Analysis method and device for detecting point mutations based on third-generation sequencing data
A technology for sequencing data and analysis methods, applied in sequence analysis, genomics, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as long running time, limited sequencing quality data distribution, and inability to meet point mutation detection well
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
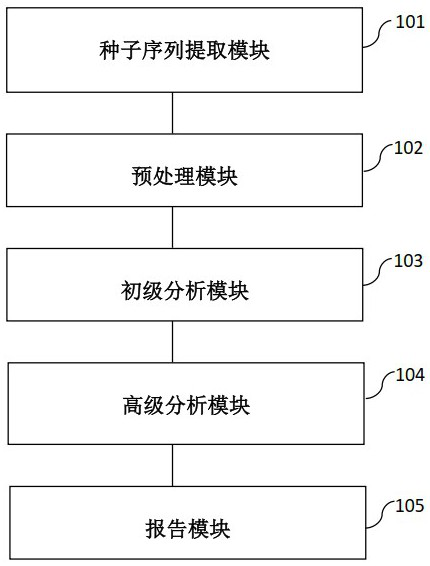
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
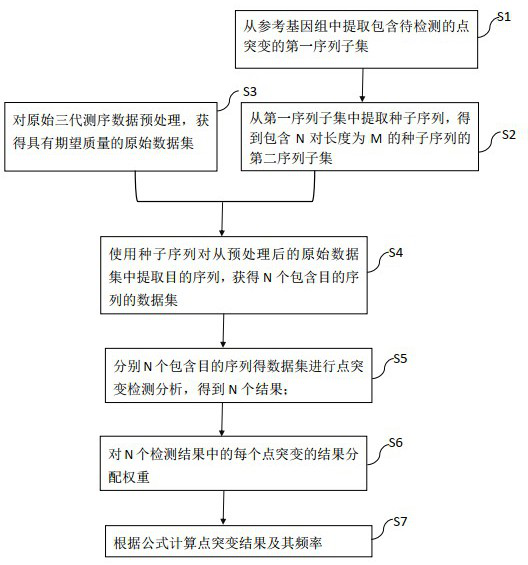
[0092] Example 1 Analysis of data using the method of the present invention
[0093] 1. will contain BRAF-V600E, EGFR-L858R, EGFR-T790M, KRAS-G13D as well as AKT1-E17K The standard sample and the standard sample of the negative control sample NA12878 were prepared by the experimental library and repeated three times. The nanopore sequencer of QNome-9604 was used for sequencing, and 6 original long-read sequencing data were obtained, including HUM964, HUM965 and HUM966 For positive control data, HUM967, HUM968 and HUM969 for negative control data.
[0094] 2. Extract 9 short sequences with a fixed length of 101 bp on the genome for the 5 target sites to be detected in step 1 according to their positions, wherein the positions of the target sites on the extracted short sequences are respectively fixed on the first 11 bases, 21 bases, 31 bases, 41 bases, 51 bases, 61 bases, 71 bases, 81 bases and 91 bases base (ie D=10bp), to obtain the final set of 9 short-sequence fragme...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com