Medium access control method for underwater acoustic network with variable number of nodes based on q-learning
A medium access control and underwater acoustic network technology, applied in digital transmission systems, climate sustainability, complex mathematical operations, etc., to achieve high throughput, improve network throughput, and low throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0048] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
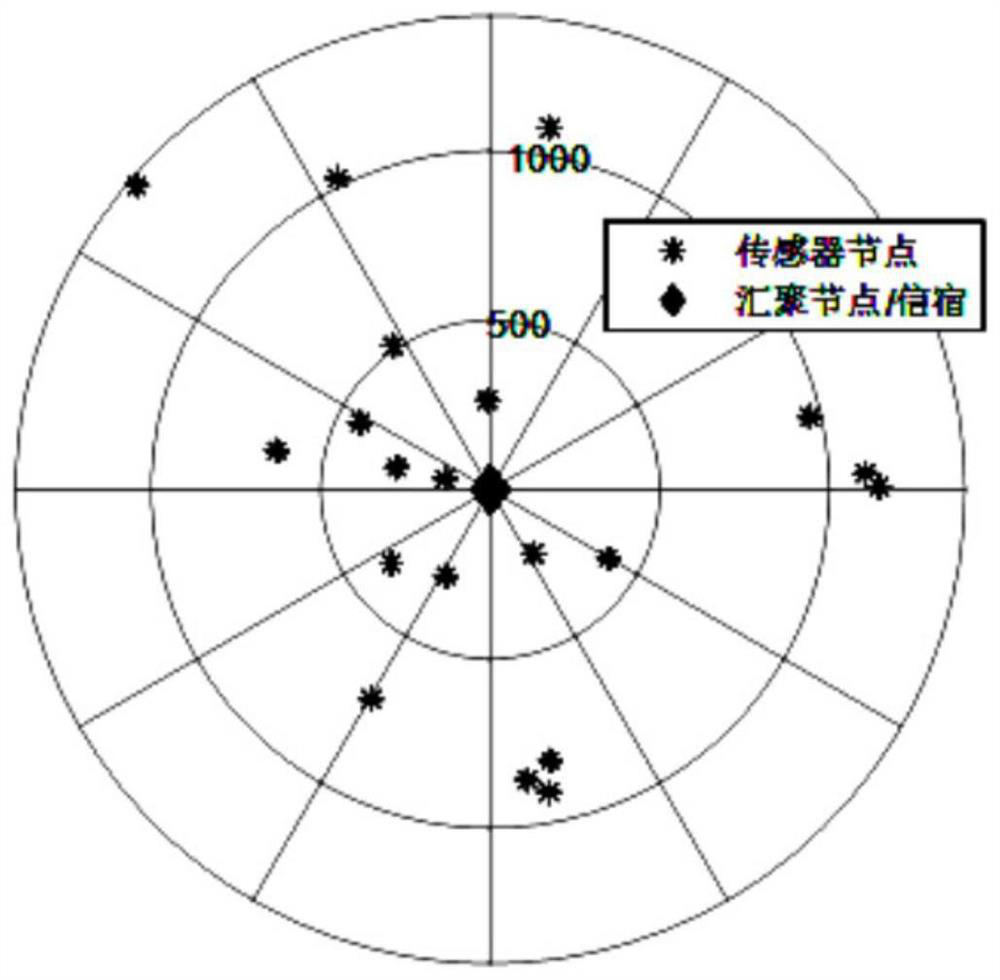
[0049] 1) Consider an underwater acoustic network, including M = 20 sensor nodes (hereinafter referred to as "nodes") and 1 sink (hereinafter referred to as "sink"), such as figure 1 shown. The node perceives information from the ocean environment, and the sink is responsible for collecting the acoustic data perceived by the node.
