Self-adaptive quasi-PR active damping low-frequency harmonic suppression method
A harmonic suppression and adaptive technology, applied in harmonic reduction devices, AC networks to reduce harmonics/ripple, output power conversion devices, etc., can solve the problem of multi-inverter grid-connected systems. Resonance suppression and other issues to reduce hardware cost and power consumption, improve the quality of grid-connected current, and reduce THD
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
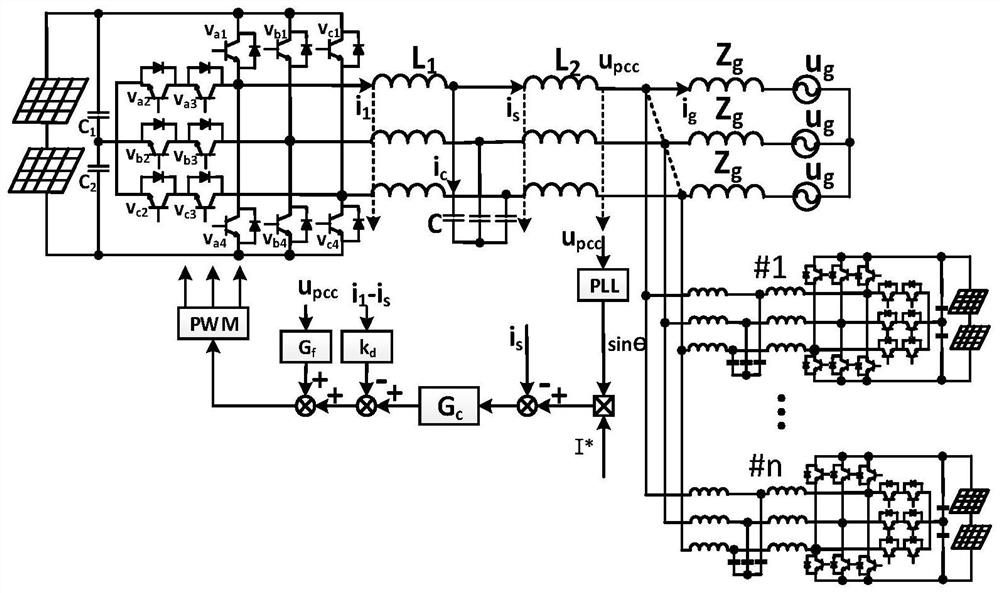
[0080] like figure 1 As shown, this embodiment discloses an adaptive quasi-PR active damping low-frequency harmonic suppression method, which includes the following steps:
[0081] An adaptive quasi-PR active damping low-frequency harmonic suppression method, comprising the following steps:
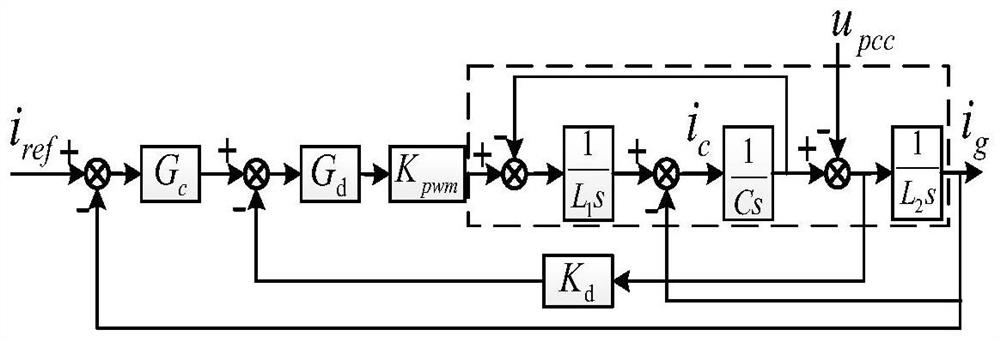
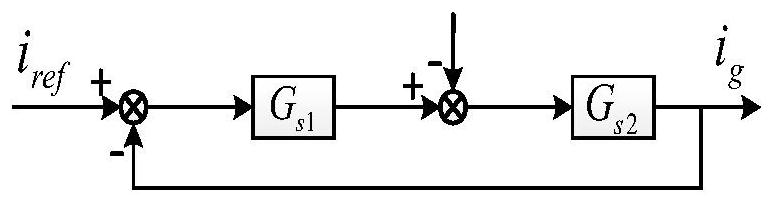
[0082] S1: Use the inverter output impedance model to analyze the harmonic mechanism of the T-type three-level inverter system under double closed-loop control. Under the output impedance model, according to the parallel connection of n units working under the same conditions and with the same parameters The inverter is a whole, and the equivalent impedance model is established from the perspective of PCC as shown in Figure 3(b). The grid-connected current function of the LCL grid-connected inverter system under double closed-loop control is derived as:
[0083]
[0084] The sum of the current sources of the inverter, u g is the grid voltage. It can be seen from equation (1) that the...
Embodiment 2
[0142] In order to verify the correctness of the proposed control method, Matalab is used for simulation, and three T-type three-level grid-connected inverter models are built in MATLAB / Simulink simulation software. In this embodiment, the simulation parameters are shown in the following table:
[0143]
[0144]
[0145] PV side voltage and grid voltage u g are provided by a DC constant voltage source and an AC voltage source, respectively, where u g Contains 3rd, 5th and 7th harmonics; grid impedance Z g through the PCC point and u g Inductance in series between to simulate.
[0146] Figure 10(a) and (b) the reference current i during quasi-PR control and adaptive quasi-PR strategy, respectively ref and grid-connected current i g It can be seen from the figure that when quasi-PR control is used, the grid-connected current contains a large number of 3rd, 5th, and 7th harmonics, and the phase lags; On the other hand, the grid-connected current can also track the refe...
Embodiment 3
[0149] A photovoltaic grid-connected system adopts the adaptive quasi-PR active damping low-frequency harmonic suppression method in the previous embodiment 1, and on the basis of the conventional double closed-loop control, an adaptive quasi-PR control link is introduced, and on the basis of the quasi-PR control The phase compensation structure is introduced on the grid and the voltage proportional feedforward link is added at the PCC grid connection point, and the adaptive quasi-PR active damping low-frequency harmonic suppression method is obtained, which realizes the grid-connected current to the sinusoidal given current. And reduce the content of the 3rd, 5th, and 7th harmonics in the grid-connected current, increase the active damping of the system, and improve the system's ability to resist grid voltage disturbances. The equivalent conversion and cancellation of resonance can effectively suppress the self-resonance and parallel resonance of the LCL photovoltaic grid-conn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com