Method of Using Non-Rare Cells to Detect Rare Cells
a rare cell and non-rare cell technology, applied in the field of rare cell detection, can solve the problems of inability to fully understand the behavior of the tumor, research to fully, and lack of easily accessible and reliable experimental tools, so as to minimize bias, minimize background staining, and maximize signal/background
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
CTC Assay and Identification of CTC Subpopulation
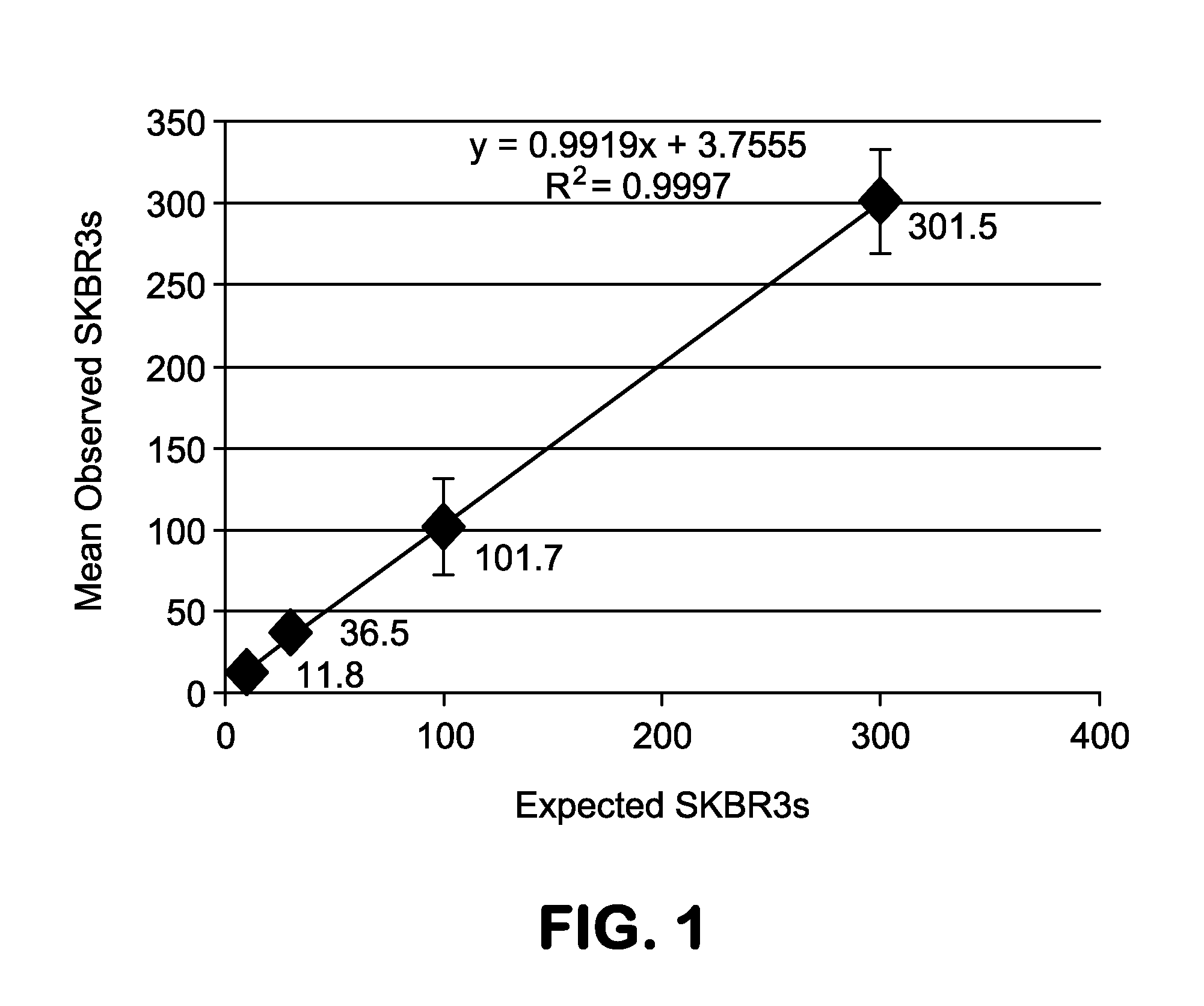
[0117]The data presented here demonstrate the methodology of the present invention as applied to CTCs and subpopulations of CTCs, such as HD-CTCs as defined herein. The assay is performed via a controlled prospective protocol to address the reliability and robustness of the assay as well as a split sample comparison with the Cellsearch®. After this technical validation, the assay was used to investigate the incidence and prevalence of CTCs and specific CTC subpopulations in patients with metastatic breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancers as well as normal controls. The specific subpopulation of CTCs targeted by the assay requires that the cell(s) have an intact nucleus, express cytokeratin and not CD45, are morphologically distinct from surrounding white blood cells (WBCs) and have cytologic features consistent with intact malignant epithelial cells suitable for downstream analysis.
[0118]The following methods and protocols were utili...
example 2
[0152]CTC Assay and Identification of Rare Cell Populations
[0153]The data presented here demonstrate identification of putative rare cell populations. Using the methodology described herein, a putative rare cell population was identified. Sample processing and imaging was performed as disclosed in Example 1. Additionally, HD-CTCs were identified and defined as in Example 1.
[0154]In performing the assay, no CTCs were assumed to be cytokeratin positive. A putative rare cell population was identified having the following characteristics: a) cytokeratin dim or negative; b) CD45 negative; and c) intact non-apoptotic appearing nucleus by DAPI imaging. FIG. 5 displays the incidence rate of the putative rare cell population across patients relative to identified HD-CTCs.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com