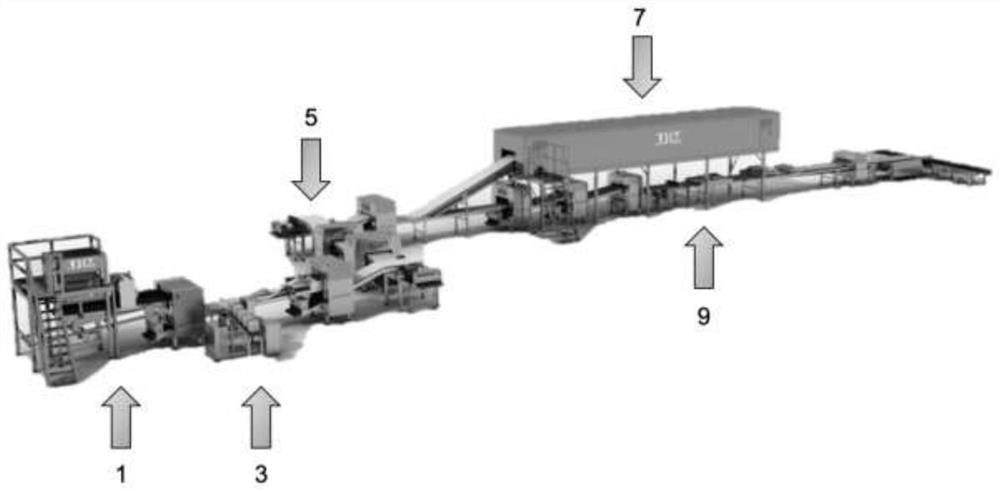
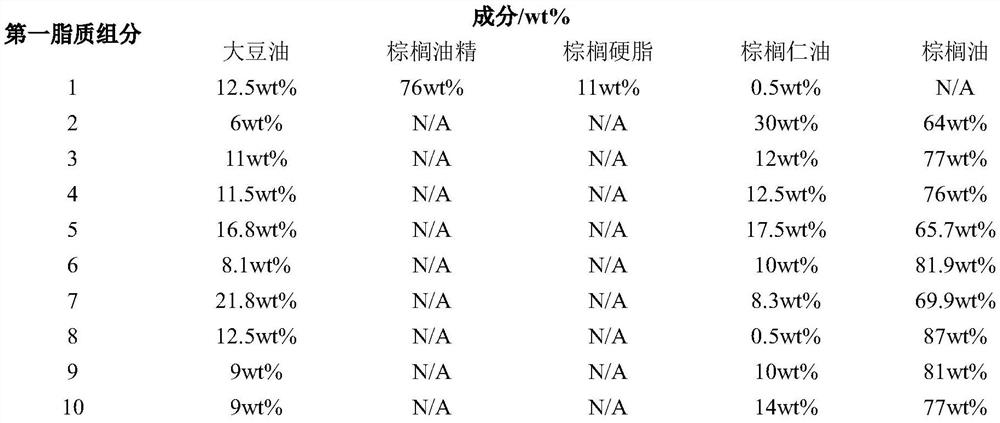
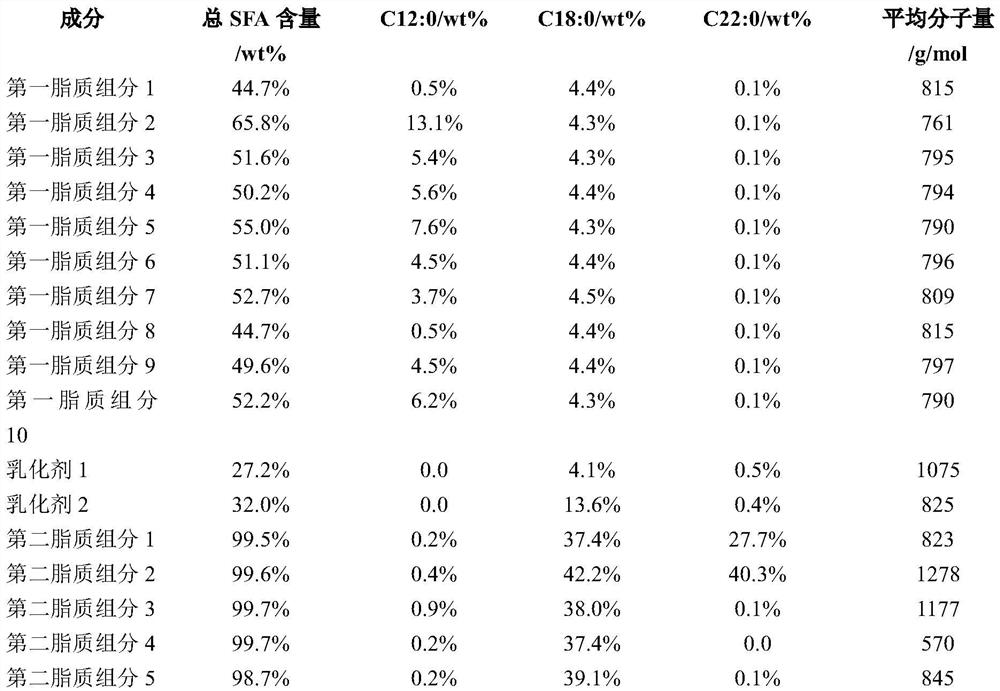
Lipid composition for baked products
A lipid composition and lipid technology, applied in the direction of baked food, edible oil/fat, edible oil/fat, can solve the problem of how to improve the plasticity and firmness of the lipid composition, and achieve the goal of improving the taste Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] In this example, the effect of SFA content on the melting point of lipid compositions was tested. The experimental results are summarized as follows.
[0096]
[0097] It can be seen from the above that when the content of one or more second lipid components is higher than 11 wt%, the melting point of the lipid phase is higher than 48°C. Furthermore, instances where the SFC of the lipid phase is higher than 12 wt% at 40° C. are not conducive to producing a good mouthfeel when the lipid phase is used in baked goods such as Danish pastries. As mentioned above, this is because SFC is related to lipid plasticity. Therefore, if the SFC is too high, the lipid composition is expected to be too firm to handle. Also, the lipid composition is expected to have a waxy mouthfeel.
Embodiment 2
[0099] In this example, the effect of the content of the second lipid component on the melting point of the lipid phase of the composition was tested.
[0100]
[0101]
[0102] It can be seen from the above that when the content of the second lipid component is higher than 11 wt%, the melting point of the lipid phase is higher than 46°C. Again, the SFC of the lipid phase is higher than the example of 12wt% at 40°C, which is not conducive to providing a good mouthfeel for baked goods. As noted above, high SFC is also expected to impair the operability of lipid compositions.
Embodiment 3
[0104] In this example, the effect of C12:0 content on the hardness of the lipid composition and its extrusion properties was explored.
[0105]
[0106]
[0107]
[0108]
[0109] It can be seen from the above that the C12:0 content in the lipid composition is related to the hardness of the composition. Specifically, when the C18:0 content and the C22:0 content are given, the hardness of the composition increases with the increase of the C12:0 content. Likewise, when the C12:0 content is reduced, the hardness of the composition is also reduced.
[0110] Furthermore, the C12:0 content in the lipid composition correlates with the extrusion properties of the composition. It was shown above that a C12:0 content that was too high (above 12 wt%) resulted in a lipid composition that was too hard to extrude. On the other hand, too low C12:0 content can make the extruded lipid composition viscous and lack of ductility, which is not conducive to subsequent processing.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com