Seedling raising method for leguminous plants in dry-hot valley area
A technology for leguminous plants and dry-hot river valleys, which is applied in the fields of leguminous plant cultivation, botanical equipment and methods, plant growth regulators, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of increasing the germination rate, increasing the germination time, and increasing the root length of the seedlings
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
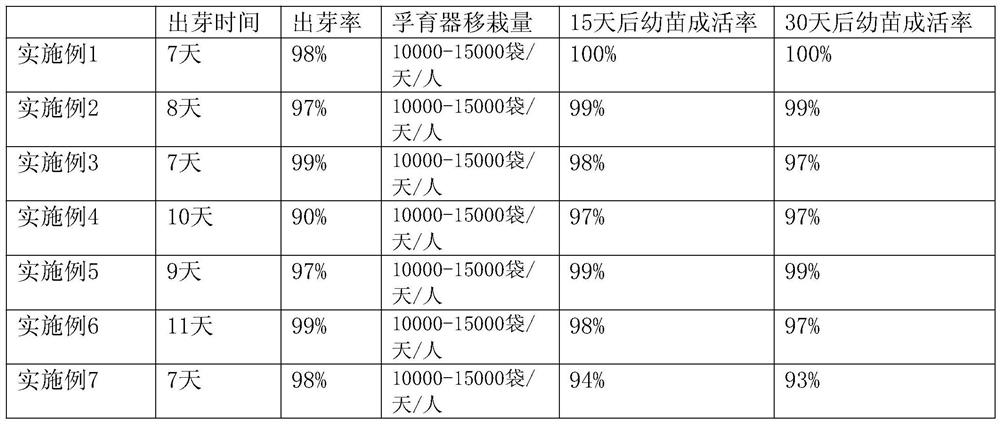
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] A method for cultivating seedlings of legumes in hot and dry valley areas comprises the following steps:
[0027] Step 1. Select excellent plants that are suitable for local growth and grow robustly, with plump grains, strong vitality, good gloss, high yield, good quality, and no pests and diseases; generally, it will bear fruit in December, and the fruit is the best when the fruit is in the shape of a yellow-brown lentil. Seed collection period; seeds with a weight of more than 25,000 seeds / kg;
[0028] Step 2. Collect the selected seeds and dry them in the sun for 1 day; then use 0.01mg·L -1 The daidzin solution soaks the dried seeds for 1 hour, then mixes and adds 100umol.L -1 The salicylic acid continued to soak the seeds for half an hour and took out for subsequent use; the parts by weight of the daidzin solution were 80 parts, and the parts by weight of the salicylic acid were 20 parts;
[0029] Step 3. The germination bed should be located in a place with relat...
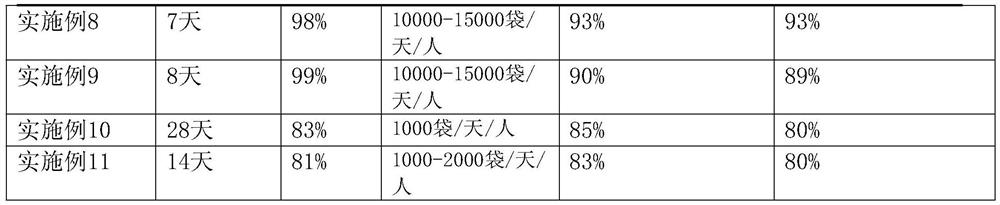
Embodiment 2
[0049] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that in step 2, the selected seeds will be collected and dried for 2 days; -1 The daidzin solution soaks the air-dried seeds for 2 hours; the weight part of the daidzin solution is 90 parts, and the weight part of salicylic acid is 30 parts;
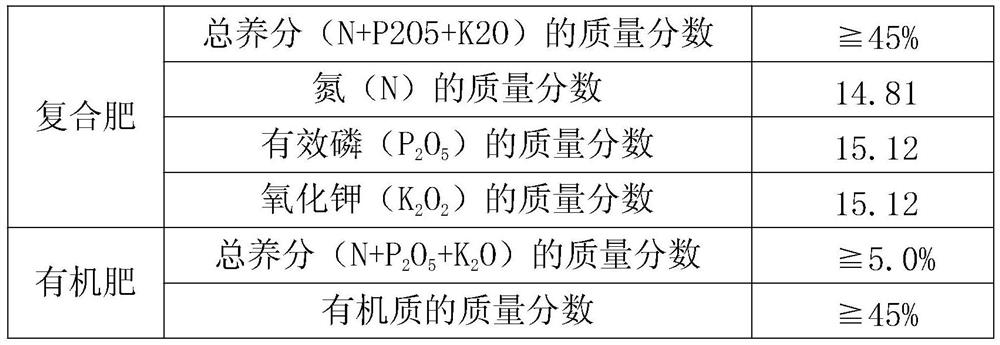
[0050] In step 3, the width of the germination bed should be 1.3m, and the length can be adjusted voluntarily according to the overall length of the nursery shed, generally controlled at 18m, and the width of the trail is 50cm; in step 5, observe the seed expansion every day after the 4th day; in step 8, in Fu Fill the substrate in the breeding container, the components and parts by weight of the substrate are: 40 parts of sand, 40 parts of clay, 4 parts of Cu tailings sand, 4 parts of deer powder, 4 parts of kudzu powder, 20 parts of organic fertilizer, 4 parts of compound fertilizer servings; 18 bags per row in step 9.
Embodiment 3
[0052] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that in step 2, the selected seeds will be collected and dried for 2 days; -1 The daidzin solution soaks the air-dried seeds for 2 hours; the weight part of the daidzin solution is 100 parts, and the weight part of salicylic acid is 35 parts;
[0053] In step 3, the width of the germination bed should be 1.5m, and the length can be adjusted voluntarily according to the overall length of the nursery shed, generally controlled at 20m, and the width of the trail is 50cm; in step 5, observe the seed expansion every day after the 5th day; step 8, in Fu Fill the substrate in the breeding container, the components and parts by weight of the substrate are: 45 parts of sandy soil, 50 parts of clay, 6 parts of Cu tailings sand, 6 parts of deer powder, 6 parts of kudzu powder, 25 parts of organic fertilizer, 5 parts of compound fertilizer servings; 20 bags per row in step 9.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com