A method for controlling the machining deformation of long beam parts
A part processing and deformation control technology, applied in metal processing and other directions, can solve the problems of small buffering effect of side bending deformation, the number of stress relief grooves, size constraints, deformation cannot be ignored, etc., to ensure processing quality and reduce side bending The amount of deformation and the effect of reducing artificial intervention points
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
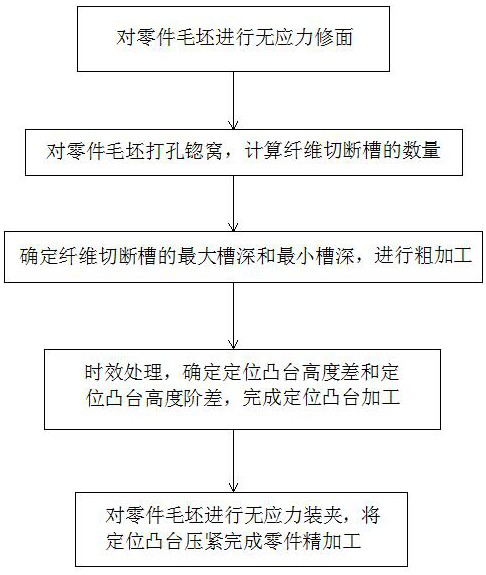
[0054] see Figure 1-Figure 5 , a processing deformation control method for long beam parts, comprising the following steps:
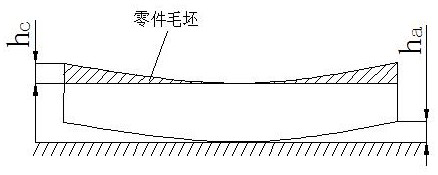
[0055] a. Set the blank of the part horizontally, observe the deformation of the blank of the part, the maximum deformation is h a , and then perform stress-free shaving on the part blank, and the amount of stress-free shaving is , so that h c ≥h a ;
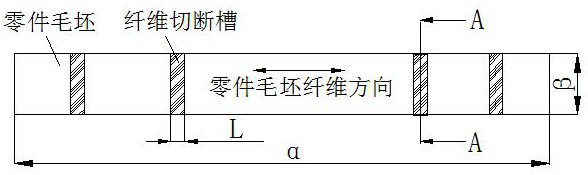
[0056] b. Punch the part blank and countersink, according to the length of the part blank and part blank width Calculate the number n of fiber cutting grooves, and evenly arrange fiber cutting grooves;
[0057] c. According to the maximum groove depth allowance distribution D of the part blank 1 and the minimum groove depth allowance distribution D 2 Determine the maximum groove depth h of the fiber cutting groove e and the minimum groove depth h f , select a tool with a diameter of D for rough machining, and the width of the rough machining fiber cutting groove is L, so that D<L≤2D;
[005...
Embodiment 2
[0062] see Figure 1-Figure 5 , a processing deformation control method for long beam parts, comprising the following steps:
[0063] a. Set the blank of the part horizontally, observe the deformation of the blank of the part, the maximum deformation is h a , and then perform stress-free shaving on the part blank, and the amount of stress-free shaving is , so that h c ≥h a ;
[0064] b. Punch the part blank and countersink, according to the length of the part blank and part blank width Calculate the number n of fiber cutting grooves, and evenly arrange fiber cutting grooves;
[0065] c. According to the maximum groove depth allowance distribution D of the part blank 1 and the minimum groove depth allowance distribution D 2 Determine the maximum groove depth h of the fiber cutting groove e and the minimum groove depth h f , select a tool with a diameter of D for rough machining, and the width of the rough machining fiber cutting groove is L, so that D<L≤2D;
[006...
Embodiment 3
[0071] see Figure 1-Figure 5 , a processing deformation control method for long beam parts, comprising the following steps:
[0072] a. Set the blank of the part horizontally, observe the deformation of the blank of the part, the maximum deformation is h a , and then perform stress-free shaving on the part blank, and the amount of stress-free shaving is , so that h c ≥h a ;
[0073] b. Punch the part blank and countersink, according to the length of the part blank and part blank width Calculate the number n of fiber cutting grooves, and evenly arrange fiber cutting grooves;
[0074] c. According to the maximum groove depth allowance distribution D of the part blank 1 and the minimum groove depth allowance distribution D 2 Determine the maximum groove depth h of the fiber cutting groove e and the minimum groove depth h f , select a tool with a diameter of D for roughing, and the width of the roughing fiber cutting groove is L, so that D<L≤2D;
[0075] d. After th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com