Transmitting and receiving separated laser radar optical system
A laser radar and optical system technology, applied in radio wave measurement systems, measurement devices, electromagnetic wave re-radiation and other directions, can solve the problems of narrowing the distance between the sending and receiving ends, expanding the scanning angle, and difficulty in installation and adjustment, and achieves the reduction of constraints and elimination of Interference, the effect of facilitating the design and adjustment of the optical path
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
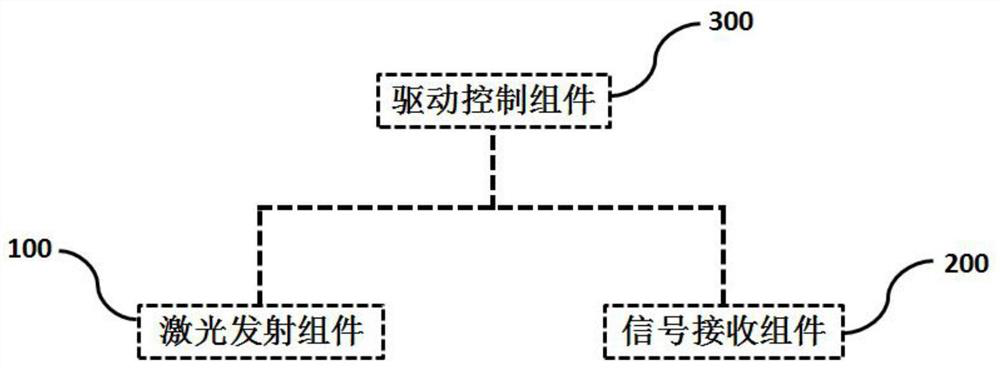
[0031] The present invention provides a laser radar optical system with separate sending and receiving, its structure is as follows figure 1 As shown, the transceiver laser radar optical system includes a laser emitting component 100 , a signal receiving component 200 and a drive control component 300 .
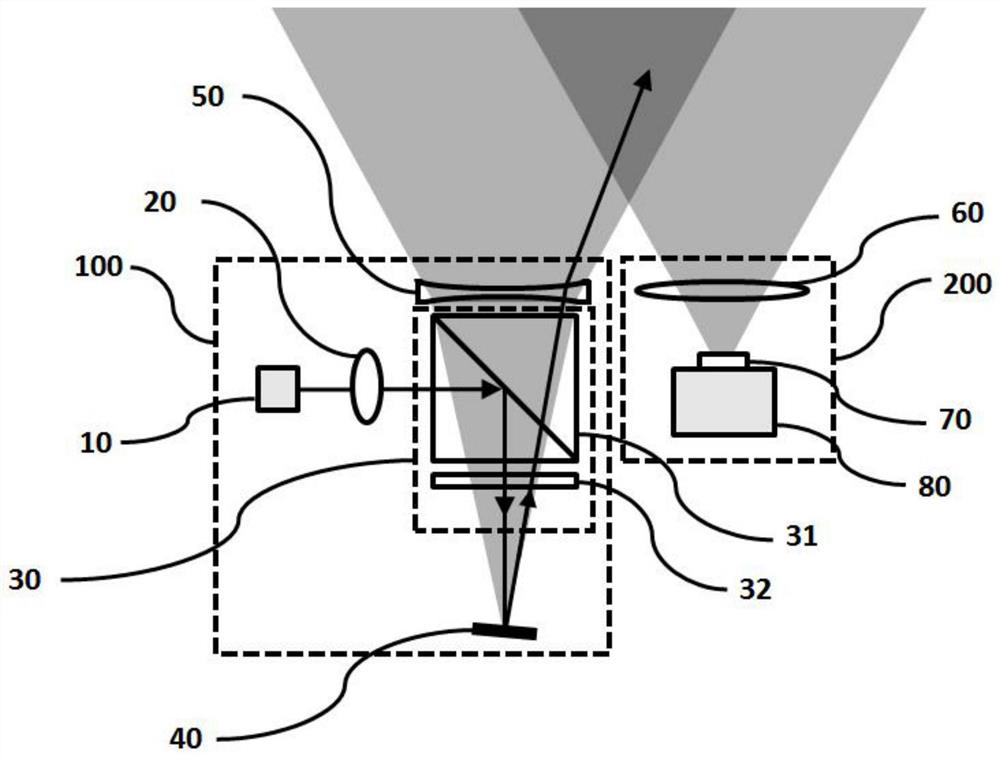
[0032] The laser emitting assembly 100 is used to emit a laser scanning signal to a target object and realize beam scanning; the laser emitting assembly 100 includes a laser light source 10, a beam shaping module 20, a polarization transflective module 30, a projection unit 40 and a field of view expansion unit 50 .
