Separation equipment and method for micro-plastic in plateau lake sediments
A technology for separating equipment and sediments, applied in centrifuges and other directions, can solve problems such as inconvenience, high cost, and inability to classify and separate microplastics, and achieve the effects of improving accuracy, saving production costs, and improving filtering effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
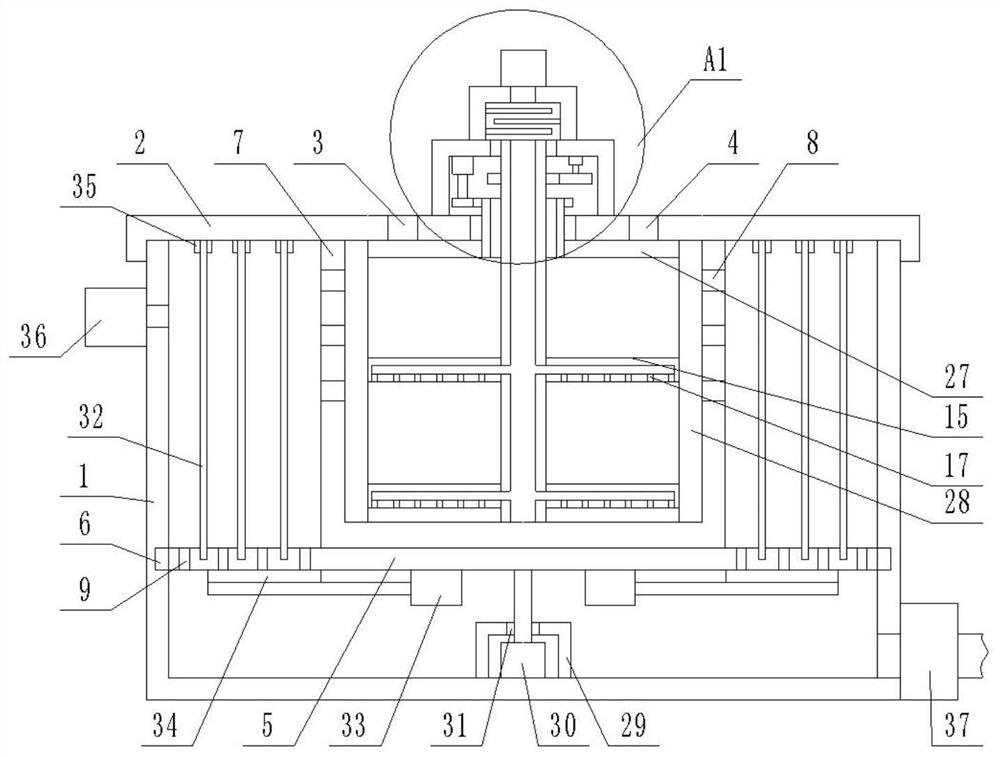
[0035] refer to Figure 1-2 , this embodiment discloses a separation device for microplastics in plateau lake sediments, including: a separation cylinder 1, the top surface of the separation cylinder 1 is open, and the top surface of the separation cylinder 1 is detachably connected with an end cover 2, the end cover 2 There is a stirring device on the top, the top surface of the end cover 2 is provided with a ventilation hole 3 and a feeding hole 4, and the end cover 2 is provided with a centrifugal device;
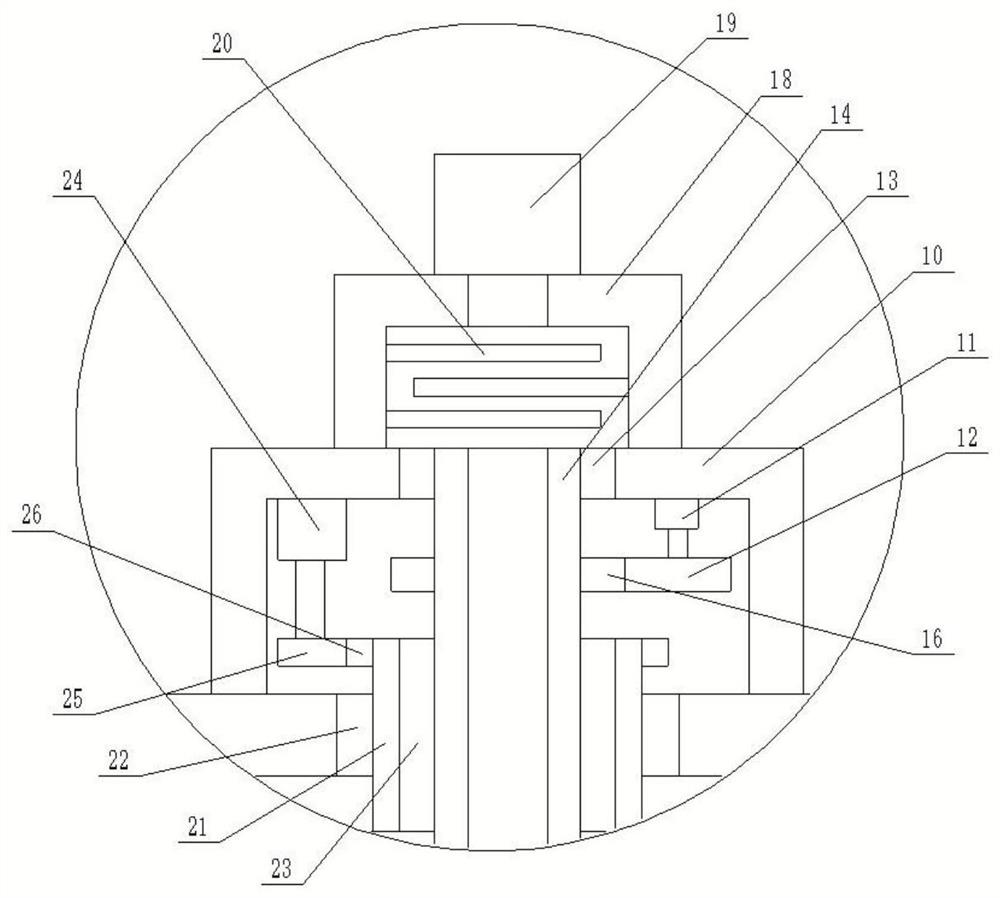
[0036] The centrifugal device includes a rotating mechanism, the rotating mechanism is arranged at the bottom of the inner cavity of the separation cylinder 1, and the top surface of the rotating mechanism is fixedly connected with a centrifugal plate 5, and a first sealed bearing 6 is arranged between the peripheral wall of the centrifugal plate 5 and the inner wall of the separation cylinder 1, and the centrifugal plate 5 The bottom surface and the bottom of the inner ...
