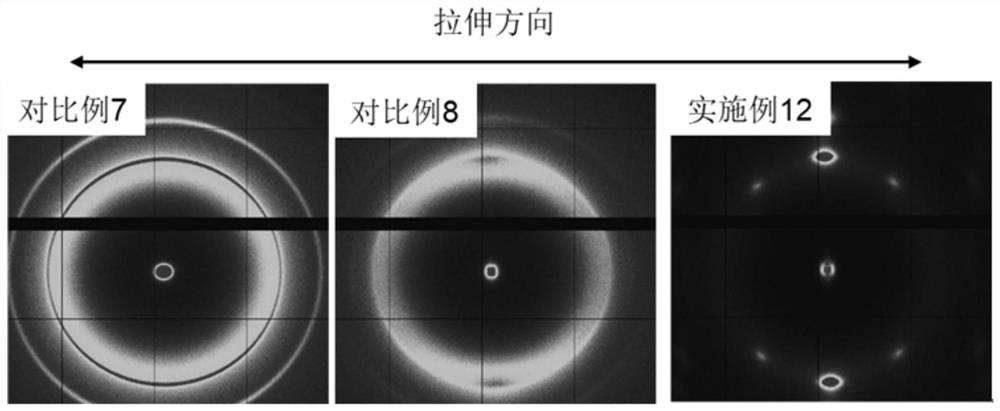
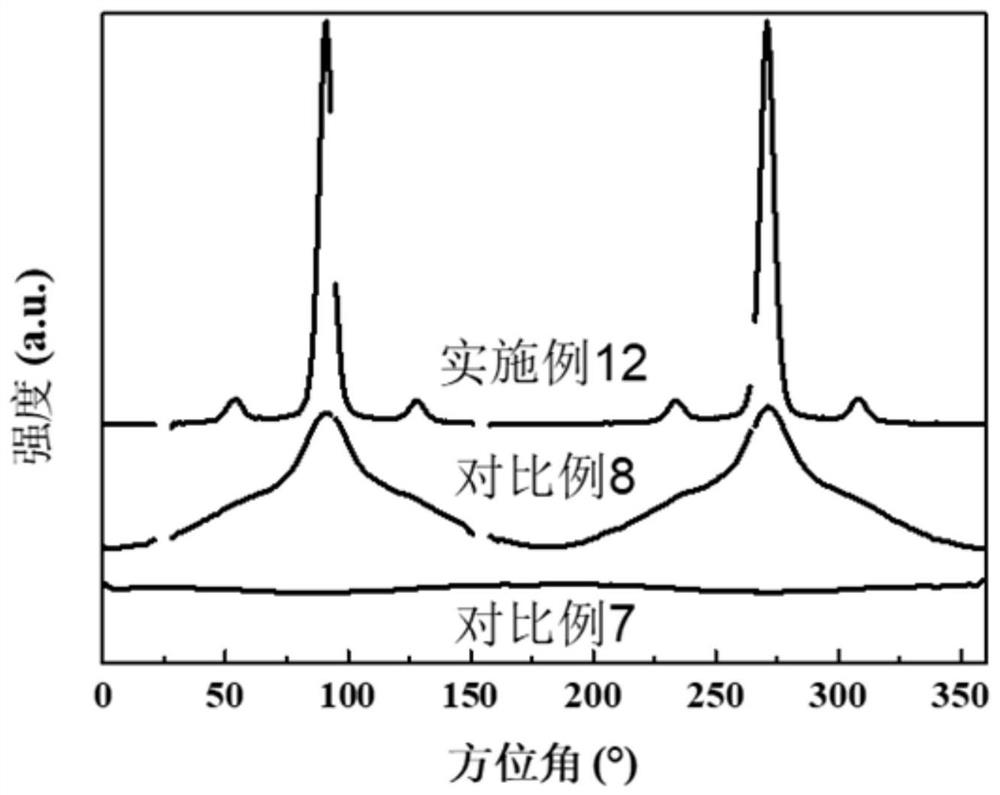
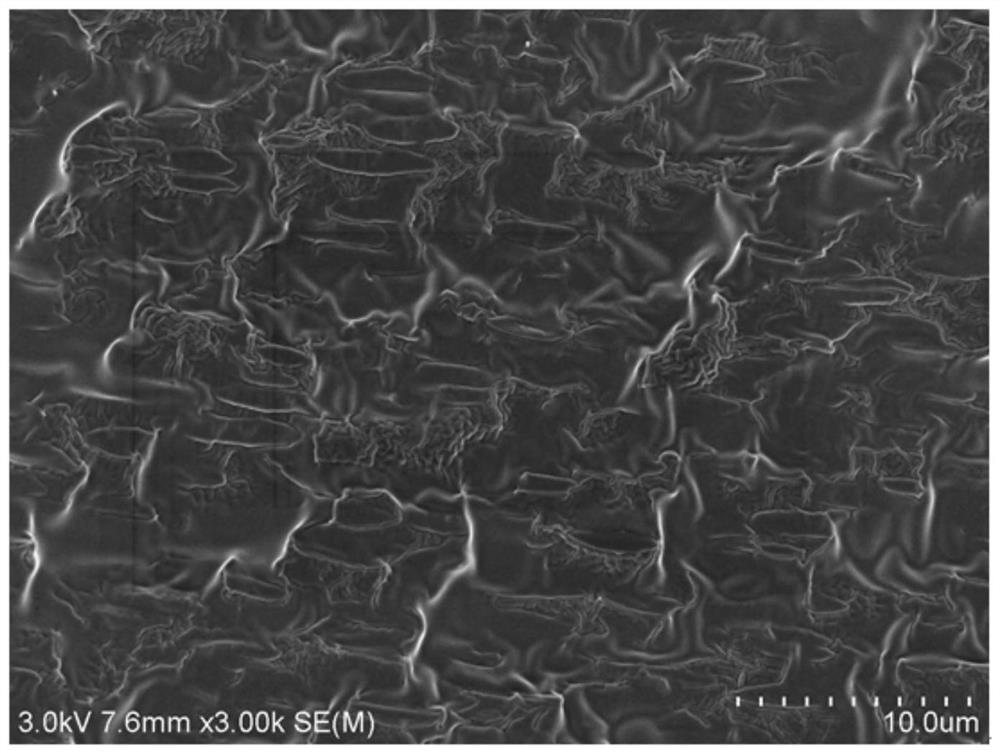
A kind of strong and tough polyester composite material and preparation method thereof
A polyester composite material and polymer technology, applied in the direction of climate sustainability, sustainable manufacturing/processing, bio-packaging, etc., to achieve the effect of simple and easy-to-obtain equipment, increase tensile strength, and improve key common problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] 80 parts of polyglycolic acid, 20 parts of polyadipate / butylene terephthalate, 0.3 parts of epoxy chain extender ADR437, tetra[β-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4- 0.3 part of hydroxyphenyl) propionic acid] pentaerythritol ester, 2 parts of talc powder were fully dried and added in the twin-screw extruder in proportion by weight to melt and blend and extrude and granulate to obtain blend A, and the melt-blending temperature was 220 ℃ °C; melt-extrude the dried blend A at 230 °C through a single-screw extruder, lower the melt extrudate to 170 °C and perform pre-stretching with a stretching ratio of 2; The treated extrudate was rapidly cooled to 50°C (25°C above the glass transition temperature of polyglycolic acid) for secondary stretching, and the stretching ratio was 8. Finally, a strong and tough polyester composite material was obtained after heat treatment at 100°C. .
Embodiment 2
[0052] Compared with Example 1, only the second stretching factor is different:
