Method for inducing muscle stem cell expansion
A technology of muscle cells and stem cells, applied in the material field of inducing the expansion of adult muscle stem cells, which can solve the problems of insufficient donor cells, loss of damage repair, loss of stemness of muscle stem cells, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
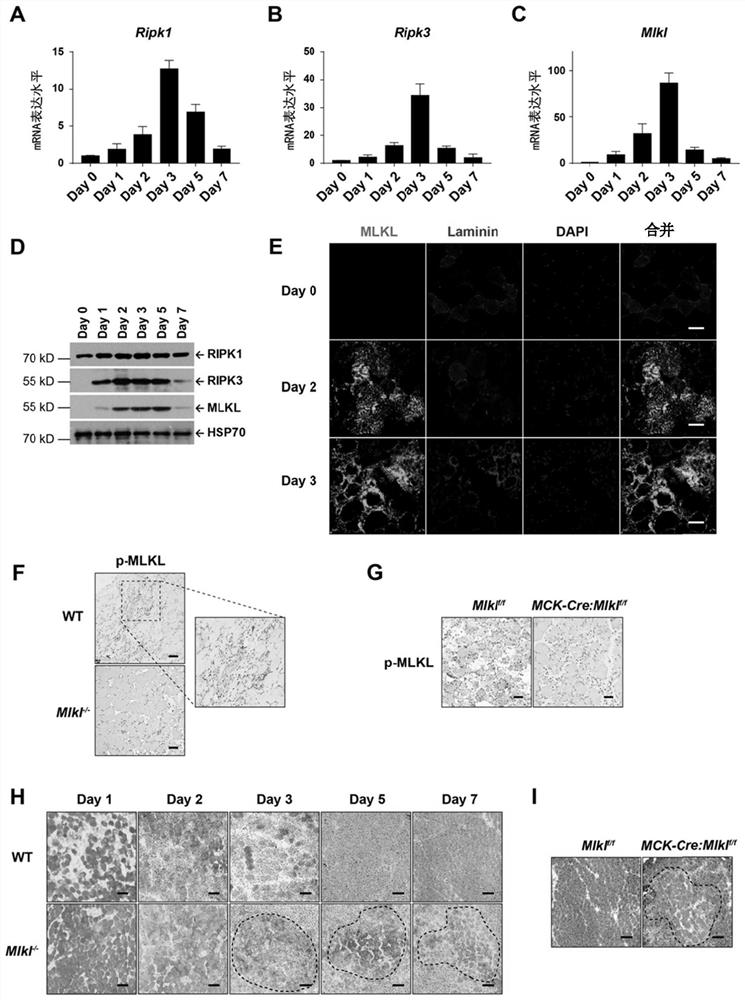
[0235] Example 1. After acute muscle injury, RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL is highly expressed in muscle fiber cells and programmed necrosis occurs.
[0236] In the process of muscle degeneration after muscle injury, myofiber cells undergo necrosis (Chargé and Rudnicki, 2004). We established an acute injury model of tibialis anterior muscle by injecting cardiotoxin (CTX), so as to study whether necroptosis is involved in the repair process of muscle tissue injury. CTX is a polypeptide isolated from snake venom, which can cause severe contraction of muscle fiber cells by excessively activating nerves, resulting in depolarization of muscle fiber cells and damage to cell membranes, resulting in muscle damage (Chargé and Rudnicki, 2004; Shiau et al. ,1976). It is widely used in the study of skeletal muscle regeneration (Garry et al., 2016; Hardy et al., 2016).
[0237] The modeling method was to inject a total of 100 μl of CTX solution with a concentration of 10 μM into the tibialis anterior...
Embodiment 2
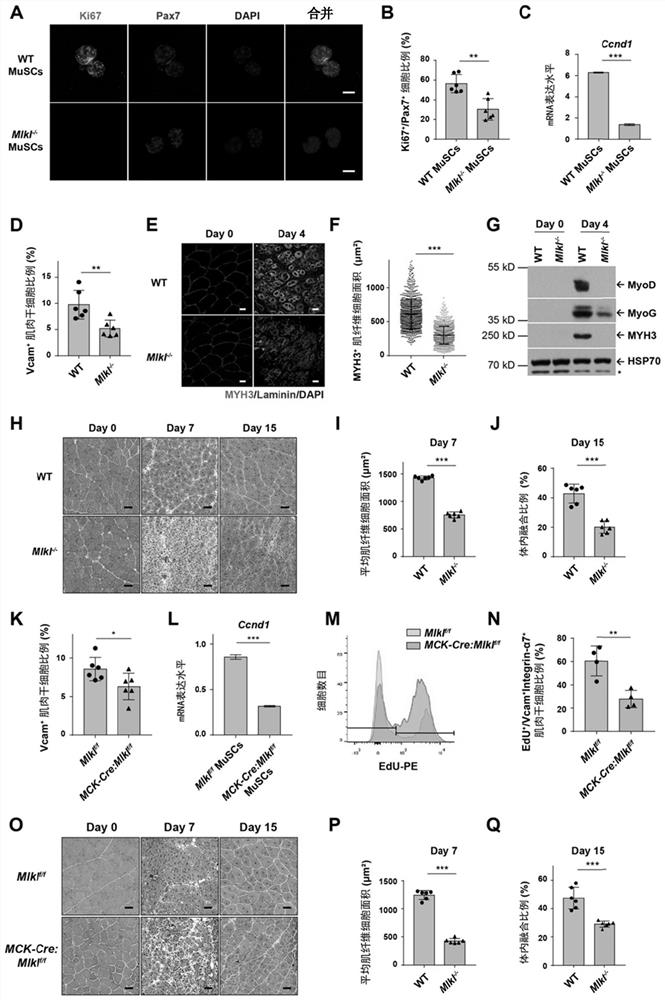
[0241] Example 2. The absence of programmed necrosis in muscle fiber cells affects the proliferation of muscle stem cells and the process of muscle injury repair.
