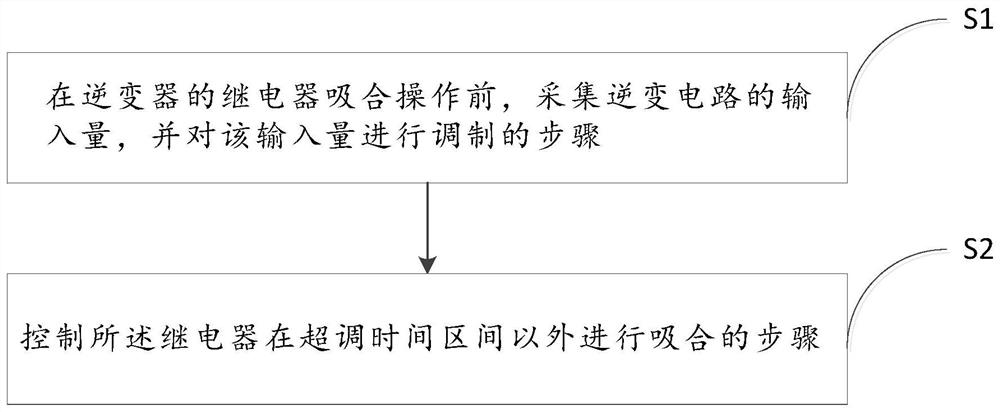
Inverter output relay pull-in impact current suppression method and device
A technology for outputting relays and inrush currents, applied in the direction of output power conversion devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as increased equipment costs, incomplete suppression, and limited scope of application, so as to improve applicability and eliminate the impact of relay pull-in The effect of current
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
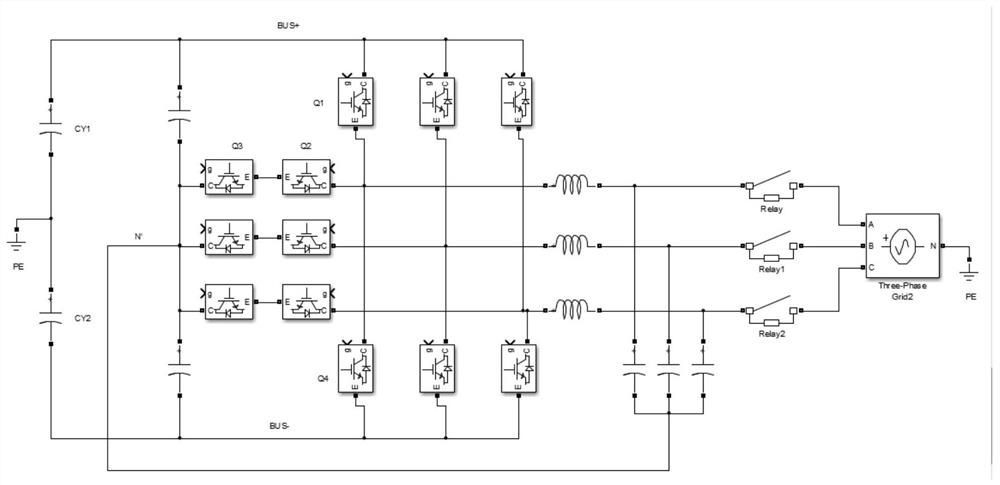
[0034] Let us first talk about the topology structure corresponding to the method for suppressing the inrush current of the inverter output relay in the present invention. figure 1 It is a schematic diagram showing the main circuit structure of a three-phase T-type three-level inverter provided in a preferred embodiment of the present invention. It should be noted that this preferred embodiment of the present invention is only illustrated by taking a three-phase T-type three-level inverter as an example, and the application of the preferred embodiment of the present invention should not be affected by the topology of the inverter. Inverting circuits of different topologies can modulate the corresponding input quantities according to the same principle, so as to achieve the technical purpose of this preferred embodiment of the present invention as well.
[0035] see figure 1 ,according to figure 1 In the direction presented, the main circuit in Embodiment 1 includes a DC side...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Figure 4It is a schematic diagram showing the main circuit structure of the three-phase I-type three-level inverter provided in the second embodiment of the present invention; in the second embodiment of the present invention, the DC / AC converter is also a three-level topology, and The difference from the first embodiment is that the first embodiment is a three-phase T-type three-level inverter, while the second embodiment is a three-phase I-type three-level inverter.
[0047] The second embodiment uses the same method as the first embodiment to define and distinguish the relays (IGBTs) in the circuit, and arrange the switches in the same order as the first embodiment. Therefore, the circuit corresponding to the second embodiment can collect and modulate the input quantity in the same manner as the first embodiment, and the specific process can refer to the same part in the first embodiment, which will not be repeated here.
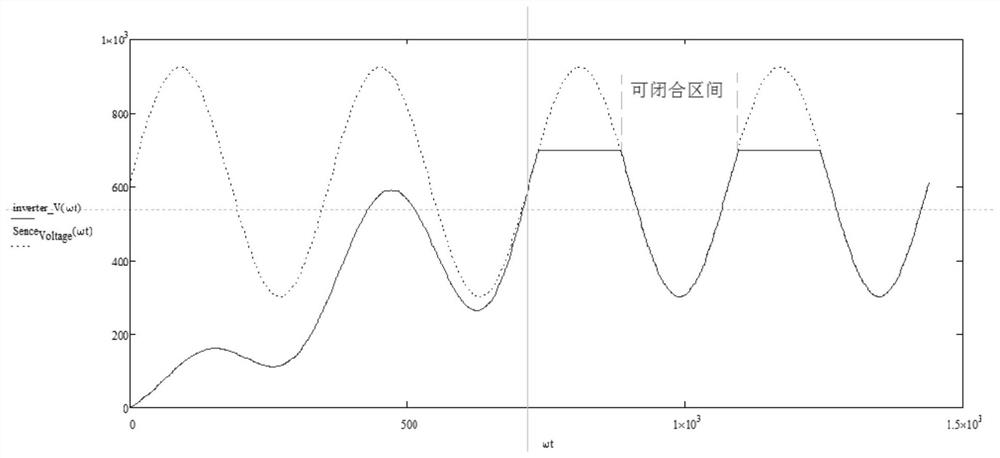
[0048] As for the determination of the ove...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram showing the main circuit structure of the two-level three-phase inverter circuit provided in another preferred embodiment of the present invention. see Figure 5 , in the third embodiment, a two-level three-phase inverter circuit is provided, according to Figure 5 In the direction presented, the circuit in Embodiment 3 includes a DC side and an AC side from left to right, and the DC ports on the DC side are respectively connected to the positive pole of the DC bus of the inverter, the midpoint of the DC bus, and the negative pole of the DC bus. On the AC side, one end of the same three AC switches is connected to the AC side of the DC / AC converter through the AC filter, and the other side of the three AC switches is connected to the AC port. As in Embodiment 1, define the left end of the inductance and capacitance as the first segment, and the right end as the second end, see Figure 5 , the first ends of the three inductors are r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com