Method for controlling liquid drops in multiple directions on single-plane light-operated electrowetting device
An electrowetting and single-plane technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, laboratory utensils, laboratory containers, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the application range, compressing the volume of droplets, chip integration, etc., to improve the degree of freedom and flexibility, improve the success rate, and achieve convenient results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
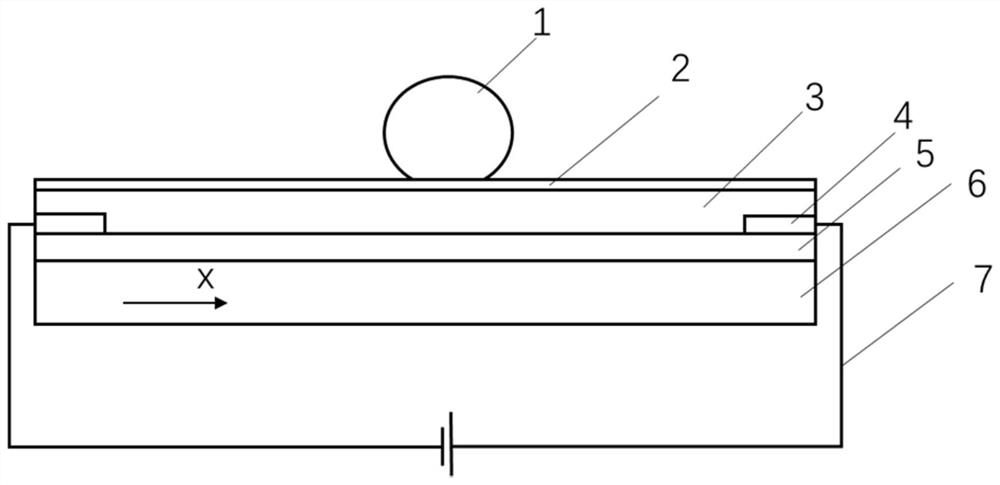
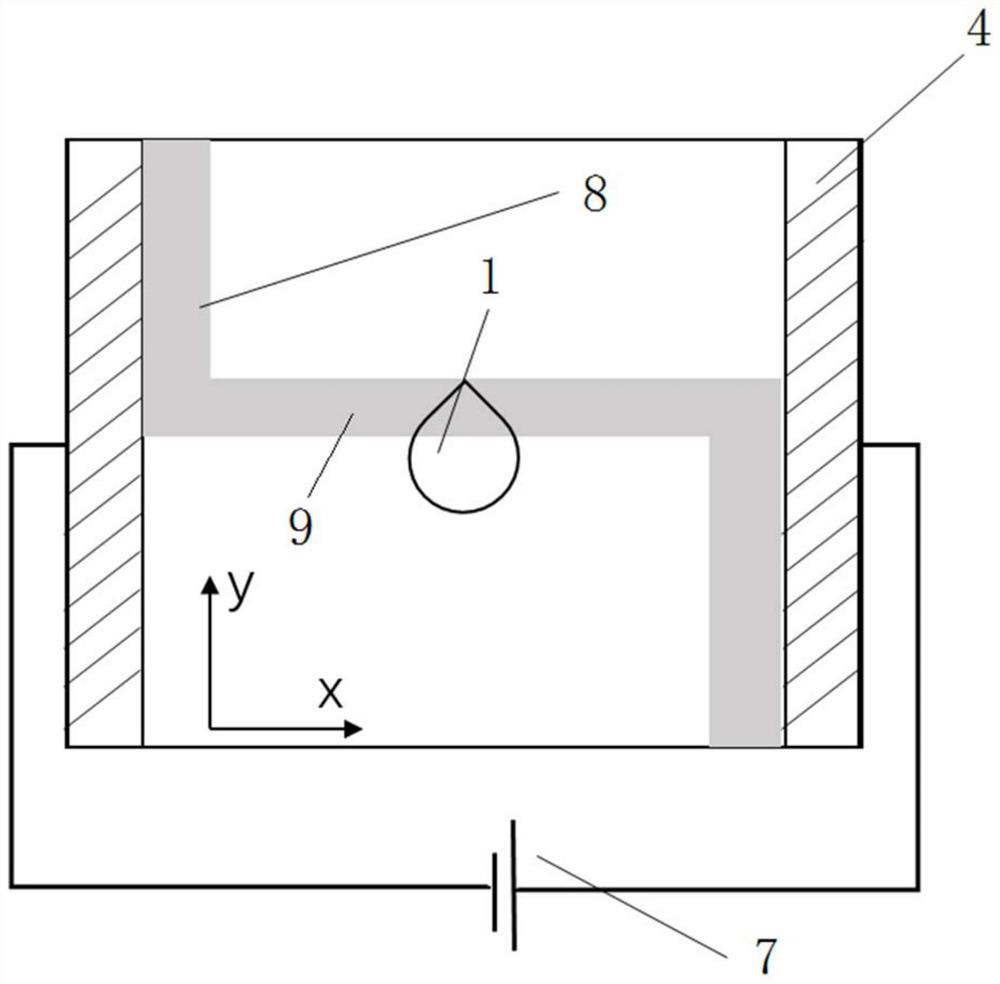
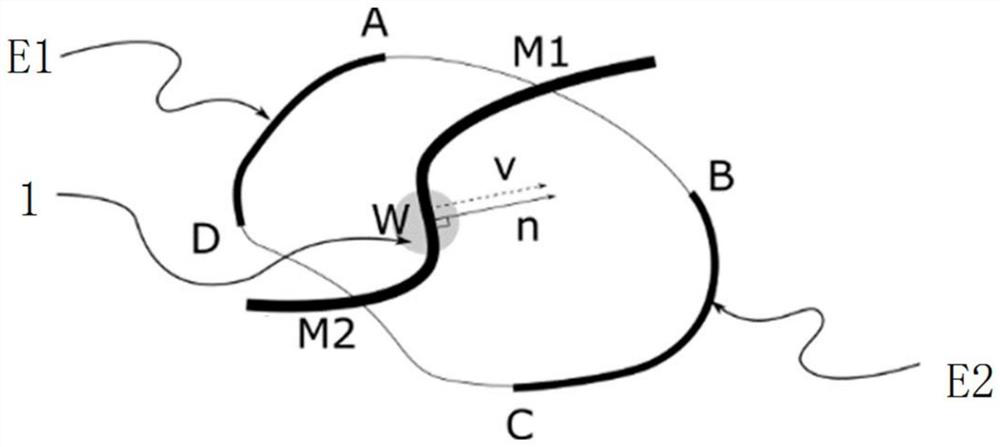
[0035] The present invention designs a method for manipulating droplets in multiple directions based on a single-plane light-controlled electro-wetting device. The basic principle of the single-plane light-controlled electro-wetting device is: the bias voltage applied to the electrodes 4 at both ends of the device is A transverse electric field is generated in the direction between the electrodes 4. When the light hits the surface of the photoconductive material, its conductivity increases, and the conductivity is smaller in places without light. By projecting dark stripes (no light) to a certain position on the chip, the stripes The resistivity of the covered area increases, and the dielectric layer 3 above it induces a large voltage drop. According to the Lippman-Young equation, the contact angle of the droplet 1 above the area decreases accordingly. If a dark fringe is applied over one side of droplet 1, the contact angle of droplet 1 changes asymmetrically, thereby driving ...
specific example
[0053] A specific example of the present invention is provided below, and its concrete realization process is:
[0054] 1. Put the purchased 4-inch single-sided polished silicon wafer into acetone solution for cleaning, rinse the surface of the silicon wafer with a dropper repeatedly until there is no debris or air bubbles left; put the silicon wafer into isopropanol solution for cleaning, wash away Residual acetone; rinse with deionized water repeatedly to remove the surface organic solvent; dry the silicon wafer surface with a nitrogen gun, and bake it on a hot plate at 100°C for 3-5 minutes until the silicon wafer is completely dried. The deposition of photoconductive thin film α-Si was carried out by PECVD. At 300℃ deposition temperature, the chamber pressure is 50-100Pa, SiH 4 The flow is 20sccm, H 2 The flow rate was 40sccm and the deposition power was 50W. Under this deposition power, the deposition rate of α-Si is about 5-10 nm / min, and the deposition is 100 min to ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com