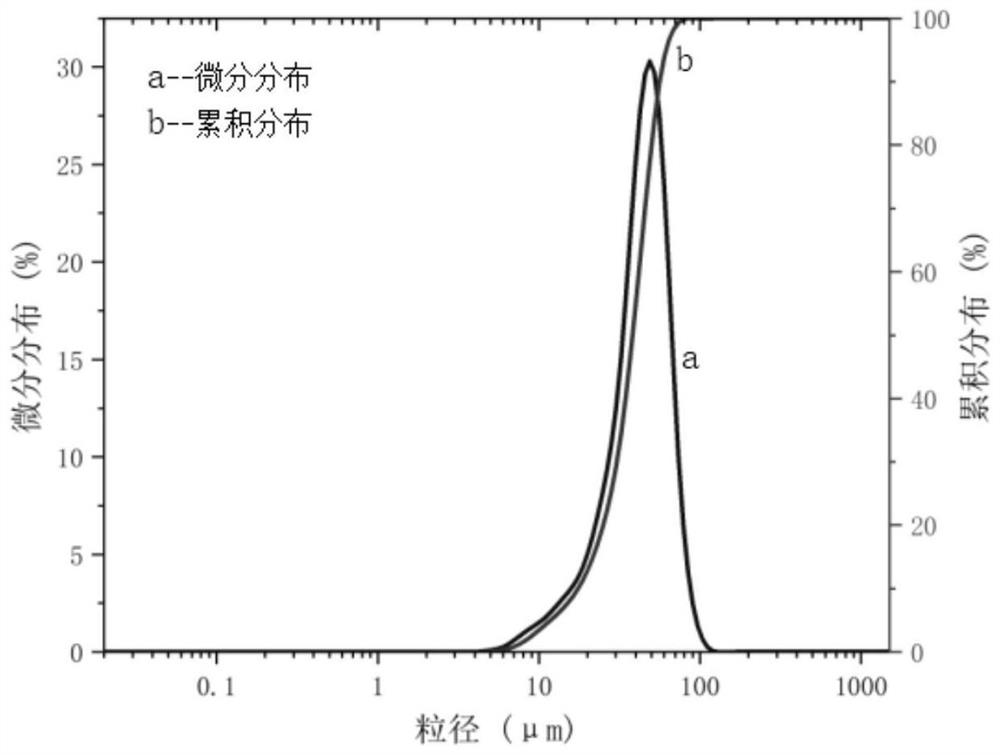
Selective laser melting forming method for TC4 titanium alloy workpiece
A technology of selective laser melting and forming method, which is applied in the direction of additive manufacturing and additive processing, and can solve problems such as poor density and poor surface roughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1: The selective area laser melting forming method of the TC4 titanium alloy parts of the present embodiment is carried out according to the following steps:
[0024] 1. Use 3D modeling software to model parts and process data, and convert it into a data format (STL file) that can be sliced;
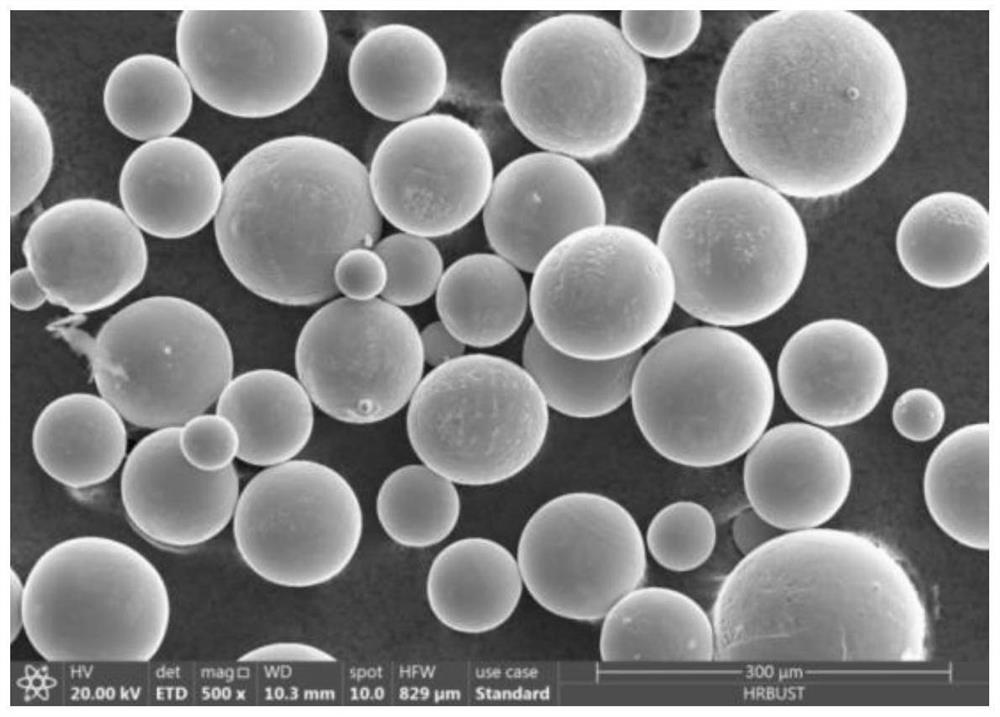
[0025] 2. Create a support at the bottom of the established model, slice the 3D model and the support together to obtain the contour data of the interface of each layer, and import this data into the AFS-M260 metal powder (SLM) 3D printer;
[0026] 3. According to the program, the AFS-M260 metal powder (SLM) 3D printer controls the powder spreading device to spread the powder on the substrate of the forming cylinder according to the powder thickness of 60 μm;