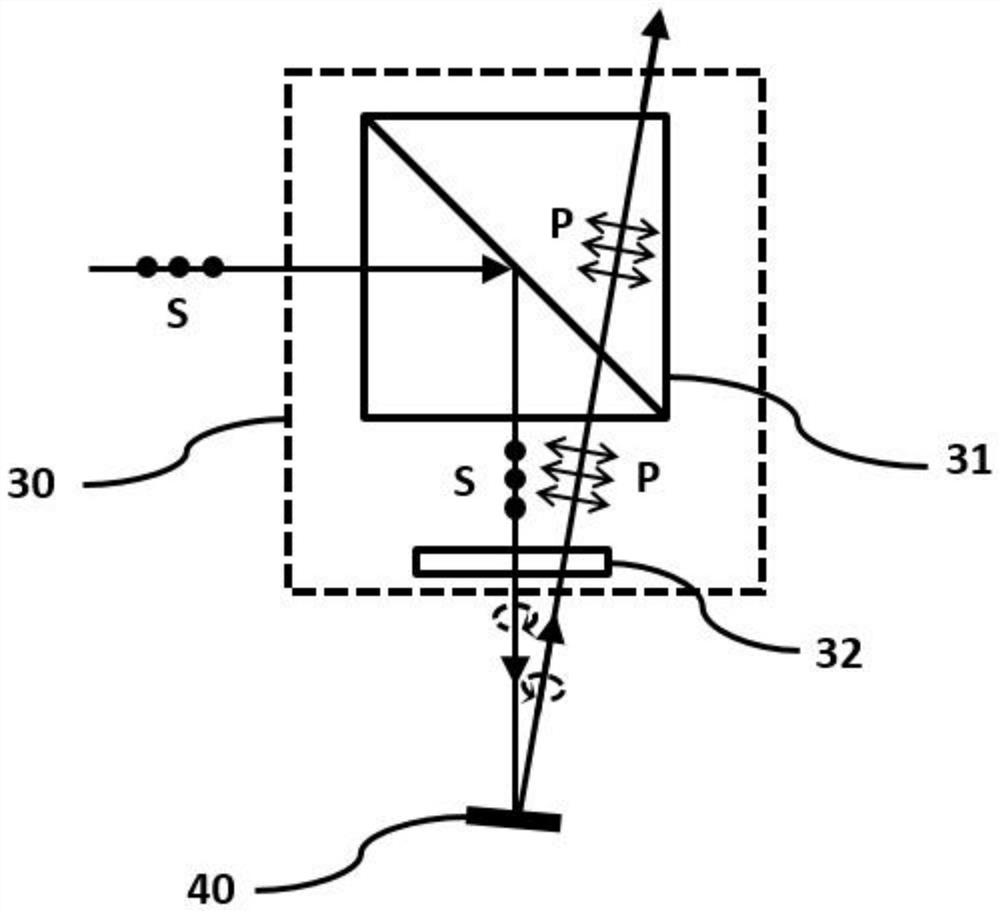
[0033] Such as figure 2 As shown, the laser light source 10 actively emits a laser beam, and the laser beam is shaped and collimated by the beam shaping module 20 to obtain an approximately collimated beam and reduce the divergence angle of the beam so that the laser beam can project a longer distance. Since the beams emitted by the laser light source 10 have...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Such as Figure 4 As shown, an auxiliary system 90 is added on the basis of Example 1, and the auxiliary system 90 includes a polarizing unit 91 and an aperture 92 .
[0045] The polarizing unit 91 is used to polarize the laser beam and optimize the linear polarization of the laser beam. The polarizing unit 91 can be selected but not limited to a linear polarizer; the diaphragm 92 is used to limit the beam. In the beam shaping module 20 pairs of laser beams refine the beam on the basis of shaping and collimation.
[0046] The polarizing unit 91 and the diaphragm 92 are located between the beam shaping module 20 and the polarized transflective module 30, and the area of the polarizing unit 91 needs to be greater than the area of the beam spot passed through; the laser beam passes through the polarizing unit 91 and the light beam. There is no specific requirement on the order of the diaphragms 92 , and the example here is to pass through the polarizing unit 91 first ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com