Tunable laser wavelength searching method and device
A technology for tuning lasers and lasers, which is applied in the field of optical communication and can solve the problems of difficulty in obtaining the corresponding relationship between the tuning current and the wavelength of the tunable laser.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
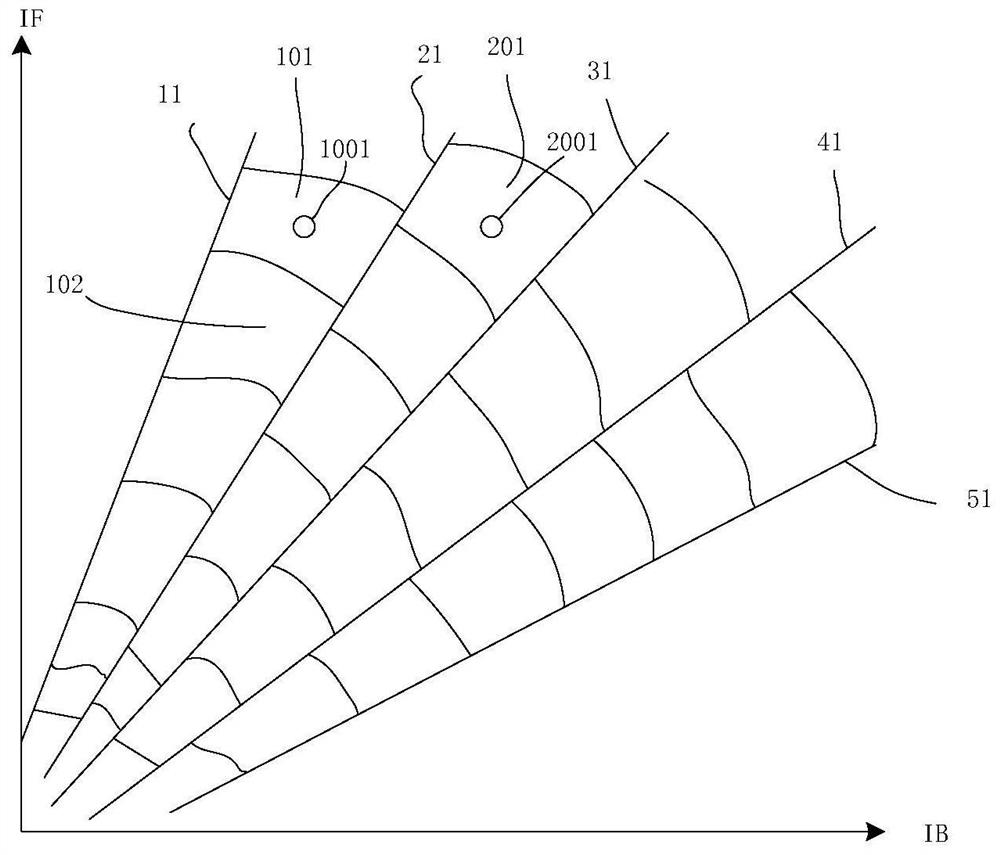
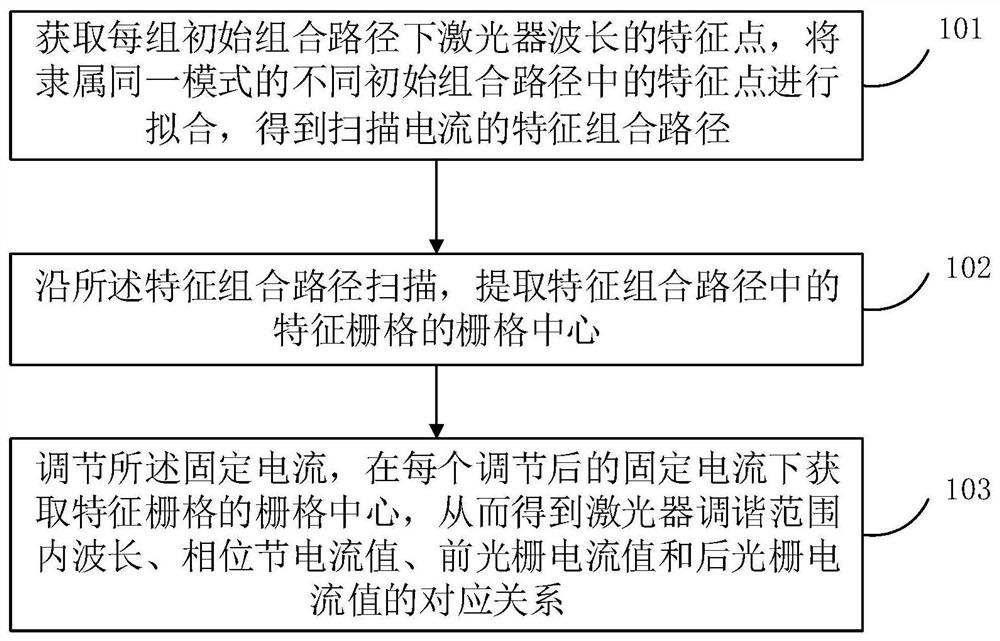
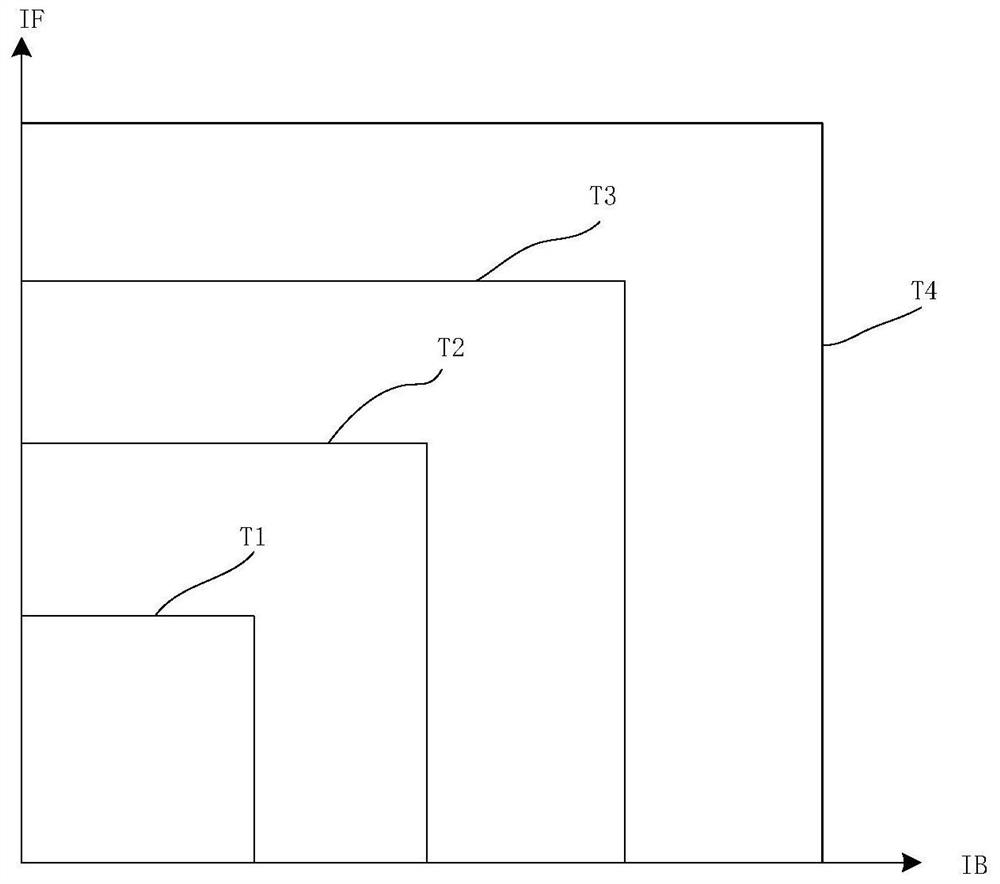
[0038] For a typical SGDBR laser, the typical distribution law of the output wavelength in the plane of the front grating current IF and the back grating current IB is as follows: figure 1 shown. The wavelength of the light emitted by the laser is in the plane of the combination of the front grating current and the rear grating current, and its distribution is not continuous. figure 1The figure shows that each diagonal region divided by the five boundaries of 11-51 corresponds to a specific pair of reflection peaks in the comb-shaped reflection peaks generated by the front and rear grating currents, and the wavelength will appear at the boundary of the diagonal region. Jump. In the actual use of the laser, the boundary shape of the wavelength hopping is approximately straight but not regular. For simplicity, figure 1 The mid-wavelength distribution jump boundary 11-51 is indicated by a straight line. At the same time, in the same diagonal area, the wavelength distribution i...
Embodiment 2
[0086] On the basis of the method for searching the wavelength of the tunable laser provided in the above-mentioned embodiment 1, the present invention also provides a device for searching the wavelength of the tunable laser that can be used to realize the above method, such as Figure 14 Shown is a schematic diagram of the device architecture of the embodiment of the present invention. The device for tunable laser wavelength search in this embodiment includes one or more processors 11 and memory 12 . in, Figure 14 A processor 11 is taken as an example.
[0087] Processor 11 and memory 12 can be connected by bus or other means, Figure 14 Take connection via bus as an example.
[0088] Memory 12 is a non-volatile computer-readable storage medium for a tunable laser wavelength search method, and can be used to store non-volatile software programs, non-volatile computer-executable programs and modules, such as the tunable laser in Embodiment 1. Laser wavelength search metho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com