Method for improving meat performance of beef cattle by using EDG1 gene
A gene and beef cattle technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of poor fat deposition, slow growth rate of Qinchuan cattle, and low meat production, and achieve the effect of improving meat production performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
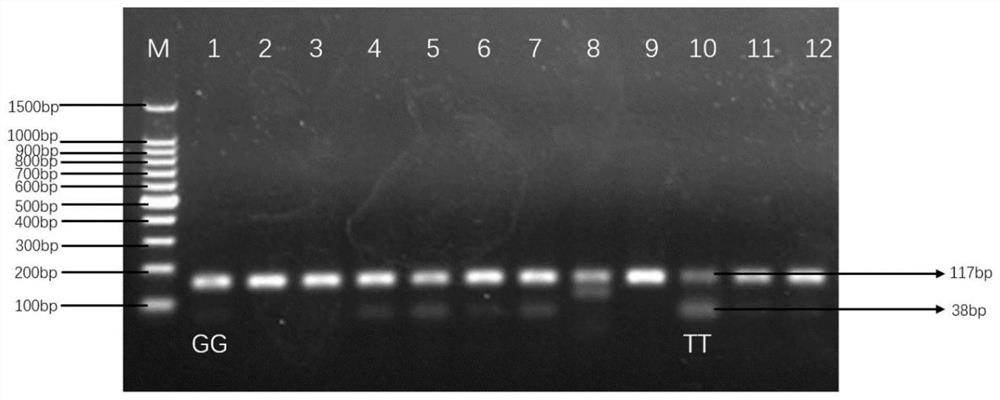
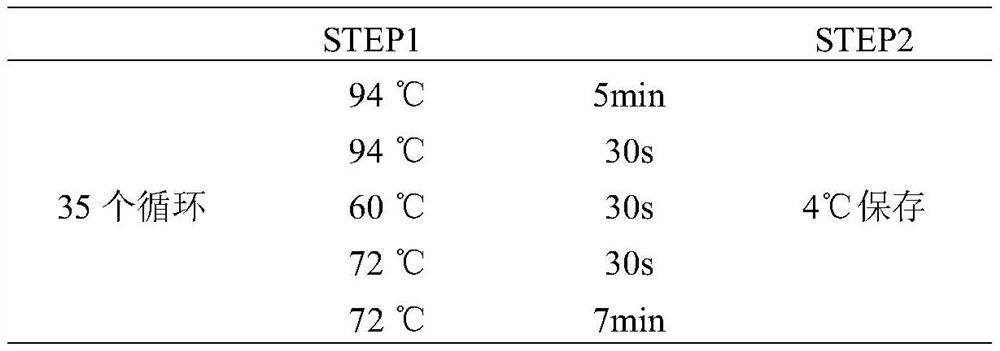
[0027] Example 1 Obtaining SNP Detection Fragments of Qinchuan Cattle and Chinese Simmental Cattle EDG1 Gene and Establishment of Polymorphism Site Detection Method
[0028] 1. Extraction of Genomic DNA from Qinchuan Cattle and Chinese Simmental Cattle
[0029] The test cattle of the present invention are 350 Qinchuan adult cows (age 18-24 months old, at least three generations unrelated) of the National Beef Cattle Improvement Center of Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, and 260 Chinese Ximen cows of Chifeng Shengquan Ecological Animal Husbandry Co., Ltd. Tahr cattle (age 14-18 months). The genomic DNA of Qinchuan cattle and Chinese Simmental cattle was extracted using the blood genomic DNA extraction kit produced by Beijing Tiangen Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., and the specific steps refer to the kit instructions. Evaluate the quality and quantity of the extracted DNA, evaluate it by agarose gel electrophoresis, and store it at -40°C for future use.
[0030...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2 Detection of polymorphic distribution of molecular markers in Qinchuan cattle, Chinese Simmental cattle and other local beef cattle breeds
[0045] The genetic diversity of EDG1 gene g.42041062G>T site was detected in 7 cattle populations, and the detection results are shown in Table 3.
[0046] Table 3 The genotype frequency and allele frequency of EDG1 gene g.42041062G>T locus in cattle population
[0047]
[0048] Note: QC, Qinchuan cattle; LX, Luxi cattle; MGC, Mongolian cattle group (Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China); MGG, Mongolian cattle group (Mongolia); WL, Wuling cattle; LL, Longlin cattle; CS, China Simmental.
[0049] From the results in Table 3, it can be seen that the genotype frequencies of the g.42041062G>T site of the Chinese Qinchuan cattle EDG1 gene are: TT (0.034), GT (0.237), GG (0.729), and the G allele frequency (0.847) is higher than T allele frequency (0.153); Chinese Luxi yellow cattle, Chinese Inner Mongolia Mongolian cat...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3 Investigation of the relationship between g.42041062G>T molecular markers and meat performance of Qinchuan cattle and Chinese Simmental cattle
[0051] In order to determine whether the g.42041062G>T site of the EDG1 gene is related to the difference in meat performance between Qinchuan cattle and Chinese Simmental cattle, the method established in Example 1 was used for polymorphism detection, and SPSS 19.0 software was used to analyze c.*188G >The correlation between the three genotypes of A site and the meat performance of Qinchuan cattle and Chinese Simmental cattle.
[0052] The mathematical model adopted is: Y ijklm =μ+G i +A j +F k +S l +S m +e ijklm ;
[0053] Among them, Y ijklm is the observed value of the trait, μ is the average value of the trait, G i is the genotype effect, A j is the fixed effect caused by age, F k is the pasture environmental effect, S l is the gender effect, S m is the family effect, e ijklm is a random error.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com