[0053] 80 parts of polyglycolic acid, 20 parts of polyadipate / butylene terephthalate, 0.3 parts of epoxy chain extender ADR437, tetra[β-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4- 0.3 part of hydroxyphenyl) propionic acid] pentaerythritol ester, 2 parts of talc powder were fully dried and added in the twin-screw extruder in proportion by weight to melt and blend and extrude and granulate to obtain blend A, and the melt-blending temperature was 220 ℃ °C; melt-extrude the dried blend A at 235 °C through a single-screw extruder, directly reduce the melt extrudate to 170 °C and perform pre-stretching with a stretching ratio of 2; The stretched extrudate was rapidly cooled to 50 °C for secondary stretching, and the stretching ratio was 5. Finally, a strong and tough polyester composite material was obtained after heat treatment at 100 °C.
Embodiment 3
[0055] Compared with Example 1, only the second stretching factor is different:
[0056] 80 parts of polyglycolic acid, 20 parts of polyadipate / butylene terephthalate, 0.3 parts of epoxy chain extender ADR437, tetra[β-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4- 0.3 part of hydroxyphenyl) propionic acid] pentaerythritol ester, 2 parts of talc powder were fully dried and added in the twin-screw extruder in proportion by weight to melt and blend and extrude and granulate to obtain blend A, and the melt-blending temperature was 220 ℃ °C; melt-extrude the dried blend A at 230 °C through a single-screw extruder, directly reduce the melt extrudate to 170 °C and carry out pre-stretching with a stretching ratio of 2; The stretched extrudate was rapidly cooled to 50°C for secondary stretching with a draw ratio of 3, and finally heat-treated at 100°C to obtain a strong and tough polyester composite material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com