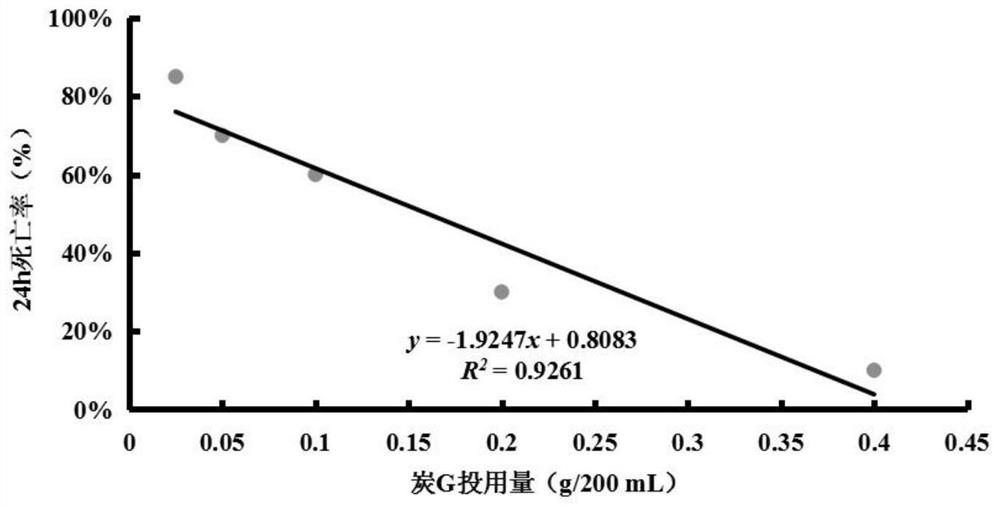
[0068] Example 3: Acute Toxicity Test of Daphnia magna under Charcoal G Adsorption of PAHs
[0069] Pipette 1.266mL of the saturated test solution of the four PAHs mixtures into six 250mL volumetric flasks, and dilute to volume with ISO standard dilution water to obtain the PAHs solution at the lowest total lethal concentration of 0.51mg / L. Transfer the 200mL solutions in five volumetric flasks to five 250mL corked Erlenmeyer flasks respectively, then weigh 0.025g, 0.05g, 0.10g, 0.20g, and 0.40g of carbon G into the above-mentioned Erlenmeyer flasks, and Mix and adsorb in a shaker at 20°C at 150r / min for 24 hours, and the filtrate filtered through a 0.45 μm pore size filter membrane was used as the test solution, and 200 mL of PAHs solution was taken from the sixth volumetric flask as a blank control.
[0070] The test adopts the static method, and the control group and the test group are set for 4 repetitions, with 5 Daphnia magna and 50 mL of the test solution for each repet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com