Gene therapy for recessive dystrophy epidermis bullosa using genetically corrected autologous keratinocytes
A cell and gene technology, applied in the field of gene therapy for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa using genetically corrected autologous keratinocytes, which can solve systemic toxicity and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
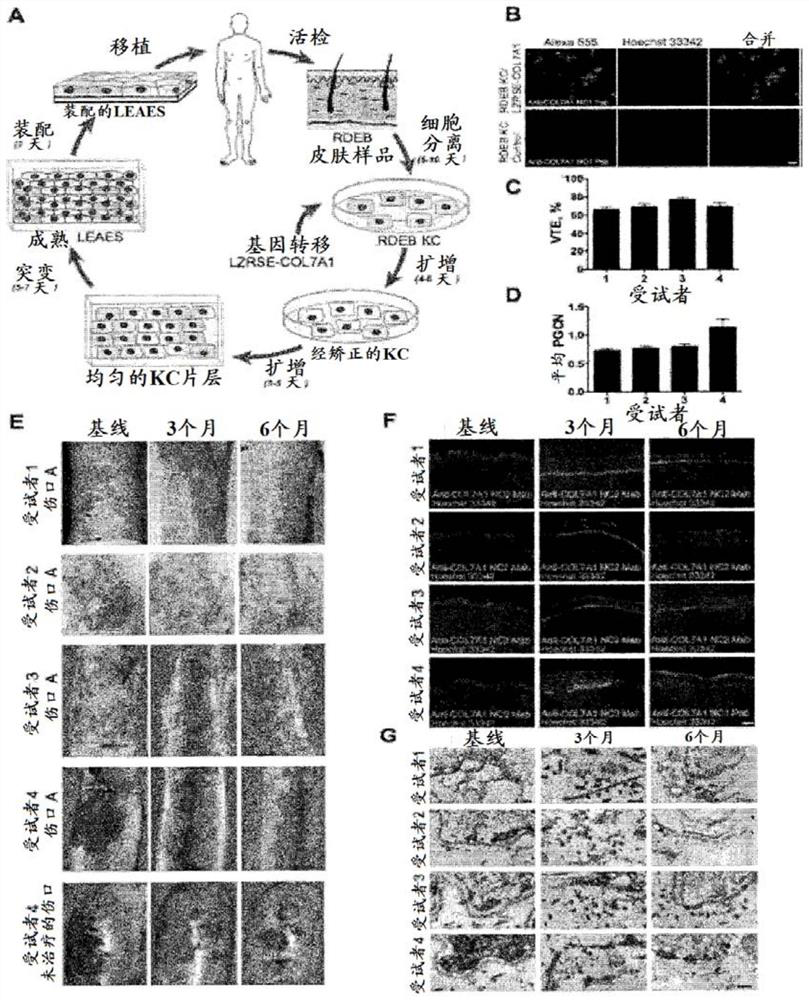
[0114] Cellular reprogramming of autologous cells as a treatment for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB).
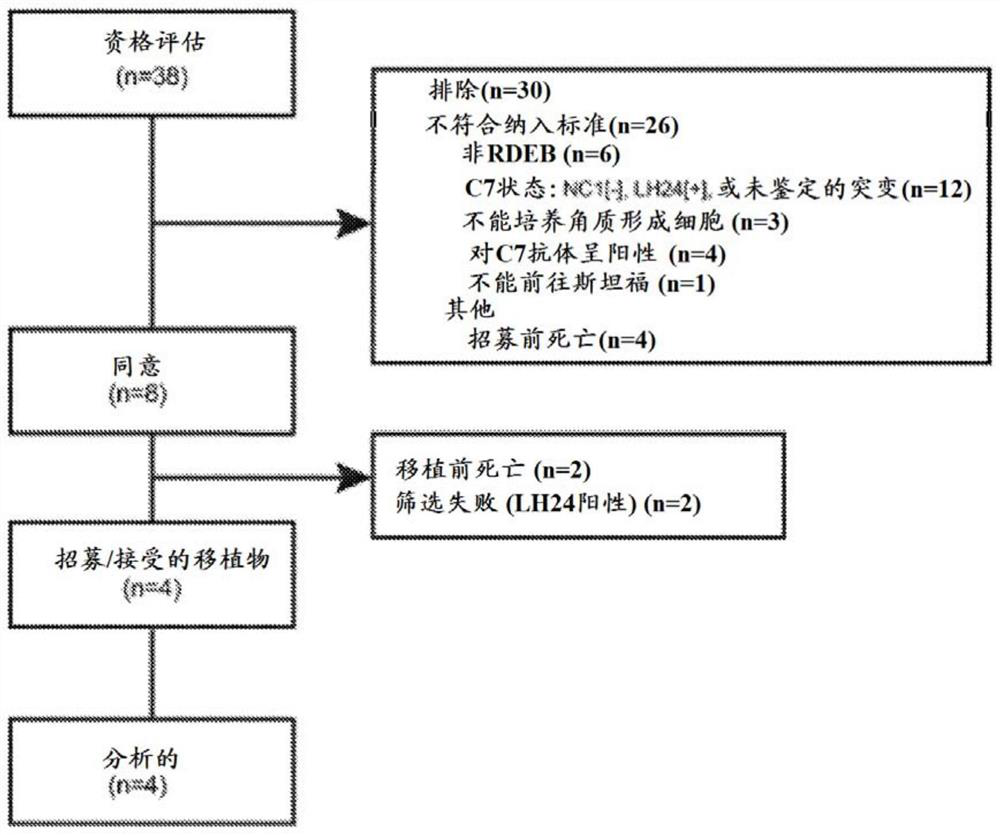
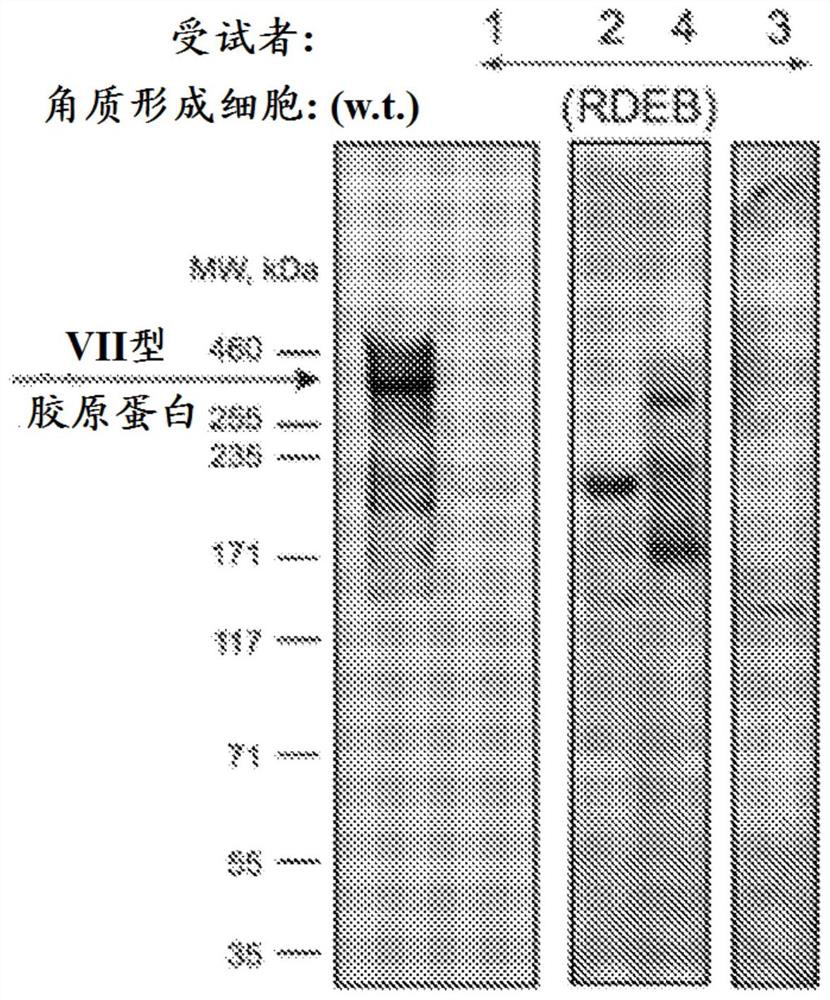
[0115] Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB) is a severe blistering skin disease caused by loss-of-function mutations in COL7A1, the gene encoding collagen type VII (C7). C7 is a major component of anchoring fibrils (AF), which stabilize the basement membrane zone (BMZ) of the epidermis to the dermis. C7 performs this function by using multiple domains including the amino-terminal non-collagen NC1 domain that binds BMZ ligands, the central collagen domain that assembles into a triple helix, and the NC2 domain that catalyzes the assembly of C7 into AF . Loss of these functional C7 domains in RDEB results in severe BMZ segregation. This produces extensive and painful blistering, erosion, and scarring, which in turn leads to the aggressive and often fatal form of SCC that occurs in the second and third decades. Despite advances in molecular diag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com