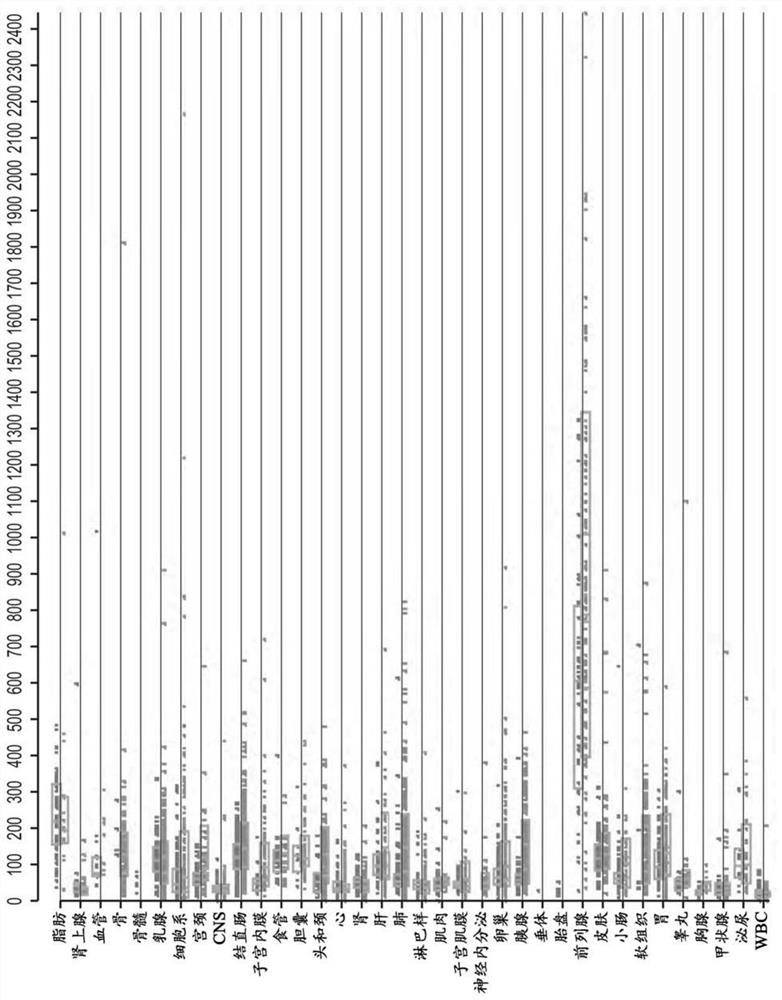
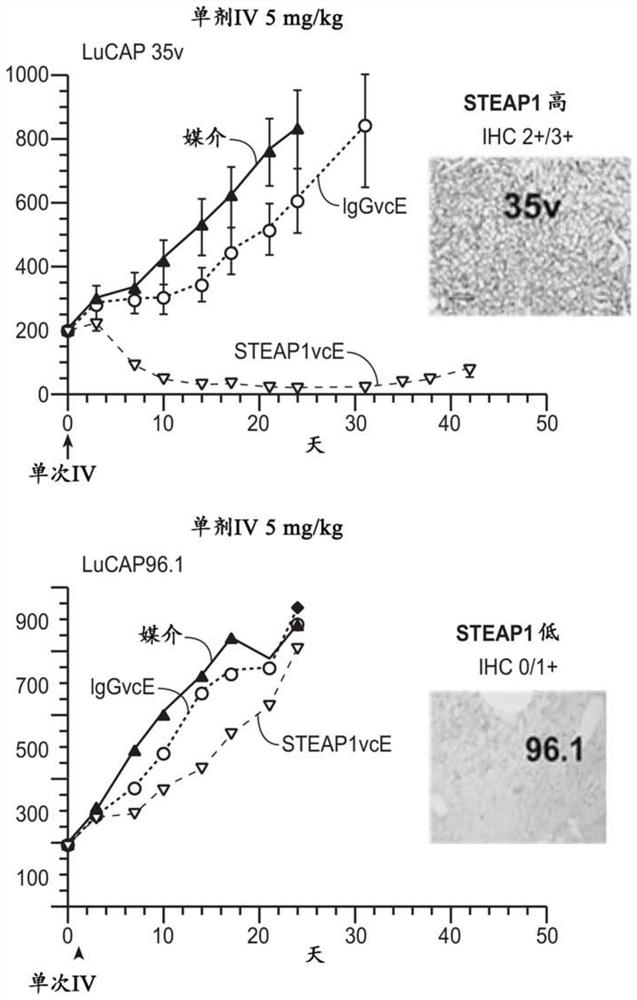
Compositions and methods for prostate cancer analysis
A technology for prostate cancer and composition, applied in the field of oncology and cancer diagnosis, capable of solving problems such as sensitivity limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0158] Example 1: Immunofluorescence-based detection of STETC1 expression levels on CTCs
[0159] As shown in this example, immunofluorescence-based assays were able to demonstrate robust detection of STEAP1 on the surface of CTCs, as well as a reduction in the total number of CTCs and STEAP1+CTCs following treatment.