Embodiment 2
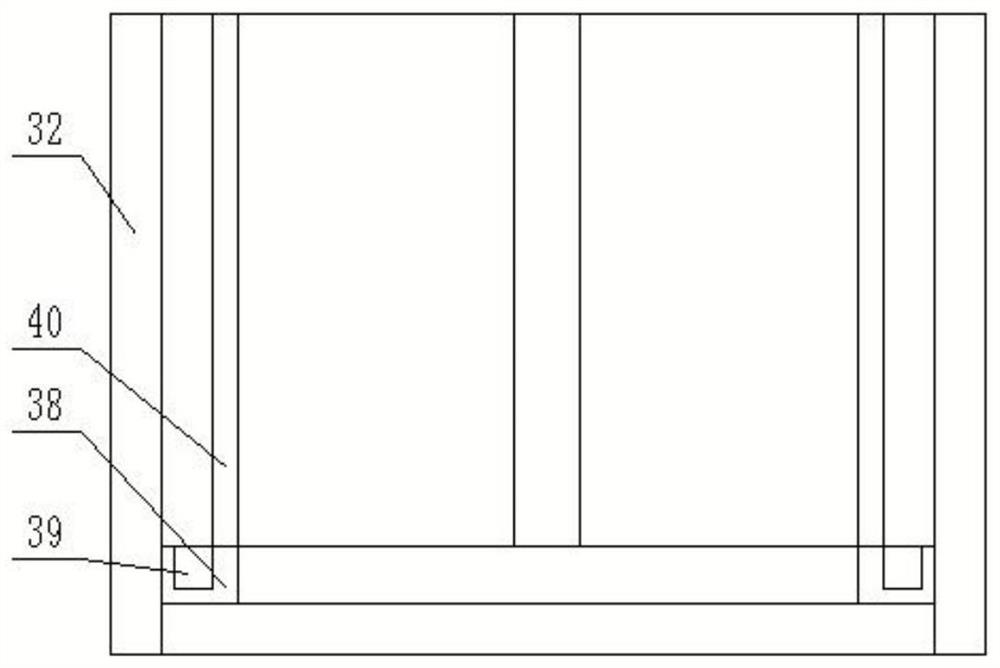
[0067] refer to Figure 3-4In order to facilitate the collection of microplastic particles attached to the annular filter screen 32 after completing the filtration, a collection mechanism is provided. The collection mechanism includes a collection ring 38, the outer wall of the collection ring 38 abuts against the bottom of the inner wall of the annular filter screen 32, and the collection ring 38 An annular collection groove 39 is provided on the top surface, and a plurality of lifting rods 40 are fixedly connected to the top surface of the collection ring 38;
[0068] After the filtration is completed, take out the annular filter 32 and the collection mechanism, pull the lifting rod 40 upward, and during the upward movement of the collection ring 38, the microplastic particles attached to the annular filter 32 will be collected and stored in the annular collection tank 39 , improving the collection efficiency of microplastic particles.
Embodiment 3
[0070] refer to Figure 5 , the set mud pumping mechanism includes a mud pumping shell 41 consolidated on the top surface of the rotating shell, and a mud pumping pipe 42 is arranged in the mud pumping shell 41, and one end of the mud pumping pipe 42 is connected to the rotary motor 30 is fixedly connected to the output shaft, the top of the mud pumping pipe 42 passes through the top surface of the mud pumping shell 41 and communicates with the bottom of the inner cavity of the centrifugal cylinder 7, and the mud pumping pipe 42 is fixedly connected to the centrifugal plate 5 A first dredging pump 43 is fixedly connected to the top of the cavity of the dredging pipe 42, and one end of a dredging tube 44 is communicated with the side of the dredged shell 41, and the other end of the dredged tube 44 runs through the separation cylinder 1. The outer wall communicates with the second dredge pump 45.
[0071] After the supernatant is extracted, the microplastic separation test is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com