Mixed-solvent-resistant rubber material, preparation method and surface treatment method thereof
A technology of rubber materials and mixed solvents, which is applied in the field of mixed solvent-resistant rubber materials and their surface treatment, which can solve the problems of unsatisfactory liquid resistance and achieve the effects of reducing rubber swelling, increasing cross-linking density, and reducing penetration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
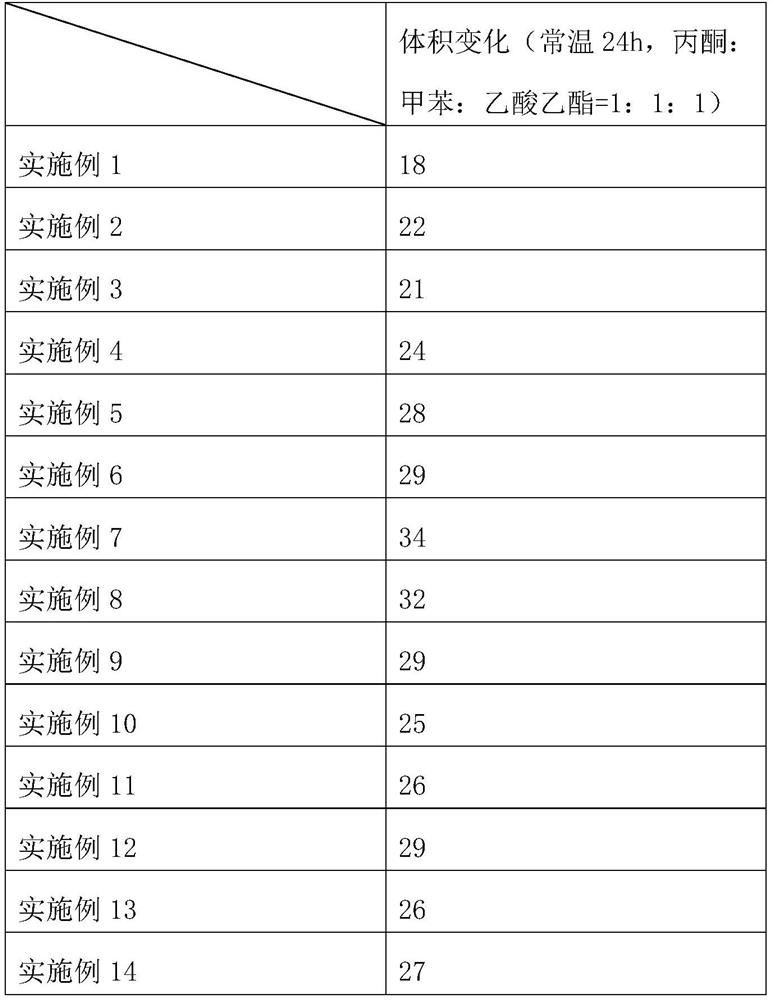
Examples
Embodiment 1
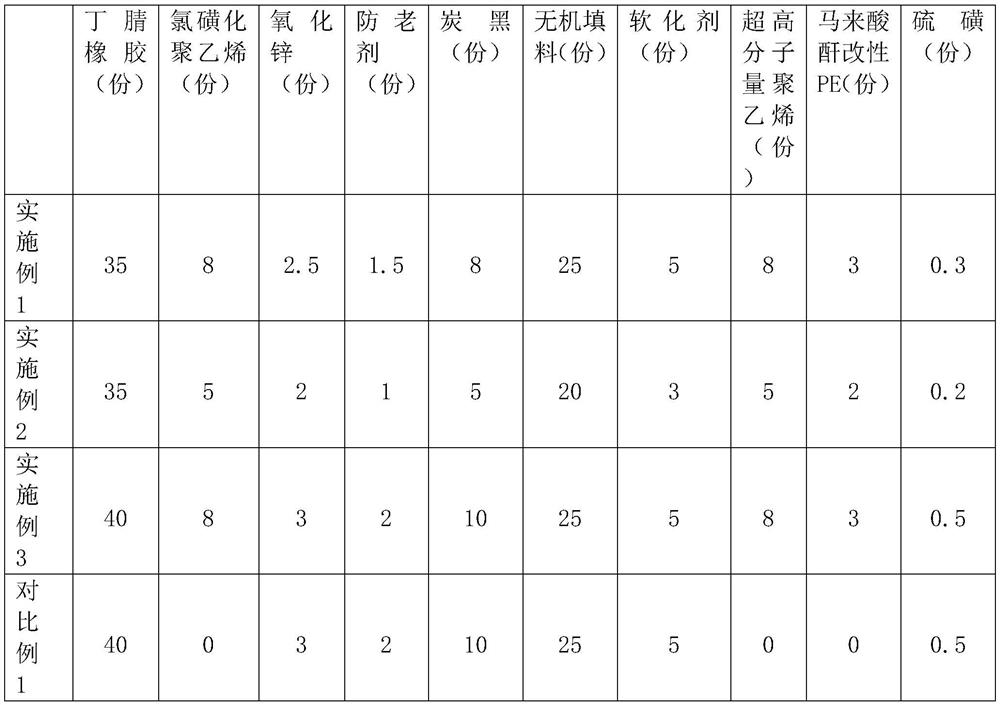
[0032] Summary of the plan: a rubber material resistant to mixed solvents, the rubber material is composed of the following components in parts by weight: 35-40 parts of nitrile rubber, 5-8 parts of chlorosulfonated polyethylene, 2 parts of zinc oxide ~3 parts, 1~2 parts of antioxidant, 5~10 parts of carbon black, 20~25 parts of inorganic filler, 2~3 parts of microcrystalline wax, 3~5 parts of softener, 5~8 parts of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, 2-3 parts of maleic anhydride modified PE, 0.2-0.5 parts of sulfur, and 1-2 parts of accelerator.
[0033] Specifically, 35 parts of nitrile rubber in this embodiment, 8 parts of chlorosulfonated polyethylene, 2.5 parts of zinc oxide, 1.5 parts of anti-aging agent, 8 parts of carbon black, 25 parts of inorganic filler, 5 parts of softening agent, ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene 8 parts of ethylene, 0.3 parts of sulfur, 2.5 parts of microcrystalline wax, 4 parts of softener, 2.5 parts of maleic anhydride modified PE...
Embodiment 2~3
[0041] Embodiment 2~3 and comparative example 1
[0042] The difference between Examples 2-3 and Comparative Example 1 and Example 1 is that the ratio of each component is different, and the composition ratio of the rubber material is shown in Table 1.
[0043] Table 1: The composition ratio of the rubber material in Examples 1 to 3 and Comparative Example 1
[0044]
[0045] Wherein, the rubber materials of Example 2, Example 3 and Comparative Example 1 also include 2.5 parts of microcrystalline wax, 4 parts of softener, 2.5 parts of maleic anhydride modified PE, and 1.5 parts of accelerator.
Embodiment 4
[0047] The difference between Example 4 and Example 1 is that the chlorine content of the chlorosulfonated polyethylene in the rubber material of Example 4 is 80%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com