[0160] Samples were processed and analyzed using the four-channel Epic CTC platform as described herein. Blood samples were collected from 42 patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) before and after treatment with STEAP1-ADC. After Epic Sciences receives a patient blood sample, the whole blood is lysed and the nucleated cells (approximately 3x10 per slide 6 ) were deposited on microscope slides and frozen at -80°C until analysis. After thawing, slides were stained with an antibody cocktail containing cytokeratin, CD45, DAPI, and 15A5 anti-STEAP1 antibody for assessment of this protein biomarker expression on CTCs. CTCs were iden...
Embodiment 2
[0162] Example 2: Evaluation of ADC Prognosis and Efficacy Using CTC Assays
[0163] Sixty patients with progressive mCRPC received STEAP1-ADC at doses ranging from 0.3-2.8 mg / kg every three weeks. ADC activity was measured by PSA decline and study time >6 months. At ≥2 mg / kg doses, a ≥50% decrease in PSA was observed in 10 / 45 (22%±12.1) patients. ADC activity was most pronounced in patients with IHC 3+ tumors. At ≥ 2 mg / kg, 20 / 45 (44% ± 14.5) patients had unfavorable ≥ 5 CTC counts per 7.5 mL at baseline and were considered evaluable. After the first treatment cycle, unfavorable to favorable CTC count transitions were observed in 11 / 20 (55%±21.8) patients and were significantly associated with PSA decline (Spearman rank r=0.74). By FACS, CTCs showed a readily detectable STEAP1+ signal in EpCAM+ / CD45- events in 14 / 29 samples (49%±31-66%). STEAP1+ events showed an EpCAM+ / CD45- signature ranging from 0-74%, and FACS sorted EpCAM+ / CD45- events demonstrated STEAP1+ RT-PCR expr...
Embodiment 3
[0165] Example 3: Signal amplification protocol increases the dynamic range of the STEAP1 CTC assay.
[0166] STEAP1 signaling was measured in SKBR3 (STEAP1 negative control) and LnCaP (STEAP1 positive control) prostate cancer cell lines in the presence and absence of the amplification protocol ( Figure 9A and 9B ). The cutoff for STEAP+ samples was a signal of >3 when using the non-amplified protocol and a signal >8 when using the amplified protocol. The non-amplified protocol shows a 7.6-fold increase in signal in the LnCaP (positive control) cell line compared to the SKBR3 (negative control) cell line. Scale-up scheme showing a 25-fold increase in signal in the LnCaP (positive control) cell line compared to the SKBR3 (negative control) cell line ( Figure 9A ). For the LnCaP (positive control) cell line, STEAP1 signal amplification resulted in an 8.1-fold increase in mean STEAP1 signal, while only increasing the background (i.e., SKBR3 negative control signal) by 2.4-f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com