[0242] In order to further investigate the effect of the blockage of myofibroblast necrosis, we compared the wild-type and Mlkl after muscle injury by FACS analysis. - / - Differences in the proportion of mouse muscle stem cells. On the 3rd day after muscle injury, the muscle stem cells were selected for immunofluorescence staining, and the results were shown in Mlkl - / - Ki67 in mouse + Pax7 + The proportion of cells also decreased ( figure 2 , A-B). Real-time quantitative PCR showed that the cell cycle protein Cyclin D1 in Mlkl - / - Compared with wild-type mice, the mRNA level in mouse muscle stem cells was significantly lower, indicating that the degree of expansion of muscle stem cells was significantly different from that of wild-type mice ( figure 2 , C-D), implying that Mlkl - / - Muscle stem cells prolif...
Embodiment 3
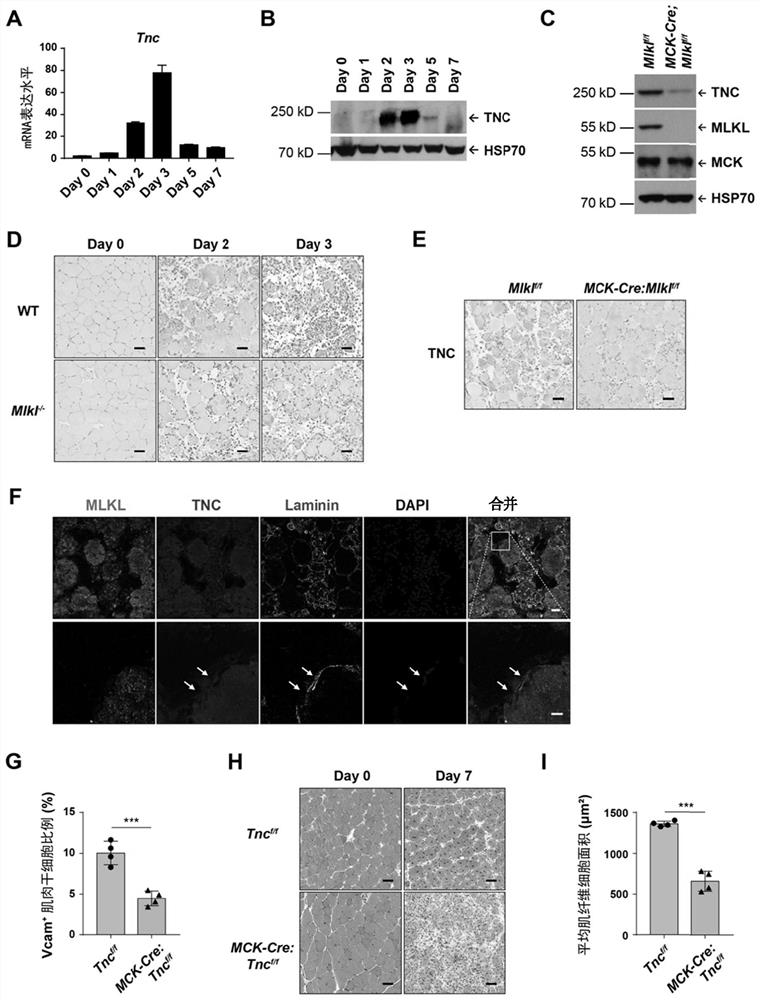
[0245] Example 3, muscle fiber cells with programmed necrosis highly express TNC and release it outside the cells to promote the proliferation of muscle stem cells.
[0246] Through a series of in-depth studies, the inventors found that muscle fiber cells undergoing programmed necrosis can promote the rapid proliferation of muscle stem cells after injury by releasing tenascin C. There is almost no mRNA expression of Tnc in normal TA. The results of real-time quantitative PCR and immunoblotting showed that the mRNA and protein levels of Tnc in TA were significantly increased after CTX injury ( image 3 , A-B). Consistent with it, the results of TNC immunohistochemical staining after TA injury showed that there was no expression of TNC in normal muscle fiber cells, but the expression of TNC was significantly increased in the damaged muscle fiber cells with swelling morphology after injury in wild-type mice ( image 3, D, upper row). After 3 days of CTX injury in wild-type mic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com