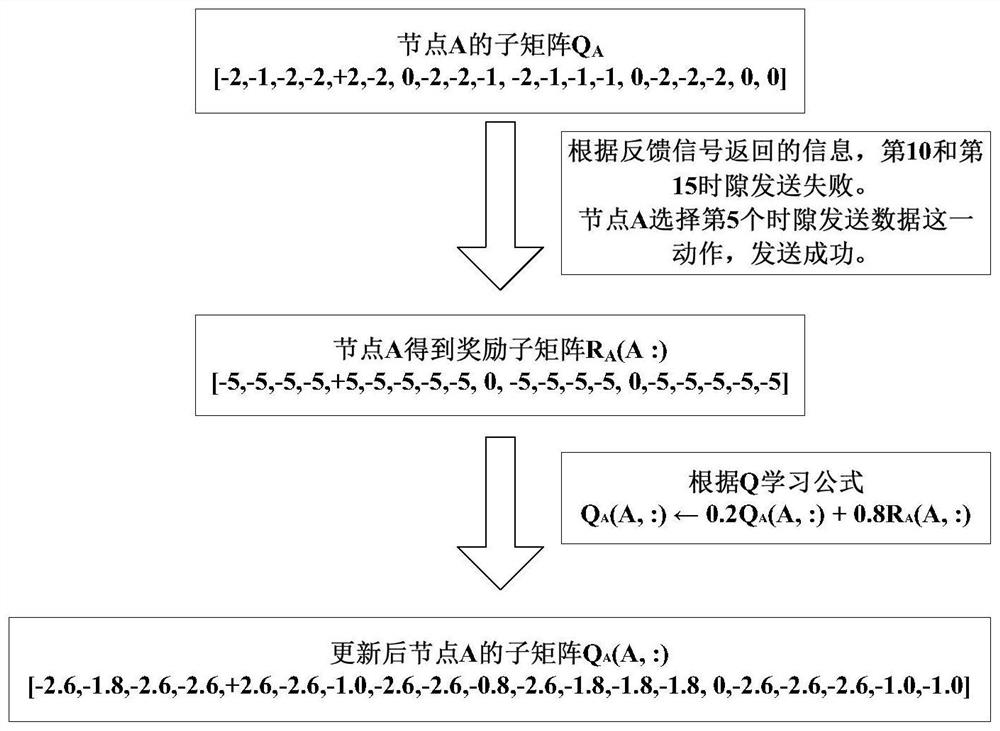
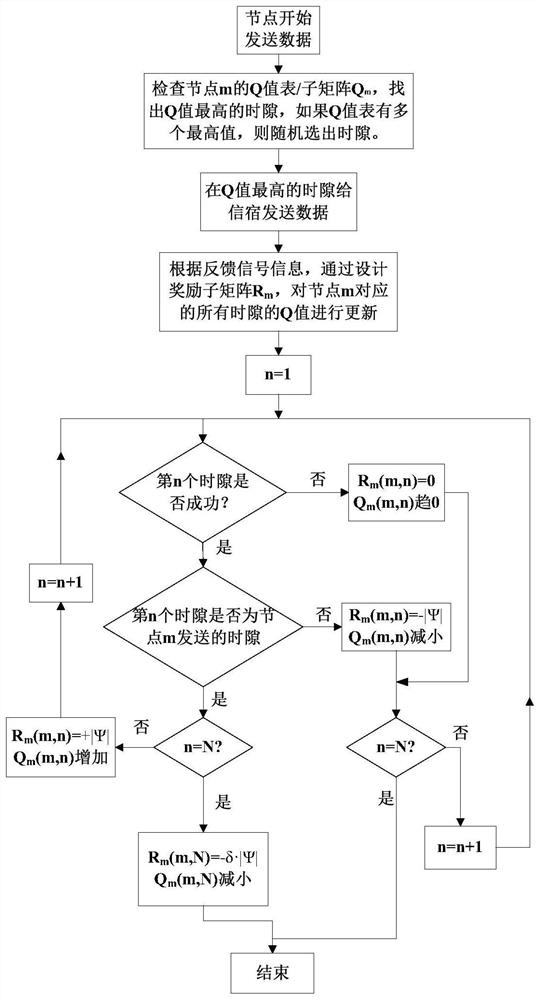
[0050] Assume that the data collection process of the sink is divided into N=20 time slots. To ensure that each node has a time slot to send data to the sink, the number of time slots can be equal to the number of underwater acoustic network nodes. In the Q learning algorithm, the Q matrix applied to media access control is a 20×20 matrix, the row m (m=1,2,...,M) of the Q matrix represents the node serial number, and the column n of the Q matrix (n=1 ,2,...,N) represent the slot number. Q(m,n) represents the Q ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com