[0027] 4. The laser scanning system scans the molten alloy powder under the conditions of laser power of 300W, scanning speed of 1.5m / s, and scanning distance of 100μm. The molten metal is cooled and solidified t...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the scanning speed in step 4 is 0.9 m / s, and the others are the same as Embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the scanning speed in step 4 is 2.4m / s, and the others are the same as Embodiment 1.
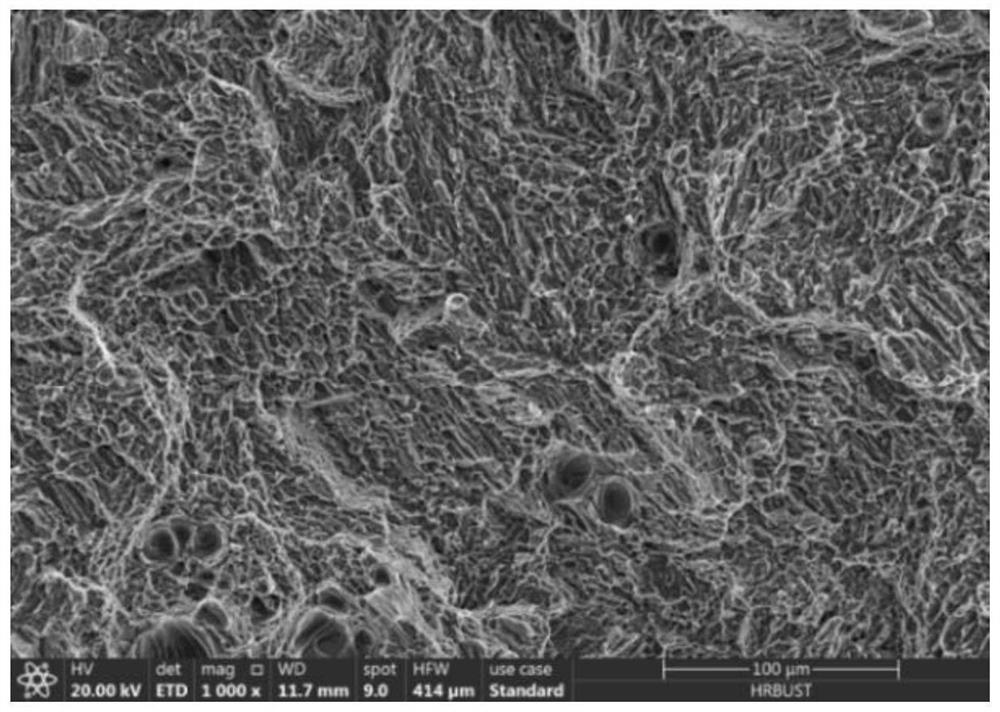
[0039] The compactness of the TC4 titanium alloy parts prepared in Examples 1, 2 and 3 is tested, and the results show that the densities of the TC4 titanium alloy parts prepared in Examples 1, 2 and 3 are respectively 98.98%, 93.7% and 94.5% %. The microstructure figure of the TC4 titanium alloy parts prepared by embodiment 2 is as follows Figure 5 shown, from Figure 5 It can be seen that the holes are seen, and the distribution of these holes is uneven and the size is different. This is because when the scanning speed is low, the laser spot stays on the powder per unit volume for a long time, and the energy absorbed by the powder per unit time is relatively small. High, the melt will appear agglomeration or even overburning, and the metal evaporation caused by high-energy input will generate recoil for...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com