Bio-ink supply system and three-dimensional bio-printing method using same
A bio-ink and supply system technology, applied in 3D printers, 3D printing systems, 3D bioprinting, and 3D printing fields, can solve problems such as high cost, physical or biological pollution of printed results, and achieve the effect of reducing power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
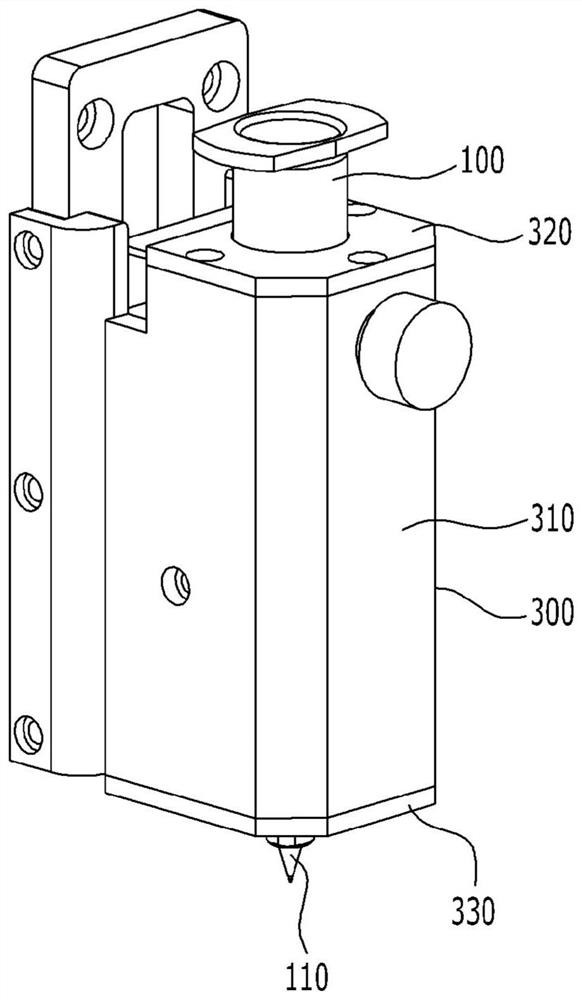
[0121]After the heating block was formed on the outer peripheral surface of the syringe from which the printing composition was discharged, a cap was formed with a thickness of 3 mm so that the heating block was wrapped with polyetherether ketone, thereby constituting a high temperature head for a 3D printer.
experiment example 1
[0124] [Experimental Example 1: Measurement of Thermal Insulation Properties]
[0125] In order to measure the thermal insulation performance of the 3D printing head of the present invention, the temperature of the heating block of the example and the comparative example was set to 100°C, and then the surface temperature of the cover of the example and the heating block of the comparative example were measured within 1 hour. surface temperature, the results are shown in Image 6 .
[0126] from the above Image 6 From the results of , in the case of the comparative example, the temperature increased from 23.8°C in the initial stage to 103.9°C in 10 minutes, and then the temperature was kept constant. In contrast, in the case of the example, the temperature rose from the initial stage 24.7°C to 81.9°C in 10 minutes, and then the temperature remained constant, so it was confirmed that the example including the cover had a thermal insulation effect of about 20°C.
[0127] Fi...
experiment example 2
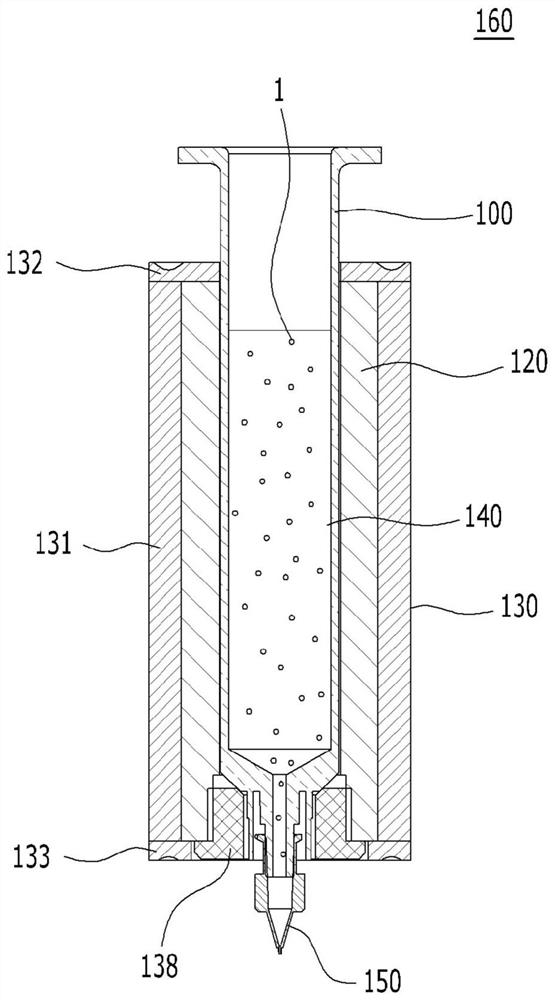
[0195] Experimental Example 2: Measurement of the printed result according to the water level of the bio-ink
[0196] Three-dimensional bioprinting was carried out by setting the same conditions as air pressure and moving speed of the syringe, and only changing the water level of the bioink in the syringe to measure the amount of bioink discharged from the syringe. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0197] [Table 1]
[0198] Water level of bio-ink (ml) Discharge (ml) 2.0 0.069±0.004 0.5 0.080±0.001
[0199] As confirmed by the results in Table 1, it can be seen that when the water level of the bioink in the syringe was 0.5 ml, the discharge amount increased by about 17% compared to when the water level of the bioink was 2.0 ml. This means that the amount of bioink expelled through the syringe during bioprinting varies according to the level of bioink in the syringe. Therefore, it can be seen that for precise bioprinting, the water level of the bi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com