Method for identifying natural antigen peptide extracted from tissue by using HLA-I candidate peptide library
A technology of HLA-I and natural antigen, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of high cost, unfavorable clinical promotion, large search space, etc., achieve high clinical practical value, and improve the effect of identification accuracy and efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] A method for identifying natural antigen peptides extracted from tissues using HLA-I candidate peptide libraries, comprising the following steps:
[0047] S1: Construction of HLA-I candidate peptide library;
[0048] S2: High-throughput mass spectrometry identification of HLA-class I molecule-related peptide complexes;
[0049] S3: Identify HLA-class I molecule-related peptide complexes based on the HLA-I candidate peptide library;
[0050] S4: identifying the HLA-I genotype of the sample;
[0051] S5: screening HLA-class I molecule-related immune peptide groups based on the binding ability of candidate peptides to HLA-class I molecules.
[0052] At present, there is no dedicated database for the identification of HLA-I molecule-related immune peptide groups, and the conventional protein database used for proteomics identification is still used. In the identification, there are high false positive data, high atypia and invalid identification, which seriously interfere...
Embodiment 2
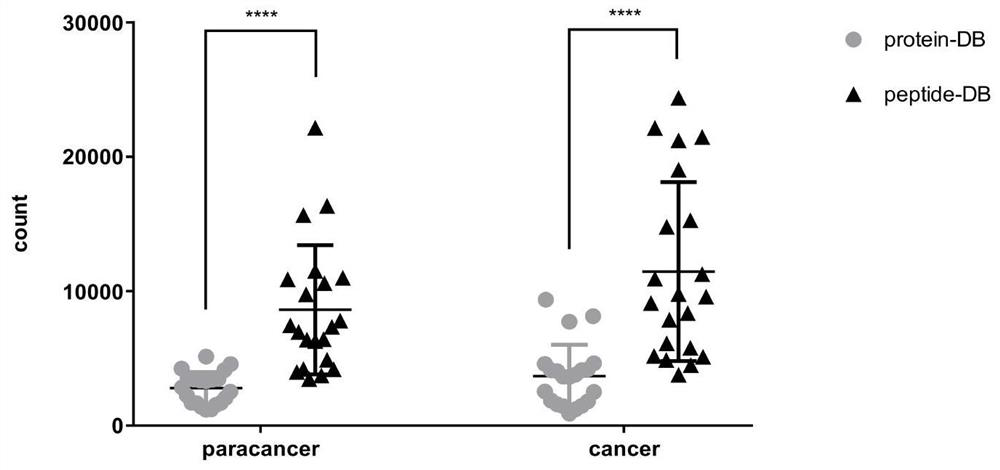
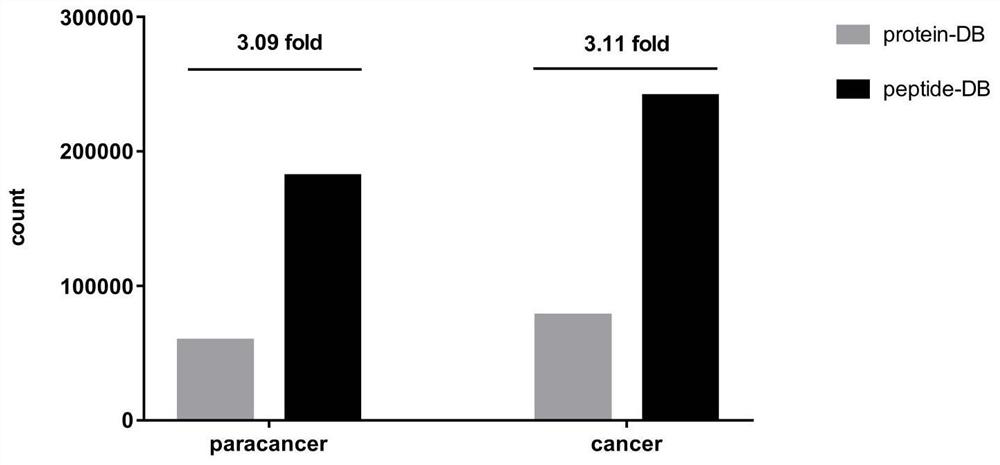
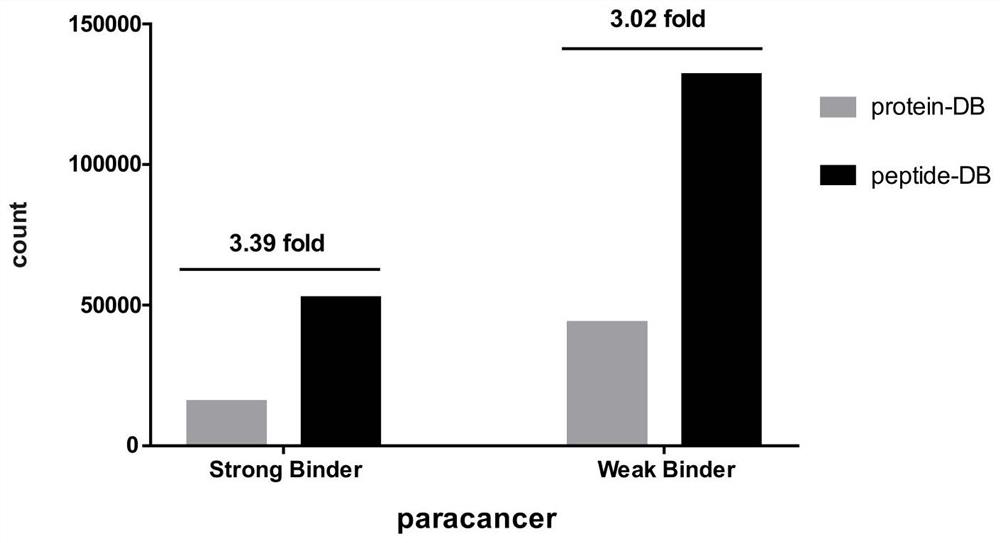
[0094] In order to verify the advantages of using the HLA-I candidate peptide library to identify HLA class I molecule-related immune peptide groups, the HLA class I molecule-related peptide complexes extracted by immunoaffinity purification were identified by traditional proteomics mass spectrometry methods and The method of the present invention conducts identification respectively, and statistically compares the output results of the two databases.
[0095] HLA-class I molecule-related peptide complex sample information
[0096] Sample source: HLA-class I molecule-related peptide complexes are directly extracted from human cervical cancer tissues and normal cervical tissues by using immunoaffinity purification technology.
[0097] Number of samples: 21 pairs of cervical cancer tissues and corresponding normal cervical tissue-derived HLA-class I molecule-related peptide complexes.
[0098] Identification of HLA class I molecule-associated peptide complexes by high-throughpu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com