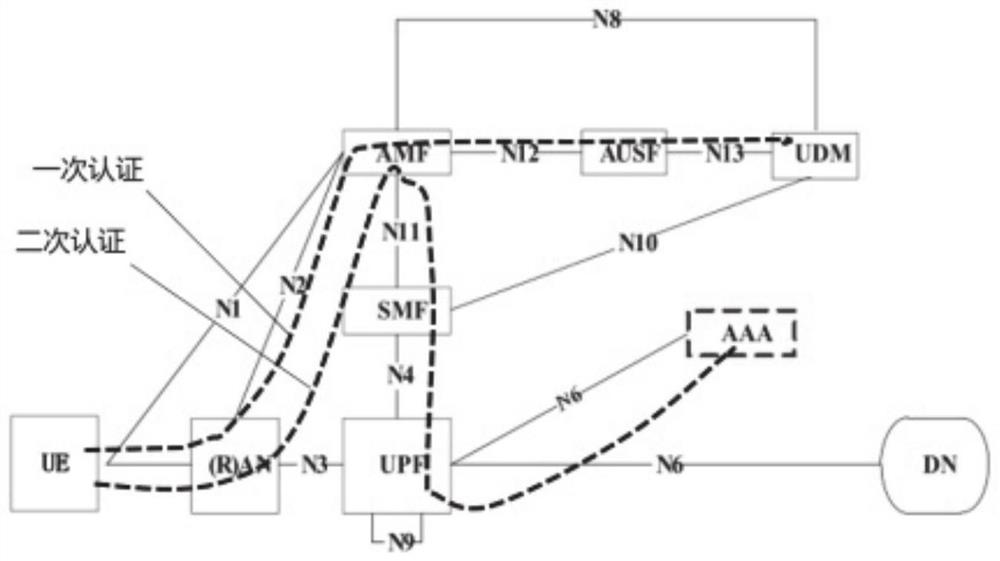
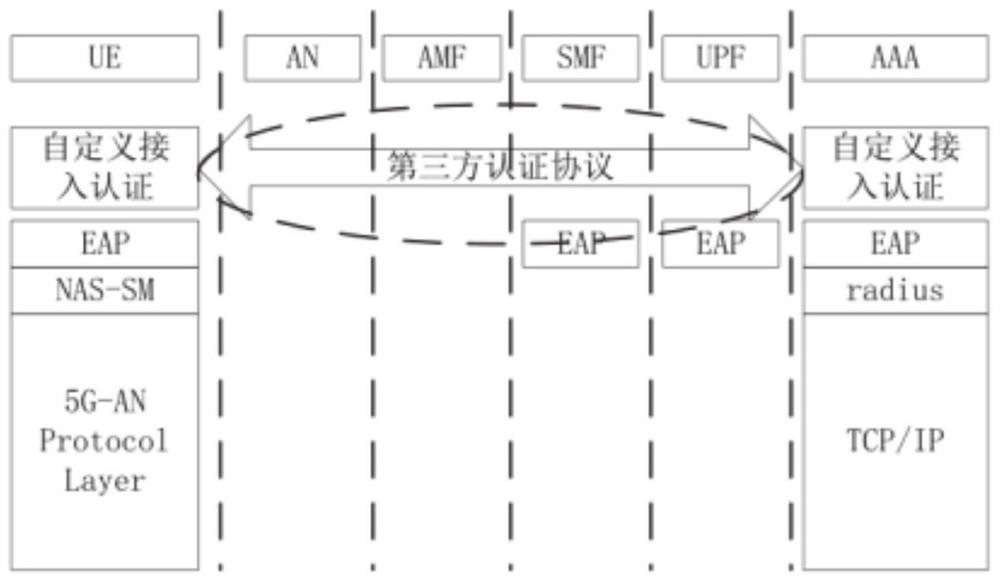
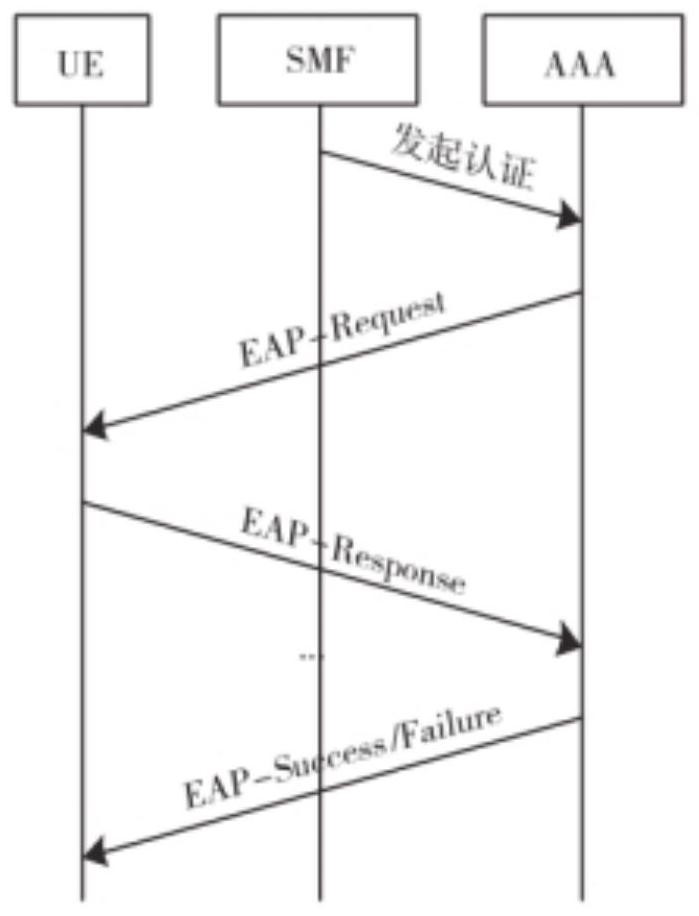
Quantum security-based rapid secondary identity authentication method and system
An identity authentication and security technology, which is applied in the field of fast secondary identity authentication methods and systems, can solve the problems of leakage of user identity information, easy leakage of user identity information, vulnerability to dictionary or offline dictionary attacks, etc., to ensure confidentiality sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0104] A secondary identity authentication method, such as Figure 4 shown, including the following steps:
[0105] Pre-order steps: UE (user equipment) and AAA (authentication server) already have a shared key K; the quantum random number generator (QRNG) on the AAA server side generates a random number R1, and the AAA server generates a serial number N1; UE The quantum random number generator at the end generates a random number R2, and the UE generates a sequence number N2.
[0106] It should be noted that the distribution and delivery of the shared key K can be realized with the help of quantum security service platform and quantum key mobile medium, and the shared key K can be generated by the QKD process or QRNG stored in the quantum security service platform Quantum key (or random number key), the quantum key can be stored in the quantum key mobile medium, so as to realize the offline distribution of the shared key K through the quantum key mobile medium.
[0107] In ...
Embodiment 2
