Weissella bacteria-derived nanovesicle and use thereof
A technology of Weissella and Weissella esophagus, applied to the composition for reducing or treating inflammatory diseases, the field of prevention
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
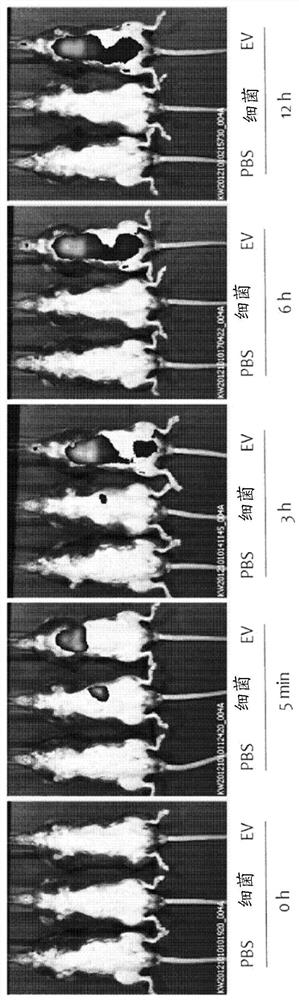
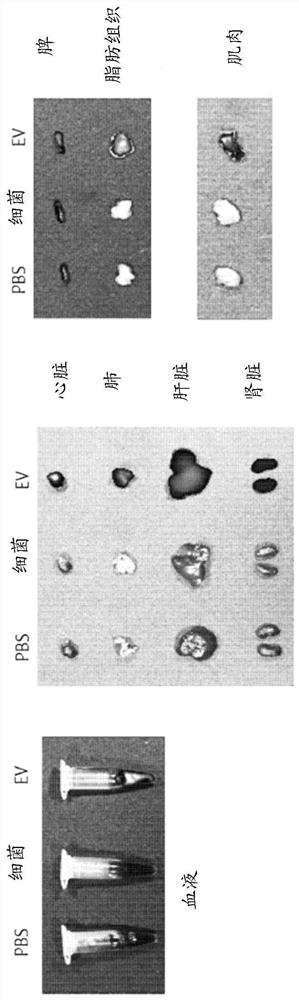
[0063] Example 1. Analysis of in vivo absorption, distribution and excretion patterns of bacteria and vesicles derived from bacteria
[0064] To assess whether bacteria and vesicles derived from bacteria are absorbed systemically through the gastrointestinal mucosa, experiments were performed as follows. A dose of 50 μg of each of fluorescently labeled bacteria and vesicles derived from bacteria in the stomach of mice was administered to the gastrointestinal tract, and after 0 minutes, 5 minutes, 3 hours, 6 hours and 12 hours Measure fluorescence. As a result of observing the whole image of the mouse, as Figure 1A As shown, bacteria were not taken up systemically, but vesicles derived from bacteria were absorbed systemically at 5 minutes after administration, and strong fluorescence was observed in the bladder at 3 hours after administration, making it possible to see that the vesicles were excreted. to the urinary tract. Furthermore, it can be seen that vesicles are pres...
Embodiment 2
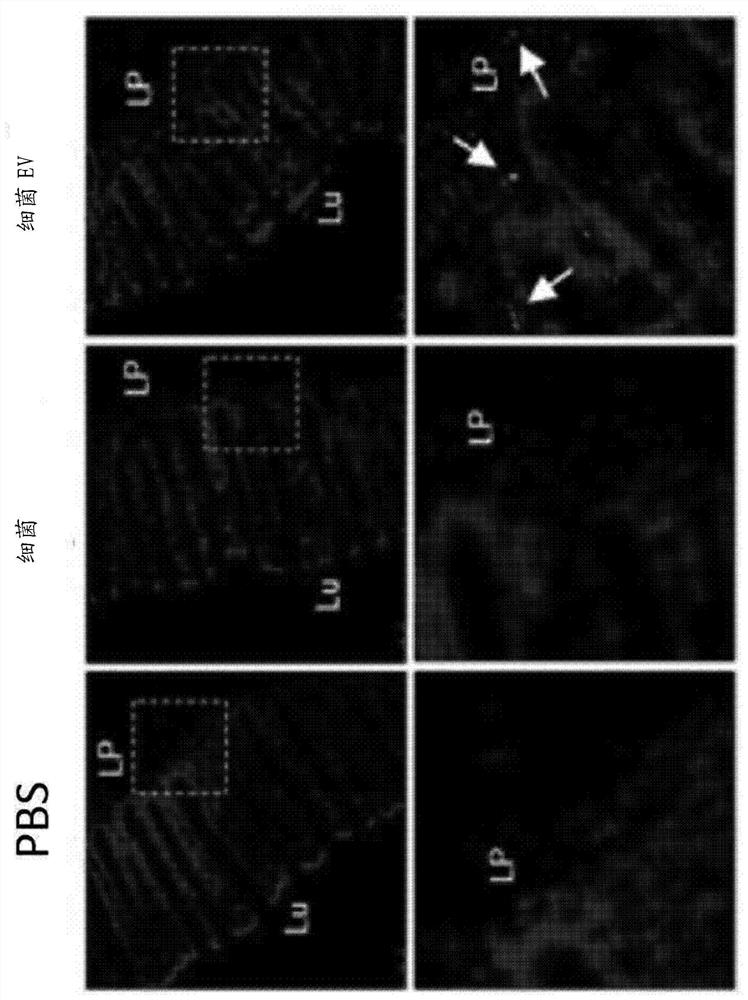
[0066] Example 2. Evaluation of whether bacteria and vesicles derived from bacteria penetrate the protective membrane of the intestinal mucosa
[0067] To assess whether bacteria and bacteria-derived vesicles that penetrate the protective membrane of the intestinal mucosa penetrate into intestinal tissue after direct administration of bacteria and bacteria-derived vesicles to the intestine, the Penetration into the intestinal tissue behind the protective membrane of the intestinal mucosa. To assess the presence of bacteria and vesicles in the intestinal mucosa, antibodies against bacteria and vesicles were prepared, attached to green fluorescent protein (GFP) and used, and in combination with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole ( DAPI) staining and observed under a microscope.
[0068] As a result, it was confirmed that bacteria cannot pass through the protective membrane of the intestinal mucosa, however, vesicles derived from bacteria permeate through the intestinal mucosa into ...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3. Isolation of vesicles from Weissella esophagus culture solution
[0070] Based on the above examples, the Weissella angustiformis strain was cultured, then vesicles were isolated therefrom and the characteristics of the isolated vesicles were analyzed. First, the Weissella angustiformis strain was cultured in a de Man-Rogosa and Sharpe (MRS) medium in an incubator at 37°C until the absorbance became 1.0 to 1.5, and then in a Luria-Bertani (LB) medium Subculture. Subsequently, the culture supernatant containing the strain was recovered and centrifuged at 10,000×g and 4°C for 20 minutes, and then the strain was removed and filtered through a 0.22 μm filter.
[0071] The filtered supernatant was concentrated by microfiltration to a volume of less than or equal to 50 ml by using a MasterFlex pump system (Cole-Parmer, US) with a 100 kDa Pellicon 2 Cassette filter membrane (Merck Millipore, US), and filtered through a 0.22 μm filter. The concentrated supernatan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com