Marker group for evaluating non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
A steatohepatitis, non-alcoholic technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problem of not systematically elucidating the function of liver EC subgroups, and achieve the effect of non-invasive and simple differentiation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Example 1: Materials and Methods
[0068] 1. Patient and clinical samples. Liver and plasma samples of patients were collected at West China Hospital of Sichuan University with informed consent. Healthy liver tissue (without fibrosis) was obtained from patients with hepatic hemangiomas who underwent endoscopic liver resection. Cirrhotic liver tissue was obtained from patients with histologically diagnosed hepatic fibrosis. Patient information used for scRNA-Seq, liquid microarray analysis, and gene expression analysis is shown in Table 1. Plasma samples were obtained from healthy volunteers (n=21), simple fatty liver (n=16), early nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (F0-F1) (n=12), and cirrhosis / fibrosis of different pathological grades Patients (no cancer) (n=75). Fibrosis grades in non-NASH livers were determined by Fibrosis-4 Index (Fib-4) and Transient Elastography (TE) using the NAFLD Fibrosis Index (NFS), Fib-4, TE and controlled attenuation parameters ( CAP) to det...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Example 2: scRNA-Seq reveals vascular dysregulation and abnormal endothelial classification in human cirrhotic liver
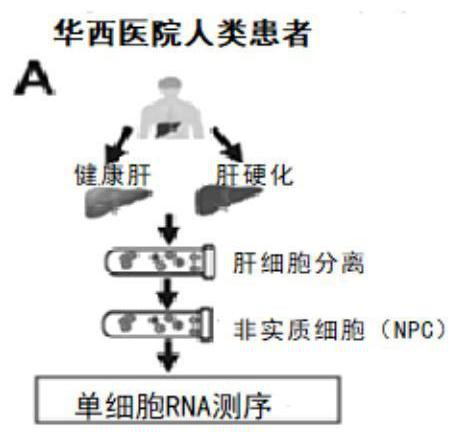
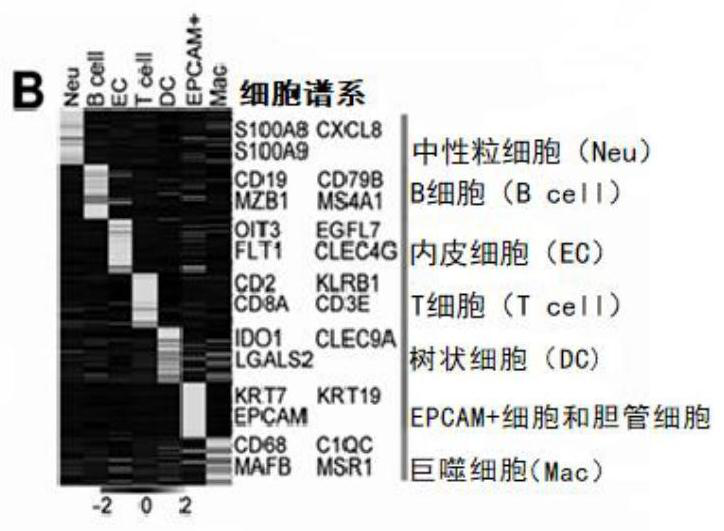
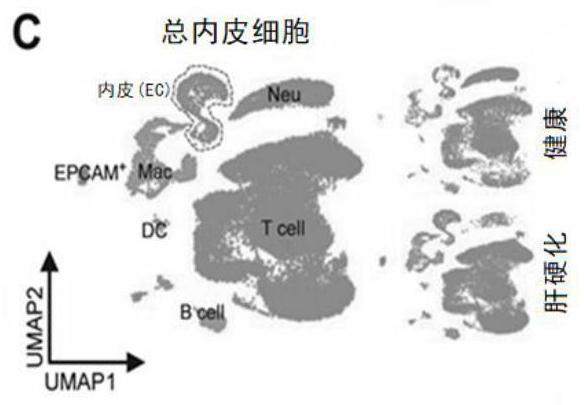
[0112] NPCs were isolated from fresh normal and cirrhotic human livers and subjected to scRNA-seq (10xgenomics) ( Figure 1A , Table S1). Healthy liver tissue (without fibrosis) was obtained from a patient with hepatic hemangioma in West China Hospital, and cirrhotic liver tissue was obtained from a patient with histologically diagnosed liver cirrhosis. 22,374 NPCs from 2 healthy livers and 2 cirrhotic livers were clustered into 25 clusters ( Figure 10A -B). Seven cell lines were defined by expression of marker genes: T cells, B cells, endothelial cells (EC), macrophages (Mac), neutrophils (Neu), dendritic cells (DC), and EPCAM + cells and bile duct cells (EPCAM + )( Figure 1B -C). Experimenters of the present invention found that among all the cell types tested, ECs had the most differential genes ( Figure 1D ). The proportion of ECs in cirrho...
Embodiment 3
[0114] Example 3: Epigenetic reprogramming of liver ECs induces pro-fibrotic "sinusoidal endothelial-macrovascular endothelial dysregulation"
[0115] Epigenetic regulation (histone modification and DNA methylation) plays an important role in the progression of liver fibrosis. However, the functional roles of histone modifications and DNA methylation in different cell lines of human cirrhotic / fibrotic NPCs remain unclear. To this end, the experimenters first determined the histone modifications of parenchymal cells and NPCs in healthy livers and cirrhotic livers. Liquid-chip analysis of histone H3 and H4 modifications showed that compared with healthy livers, NPCs in human cirrhotic livers were more Histone acetylation was significantly reduced, whereas parenchymal cells (hepatocytes) were not significantly different ( Figure 1G ), suggesting epigenetic reprogramming of NPCs in human cirrhotic livers.
[0116] The experimenters further investigated epigenetic changes in dif...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com