[0152] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that there is only symmetric encryption operation and no hash operation in the authentication process. Although the integrity of the message is not as good as that of Embodiment 1, it does not affect the realization of two-way identity authentication between UE and AAA. higher efficiency. Of course, since no hash function is used, m2, m4, and m5 need to be encrypted for transmission in the authentication process of this embodiment.
[0153] A secondary identity authentication method, such as Figure 5 shown, including the following steps:
[0154] Preparatory work (this step may not be included in some embodiments):
[0155] UE (user equipment) and AAA (authentication server) already have a shared key K; the quantum random number generator on the AAA server side generates a random number R1, and the AAA server generates a serial number N1; the quantum random number generator on the UE side generates A random ...
Embodiment 3
[0193] A fast secondary identity authentication system based on quantum security is characterized in that it includes a server end and a user end, wherein:
[0194] The server end is configured to generate a first message based on a locally generated random number and serial number, and generate a second message based on the generated random number and identity information; encrypt the first message and the second message, Obtain the first ciphertext, and send a message including the first ciphertext and the serial number;
[0195] Receive a message from the client that includes the updated local serial number, the client serial number, and the second ciphertext; verify whether the updated local serial number in the message is reasonable, and if it is reasonable, continue execution; otherwise, send an authentication error message , end the authentication process; decrypt the second ciphertext to obtain the decrypted information, extract the fourth message from it, extract the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com