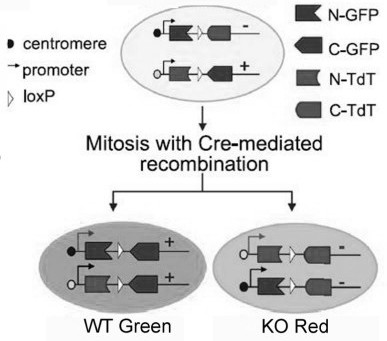
Method for marking adjacent astrocytes
A technology for labeling astrocytes, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as difficult promotion and use, low efficiency of dual fluorescent labeling, and high technical difficulty, and achieve improved labeling efficiency, strong proliferation and migration capabilities, and low technical difficulty Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
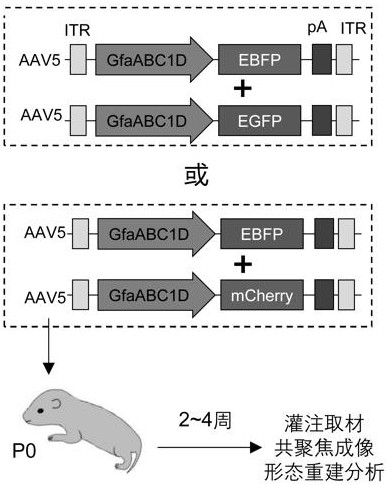
[0037] Plasmid construction and viral packaging.
[0038] Backbone plasmid: pAAV2-GfaABC1D-mRuby3-WPRE-pA (Shanghai Taiertu Biotechnology Co., Ltd., No. S0790-P), in which the GfaABC1D promoter is the human glial-derived acidic protein promoter, that is, the astrocyte-specific promoter ; mRuby3 is a red fluorescent protein; WPRE is a post-transcriptional regulatory element, which can enhance the expression of the target gene; pA is a poly A tail, which can enhance the stability of the target gene in cells.
[0039] Plasmid construction: Digest the backbone plasmid with BamHI and NotI: pAAV2-GfaABC1D-mRuby3-WPRE-pA (No. S0790-P), recover the linearized vector, and use the S0254-P (pAAV2-CAG-EBFP-WPRE-pA) plasmid As a template, the EBFP sequence fragment was amplified, and the EBFP sequence was seamlessly cloned into a linear vector to construct the pAAV2-GfaABC1D-EBFP-WPRE-pA plasmid. Using the same method, use pAAV2-hSyn-EGFP-WPRE-pA (No. S0237-P) as a template to amplify the...
experiment example 1
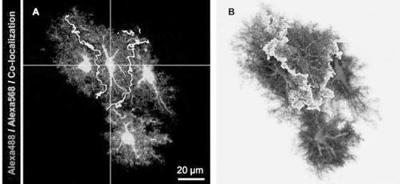
[0046] Astrocytes were labeled in the manner of Example 1, and obtained as follows Figure 4 image shown.
[0047] like Figure 4 As shown, there are labeled astrocytes on the coronal brain slice of the mouse, among which there are a large number of EBFP (purple), EGFP (green) and EBFP / EGFP double positive (white) labels in the cortex, thalamus and hypothalamus Star glue, in Figure 4 The white arrows in indicate the adjacent astrocytes labeled with EBFP and EGFP, respectively, indicating that the method of Example 1 can effectively label the adjacent astrocytes.
Embodiment 2
[0049] This example uses the same experimental method as Example 1, the difference is that the fluorescent protein combination used in this example is EGFP and mCherry, because mCherry has high photostability, but it is easy to aggregate, which is not conducive to the display of astrocytes Therefore, it is rarely used in the prior art for labeling astrocytes. In this example, AAV5-GfaABC1D-EGFP and AAV5-GfaABC1D-mCherry through plasmid construction and virus packaging Dilute to 2~5×10 11 vg / mL, mixed at a volume ratio of 2:1 and combined for injection.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com